Abstract
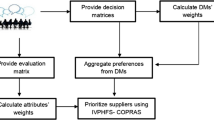
Recent studies have identified that multi-criteria group analysis methods should take the concepts of risk and uncertainty into account. In some real-life situations, determining the exact values for the potential alternatives’ performances and criteria weights is so difficult. To overcome with these situations, their values should be regarded as fuzzy and fuzzy intervals. In this respect, interval-valued hesitant fuzzy sets (IVHFSs) as a suitable modern fuzzy sets theory can be considered because this theory allows decision makers (DMs) to assign some interval-values membership degrees for an alternative in terms of selected criteria under a set to margin of errors. Hence, this paper proposes a novel soft computing approach, namely IVHF-MCGA, based on new interval-valued hesitant fuzzy complex proportional assessment (IVHF-COPRAS) method that can be applied in solving the multi-criteria group decision-making (MCGDM) problems under uncertainty. In this approach, preference values of potential alternatives versus the selected criteria and weights of each criterion are expressed by linguistic variables and then are transformed to interval-valued hesitant fuzzy elements (IVHFEs). In addition, an interval-valued hesitant fuzzy entropy (IVHF-entropy) method is extended to determine the criteria weights by considering the DMs’ opinions about the relative importance. Also, a new interval-valued hesitant fuzzy compromise solution (IVHF-CS) method is introduced to estimate the weight of each DM in the group decision-making process along with the last aggregation for the DMs’ judgments to avoid the data loss. Then, three practical applications about the robot selection, industrial site selection and rapid prototyping process selection problems are considered to explain steps of the proposed IVHF-MCGA approach and to indicate its validity and applicability. Finally, a comparative analysis between the proposed approach and fuzzy group TOPSIS method is presented based on four comparison parameters, including adequacy to changes of alternatives and criteria, agility in decision process, influence of DMs’ weights and impact of first and last aggregations, to show its suitability.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Malek L, Resare LJ (2000) Algorithm based decision support system for the concerted selection of equipment in machining/assembly cells. Int J Prod Res 38:323–339
Agrawal VP, Kohli V, Gupta S (1991) Computer aided robot selection: the ‘multiple attribute decision making’ approach. Int J Prod Res 29:1629–1644
Atanassov KT (1986) Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 20:87–96
Atanassov KT (1989) More on intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 33:37–45
Atanassov KT (2000) Two theorems for intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 110:267–269
Ayağ Z (2010) A combined fuzzy AHP-simulation approach to CAD software selection. Int J Gen Syst 39:731–756
Bhangale PP, Agrawal VP, Saha SK (2004) Attribute based specification, comparison and selection of a robot. Mech Mach Theory 39:1345–1366
Bustince H (1994) Conjuntos Intuicionistas e Intervalo valorados difusos: propiedades y construcci on. Thesis, Universidad P\_ublica de Navarra, Relaciones Intuicionistas Fuzzy
Byun HS, Lee KH (2005) A decision support system for the selection of a rapid prototyping process using the modified TOPSIS method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 26:1338–1347
Chatterjee P, Athawale VM, Chakraborty S (2010) Selection of industrial robots using compromise ranking and outranking methods. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 26:483–489
Chen N, Zeshui X, Xia M (2013) Interval-valued hesitant preference relations and their applications to group decision making. Knowl Based Syst 37:528–540
Chu T-C, Lin Y-C (2003) A fuzzy TOPSIS method for robot selection. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 21:284–290
Devi K (2011) Extension of VIKOR method in intuitionistic fuzzy environment for robot selection. Expert Syst Appl 38:14163–14168
Farhadinia B (2013) Information measures for hesitant fuzzy sets and interval-valued hesitant fuzzy sets. Inf Sci 240:129–144
Goh C-H (1997) Analytic hierarchy process for robot selection. J Manuf Syst 16:381–386
Gorzałczany MB (1987) A method of inference in approximate reasoning based on interval-valued fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 21:1–17
İç YT, Yurdakul M, Dengiz B (2013) Development of a decision support system for robot selection. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 29:142–157
Junior FR, Lima LO, Carpinetti LCR (2014) A comparison between Fuzzy AHP and Fuzzy TOPSIS methods to supplier selection. Appl Soft Comput 21:194–209
Karsak EE (2005) Choquet integral-based decision making approach for robot selection. In: Khosla R, Howlett RJ, Jain LC (eds) Choquet integral-based decision making approach for robot selection. Knowledge-based intelligent information and engineering systems. Springer, pp 635–641
Li L-G, Peng D-H (2014) Interval-valued hesitant fuzzy Hamacher synergetic weighted aggregation operators and their application to shale gas areas selection. Math Probl Eng 2014:1–25
Li G-D, Yamaguchi D, Nagai M (2007) A grey-based decision-making approach to the supplier selection problem. Math Comput Model 46(3–4):573–581
Liao H, Xu Z (2014) Subtraction and division operations over hesitant fuzzy sets. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 27:65–72
Liu H-C, Ren M-L, Jing W, Lin Q-L (2014) An interval 2-tuple linguistic MCDM method for robot evaluation and selection. Int J Prod Res 52:2867–2880
Mousavi SM, Jolai F, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R (2013a) A fuzzy stochastic multi-attribute group decision-making approach for selection problems. Group Decis Negot 22(2): 207–233
Mousavi SM, Vahdani B, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R, Ebrahimnejad S, Amiri M (2013b) A multi-stage decision-making process for multiple attributes analysis under an interval-valued fuzzy environment. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 64:1263–1273
Mousavi SM, Mirdamadi S, Siadat A, Dantan J, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R (2015) An intuitionistic fuzzy grey model for selection problems with an application to the inspection planning in manufacturing firms. Eng Appl Artif Intell 39:157–167
Ölçer Aİ, Odabaşi AY (2005) A new fuzzy multiple attributive group decision making methodology and its application to propulsion/manoeuvring system selection problem. Eur J Oper Res 166:93–114
Rao RV (2013) Multiple attribute decision making in the manufacturing environment. In: Pham DT (ed) Decision making in manufacturing environment using graph theory and fuzzy multiple attribute decision making methods. Springer
Rao RV, Patel BK, Parnichkun M (2011) Industrial robot selection using a novel decision making method considering objective and subjective preferences. Robot Auton Syst 59:367–375
Torra V (2010) Hesitant fuzzy sets. Int J Intell Syst 25:529–539
Torra V, Narukawa Y (2009) On hesitant fuzzy sets and decision. In: On hesitant fuzzy sets and decision. IEEE international conference on Fuzzy Systems, pp 1378–1382
Turksen IB (1986) Interval valued fuzzy sets based on normal forms. Fuzzy Sets Syst 20:191–210
Türkşen İB, Bilgiç T (1996) Interval valued strict preference with Zadeh triples. Fuzzy Sets Syst 78:183–195
Vahdani B, Hadipour H, Sadaghiani JS, Amiri M (2010) Extension of VIKOR method based on interval-valued fuzzy sets. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 47:1231–1239
Vahdani B, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R, Mousavi SM, Ghodratnama A (2013) Soft computing based on new interval-valued fuzzy modified multi-criteria decision-making method. Appl Soft Comput 13:165–172
Vahdani B, Mousavi SM, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R, Ghodratnama A, Mohammadi M (2014) Robot selection by a multiple criteria complex proportional assessment method under an interval-valued fuzzy environment. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 73(5–8):687–697
Vahdani B, Hadipour H (2011) Extension of the ELECTRE method based on interval-valued fuzzy sets. Soft Comput 15:569–579
Wang Y-J (2014) A fuzzy multi-criteria decision-making model by associating technique for order preference by similarity to ideal solution with relative preference relation. Inf Sci 268:169–184
Wang Y-J (2015) A fuzzy multi-criteria decision-making model based on simple additive weighting method and relative preference relation. Appl Soft Comput 30:412–420
Xu Z, Zhang X (2013) Hesitant fuzzy multi-attribute decision making based on TOPSIS with incomplete weight information. Knowl Based Syst 52:53–64
Yao J-S, Ming-Miin Y (2004) Decision making based on statistical data, signed distance and compositional rule of inference. Int J Uncertain Fuzziness Knowl Based Syst 12:161–190
Yue Z (2011) An extended TOPSIS for determining weights of decision makers with interval numbers. Knowl Based Syst 24:146–153
Zhang Z, Wang C, Tian D, Li K (2014) Induced generalized hesitant fuzzy operators and their application to multiple attribute group decision making. Comput Ind Eng 67:116–138
Zhang X, Zeshui X (2014) Interval programming method for hesitant fuzzy multi-attribute group decision making with incomplete preference over alternatives. Comput Ind Eng 75:217–229
Zhao X, Lin R, Wei G (2014) Hesitant triangular fuzzy information aggregation based on Einstein operations and their application to multiple attribute decision making. Expert Syst Appl 41:1086–1094
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gitinavard, H., Mousavi, S.M. & Vahdani, B. Soft computing-based new interval-valued hesitant fuzzy multi-criteria group assessment method with last aggregation to industrial decision problems. Soft Comput 21, 3247–3265 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-015-2006-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-015-2006-9