Abstract
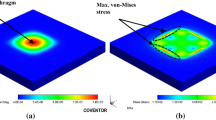
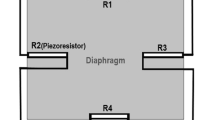
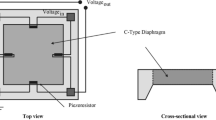
Piezoresistive sensing is one of the most frequently used transduction mechanism in pressure sensors. The piezoresistor placement on the diaphragm and the piezoresistor configuration play a pivotal role in determining the output characteristics of a pressure sensor. In this work, two different pressure sensors with different transverse piezoresistor configurations are studied to determine the effect of piezoresistor configuration on the sensitivity and non-linearity of the pressure sensors. A sensor structure with a square diaphragm size of 1,480 µm edge length and diaphragm thickness of 50 µm is chosen for the study. The design considerations for piezoresistor placement and the piezoresistor shapes are discussed in detail. The sensors are fabricated with bulk micromachined diaphragm and polysilicon piezoresistors. The sensor characteristics are determined for three temperatures, namely, −5, 25 and 55 °C and for a pressure range of 0–30 Bar. The characterization results indicate that the design with two piezoresistor arms in transverse piezoresistor configuration (2 × 2 Design) has higher sensitivity than the single arm configuration (2 × 1 Design) by about 25 % at 25 °C but it also has a higher non-linearity. The study shows the importance of selecting the proper piezoresistor configuration in the design of pressure sensors.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao M (2005) Analysis and design principles of MEMS devices. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Bian T, Yulong Z, Jiang Z, Zhang L, Liao N, Lio Y, Meng C (2009) The analysis and structural design of micro SOI pressure sensors. In: Proceedings of the 4th international conference on nano/micro eng. and molecular systems, Shenzhen, pp 55–58
Bian T, Yulong Z, Zhuangde J, Bin H (2012) The design and analysis of beam-membrane structure sensors for micro-pressure measurement. Rev Sci Instrum 83:045003
Chung GS, Kawahito S, Ishida M, Nakamura T, Kawashima M, Suzaki T (1991) High-performance pressure sensors using double silicon-on-insulator structures. Rev Sci Instrum 62(5):1341–1346
Clark SK, Wise KD (1979) Pressure sensitivity in anisotropically etched thin-diaphragm pressure sensors. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 26(12):1887–1896
Eaton WP, Smith JH (1997) Micromachined pressure sensors: review and recent developments. Smart Mat Struc 6(5):530–539
Fraga MA, Furlan H, Massi M, Oliveira IC, Koberstein LL (2010) Fabrication and characterization of a SiC/SiO2/Si piezoresistive pressure sensor. Procedia Eng 5:609–612
Gong SC, Lee C (2001) Analytical solutions of sensitivity for pressure microsensors. IEEE Sens J 1(4):340–344
Guo S, Eriksen H, Childress K, Fink A, Hoffman M (2009) High temperature smart-cut SOI pressure sensor. Sens Actuators A 154:255–260
Huang X, Zhang D (2014) A high sensitivity and high linearity pressure sensor based on a peninsula-structured diaphragm for low-pressure ranges. Sens Actuator A 216:176–189
Kumar SS, Pant BD (2012) Design of piezoresistive MEMS absolute pressure sensor. In: Proceedings of the SPIE 8549
Kumar SS, Pant BD (2013) Effect of temperature on etch rate and undercutting of (100) silicon using 25 % TMAH. In: Proceedings of the international conference on emerging technologies micro to nano (ETMN), Goa
Kumar SS, Pant BD (2014a) Design principles and considerations for the ‘ideal’ silicon piezoresistive pressure sensor: a focused review. Microsyst Technol 20:1213–1247
Kumar SS, Pant BD (2014b) Polysilicon thin film piezoresistive pressure microsensor: design, fabrication and characterization. Microsyst Technol. doi:10.1007/s00542-014-2318-1
Kumar SS, Ojha AK, Nambisan R, Sharma AK, Pant BD (2013) Design and simulation of MEMS silicon piezoresistive pressure sensor for barometric applications. In: Proceedings of the ARTCom&ARTEE PEIE&itSIP and PCIE. Elsevier, ISBN978-81-910691-8-3, pp 339–345
Kumar SS, Ojha AK, Pant BD (2014) Experimental evaluation of sensitivity and non-linearity in polysilicon piezoresistive pressure sensors with different diaphragm sizes. Microsyst Technol. doi:10.1007/s00542-014-2369-3
Li X, Liu Q, Pang S, Xu K, Tang H, Sun C (2012) High-temperature piezoresistive pressure sensor based on implantation of oxygen into silicon wafer. Sens Actuators A 179:277–282
Maier-Schneider D, Maibach J, Obermeier E (1995) A new analytical solution for the load-deflection of square membranes. J Microelectromech Syst 4:238–241
Malhaire C, Barbier D (2003) Design of a polysilicon-on-insulator pressure sensor with original polysilicon layout for harsh environment. Thin Solid Films 427:362–366
Motorola (1998) Sensor Device Data/Handbook 4th edn. Motorola Inc., Phoenix
Mukhiya R, Bagolini A, Margesin B, Zen M, Kal S (2006) (100) Bar corner compensation for CMOS compatible anisotropic TMAH etching. J Micromech Microeng 16:2458–2462
Park CS, Kang BS, Lee DW, Choi TY, Choi YS (2007) Fabrication and characterization of a pressure sensor using a pitch-based carbon fibre. Microelectron Eng 84:1316–1319
Peng CT, Lin JC, Lin CT, Chiang KN (2005) Performance and package effect of a novel piezoresistive pressure sensor fabricated by front-side etching technology. Sens Actuators A 119(1):28–37
Senturia SD (2001) Microsystem design. Kluwer, Boston
Smith CS (1954) Piezoresistance effect in germanium and silicon. Phys Rev 94:42–49
Tokoro K, Uchikawa D, Shikida M, Sato K (1998) Anisotropic etching properties of Silicon in KOH and TMAH solutions. In: Proceedings of the international symposium on micromechatronics and human science, pp 65–70
Tsai HH, Hsieh CC, Fan CW, Chen YC, Wu WT (2009) Design and characterization of temperature-robust piezoresistive micropressure sensor with double-wheatstone-bridge structure. In: Proceedings of the symposium on design, test, integration and packaging of MEMS/MOEMS, Rome, pp 363–368
Werner M, Gluche P, Adamschik M, Kohn E, Fecht HJ (1998) Review on diamond based piezoresistive sensors. Proc IEEE Int Symp Ind Electron 1:147–152
Wu CH, Zorman CA, Mehregany M (2006) Fabrication and testing of bulk micromachined silicon carbide piezoresistive pressure sensors for high temperature applications. IEEE Sens J 6:316–324
Wur DR, Davidson JL, Kang WP, Kinser DL (1995) Polycrystalline diamond pressure sensor. J Microelectromech Syst 4(1):34–41
Yu ZL, Zhao YL, Sun L, Tian B, Jiang ZD (2013) Incorporation of beams into bossed diaphragm for a high sensitivity and overload micro pressure sensor. Rev Sci Instrum 84:015004
Zhang YH, Yang C, Zhang ZH, Lin HW, Liu LT, Ren TL (2007) A novel pressure microsensor with 30-μm-thick diaphragm and meander-shaped piezoresistors partially distributed on highstress bulk silicon region. IEEE Sens J 7(12):1742–1748
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to acknowledge the generous support of the Director, CSIR-CEERI, Pilani. The authors would also like to thank all the scientific and technical staff of MEMS and Microsensors Group at CSIR-CEERI, Pilani. The financial support by Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) through PSC-201: MicroSenSys project is gratefully acknowledged. The authors would also like to thank Dr. S.C. Bose and Mr. M. Santosh from IC design group for their help in sensor characterization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S.S., Pant, B.D. Effect of piezoresistor configuration on output characteristics of piezoresistive pressure sensor: an experimental study. Microsyst Technol 22, 709–719 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-015-2451-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-015-2451-5