Abstract
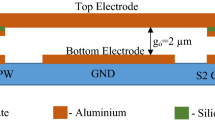
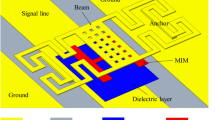
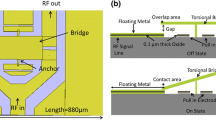
A novel torsional RF MEMS capacitive switch design on silicon substrate is presented. The optimized switch topology such as reduction in up-state capacitance results in insertion loss better than −0.1 dB till 20 GHz. Off to on state capacitance ratio is also improved by 18 fold and isolation is better than −43 dB at 9.5 GHz. The achieved on state return loss is −38 dB as compared to −21 dB at 9.5 GHz. An optimized reduction in contact area and use of floating metal layer increases the switching speed from 56 to 46 μsec. It also increases the switch reliability by alleviating the stiction.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chirag GMR, Patel D (2011) RF MEMS metal-contact switches with mN-contact and restoring forces and low process sensitivity. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 59:1230–1237
Deepak Bansal, Akshdeep Sharma, Maninder K, Rangra KJ (2012) Design of vertical packaging technology for RF MEMS Switch. In: Proc. SPIE 8549 16th International Workshop on Physics of Semiconductor Devices, 854911. doi:10.1117/12.924260
Degani Ofir, Socher Eran, Lipson Ariel, Leitner Tomer, Setter Dan J, Kaldor Shmuel, Nemirovsky Yael (1998) Pull-in study of an electrostatic torsion microactuator. J Microelectromech Syst 7(4):373–379
Dey Sukomal, Shiban Koul K (2012) Design and development of a surface micro-machined push–pull-type true-time-delay phase shifter on an alumina substrate for Ka-band T/R module application. J Micromech Microeng 22:20
Du YJ, Bao JF, Jiang JW (2013) A new design of multi-bit RF MEMS distributed phase shifters for phase error reduction. Microsyst Technol 19:237–244
Dutta Shankar, Imran Mohd, Pal Ramjay, Jain KK, Chatterjee R (2011) Effect of residual stress on RF MEMS switch. Microsyst Technol 17:1739–1745
Hung Elmer S, Senturia Stephen D (1999) Extending the travel range of analog-tuned electrostatic actuators. J Microelectromech Syst 8(4):497–505
Kim Min-Wu, Song Yong-Ha, Yang Hyun-Ho, Yoon Jun-Bo (2013) An ultra-low voltage MEMS switch using stiction-recovery actuation. J Micromech Microeng 23:7
Melle S, Bordas C, Dubuc D, Grenier K, Vendier O, Muraro JL, Cazaux JL, Plana R (2007) Investigation of stiction effect in electrostatic actuated RF MEMS devices, topical meeting on silicon monolithic integrated circuits in RF systems, pp 173–176
Mercado Lei L, Kuo Shun-Meen, Lee Tien-Yu Tom, Liu Lianjun (2004) Mechanics-based solutions to RF MEMS switch stiction problem. IEEE Trans Compon Packag Technol 27(3):560–567
Merlijn van Spengen W, Robert Puers, Robert Mertens, Ingrid De Wolf (2002) Experimental characterization of stiction due to charging in RF MEMS, Electron Devices Meeting, 2002. IEDM ’02. International, pp 901–904
Rangra Kamaljit, Margesin Benno, Lorenzelli Leandro, Giacomozzi Flavio, Collini Cristian, Zen Mario, Soncini Giovanni, del Tin Laura, Gaddi Roberto (2005) Symmetric toggle switch—a new type of RF MEMS switch for telecommunication applications: design and fabrication. Sens Actuat A 123–124:505–514
Rebeiz Gabriel M, Muldavin Jeremy B (2001) RF MEMS switches and switch circuits. IEEE Microwave Mag 2(4):59–71
Soumendu Sinha, Deepak Bansal, KJ Rangra (2012) Design and optimization of RF MEMS T-type switch for redundancy switch matrix applications, 2012 international conference on computing, electronics and electrical technologies (ICCEET). doi:10.1109/ICCEET.2012.6203826
Souvik Basu AP, Bhattacharya Enakshi (2007) Estimation of Stiction force from electrical and optical measurements on cantilever beams. J Microelectromech Syst 16:1254–1262
Tas Niels, Sonnenberg Tonny, Jansen Henri, Legtenberg Rob, Elwenspoek Miko (1996) Stiction in surface micromachining. J Micromech Microeng 6:385–397
Touati S, Lorphelin N, Kanciurzewski A, Robin R, Rollier A-S, Millet O, Segueni K (2008) Low actuation voltage totally free flexible RF MEMS switch with antistiction, system, symposium on design, test, integration and packaging of MEMS/MOEMS, 2008. MEMS/MOEMS 2008:66–70
Zhang XM, Chau FS, Quan C, Lam YL, Liu AQ (2001) A study of the static characteristics of a torsional micromirror. Sens Actuat A 90:73–81
Zhao Y-P, Wang LS, Yu TX (2003) Mechanics of adhesion in MEMS—a review. J Adhesion Sci Technol 17(4):519–546
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bansal, D., Kumar, A., Sharma, A. et al. Design of novel compact anti-stiction and low insertion loss RF MEMS switch. Microsyst Technol 20, 337–340 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-013-1812-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-013-1812-1