Abstract
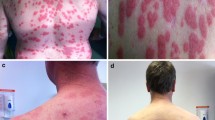
Ixazomib is a second-generation proteasome inhibitor that has been approved in the combination treatment of multiple myeloma and is currently under clinical investigation for the management of Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia. While cutaneous adverse events secondary to proteasome inhibitors have been reported, the side effect profile of ixazomib remains to be documented. We report two patients, one with multiple myeloma and one with Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia, who developed cutaneous necrotizing vasculitis after the initiation of ixazomib. Both patients exhibited no signs of systemic vasculitis and completed their anti-cancer regimens with resolution of their respective eruptions following dose reductions in ixazomib and initiation of low-dose prednisone. A collaborative effort towards the characterization of such cutaneous toxicities facilitates early intervention, maintenance of life-preserving anti-cancer therapy, and allows clinicians opportunity to better understand the pathophysiology of vasculitis. Moreover, appropriate identification and characterization of cutaneous toxicities from novel therapies allows providers to accurately identify safety concerns, treat toxicity, and improve patient quality of life.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kupperman E, Lee EC, Cao Y et al (2010) Evaluation of the proteasome inhibitor MLN9708 in preclinical models of human cancer. Cancer Res 70(5):1970–1980
Agterof MJ, Biesma DH (2005) Images in clinical Medicine. Bortezomib-induced skin lesions. N Engl J Med 352(24):2534
Min CK, Lee S, Kim YJ (2006) Cutaneous leucoclastic vasculitis (LV) following bortezomib therapy in a myeloma patient; association with pro-inflammatory cytokines. Eur J Haematol 76(3):265–268
Garcia-Navarro X, Puig L, Fernandez-Figueras MT, Dalmau J, Roe E, Alomar A (2007) Bortezomib-associated cutaneous vasculitis. Br J Dermatol 157(4):799–801. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.08073.x
Kumar SK, Berdeja JG, Niesvizky R, Lonial S, Laubach JP, Hamadani M, Stewart AK, Hari P, Roy V, Vescio R, Kaufman JL, Berg D, Liao E, di Bacco A, Estevam J, Gupta N, Hui AM, Rajkumar V, Richardson PG (2014) Safety and tolerability of ixazomib, an oral proteasome inhibitor, in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone in patients with previously untreated multiple myeloma: an open-label phase 1/2 study. Lancet Oncol 15(13):1503–1512. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(14)71125-8
Loree JM, Cai E, Sheffield BS et al (2016) Leukocytoclastic vasculitis following lenalidomide during the treatment of follicular lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 58(3):1–4
Shirley M (2016) Ixazomib: first global approval. Drugs 76(3):405–411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-016-0548-5
Paulus A, Ailawadhi S, Chanan-Khan A (2016) Novel therapeutic targets in Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 29(2):216–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beha.2016.08.020
Chhabra S (2017) Novel proteasome inhibitors and histone deacetylase inhibitors: progress in myeloma therapeutics. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 10(2):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph10020040
Kim MJ, Kim HO, Kim HY, Park YM (2009) Rituximab-induced vasculitis: a case report and review of the medical published work. J Dermatol 36(5):284–287. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1346-8138.2009.00639.x
Pour L, Hajek R, Zdenek A, Krejci M, Krivanova A, Vorlicek J (2005) Skin lesions induced by bortezomib. Haematologica 90(12 Suppl):ECR44
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alloo, A., Khosravi, H., Granter, S.R. et al. Ixazomib-induced cutaneous necrotizing vasculitis. Support Care Cancer 26, 2247–2250 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-018-4052-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-018-4052-1