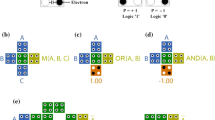
Abstract
Quantum-dot cellular automata (QCA) technology leads to rapid high-density combinatory low power exploitation to realize the reversible logic circuit in the nanoscale era. Reversible logic is an alternative to overcome excess energy indulgence of irreversible process. This paper illustrates a cost-effective, energy-efficient Universal Reversible Logic Gate in QCA framework which is capable of designing power analysis attack resistable hardware cryptographical circuit. The proposed (URLGs: U1 and U2) has been tested with simulator QCADesigner V2.0.3, outshined the existing pattern relating to the area, gate count, garbage count, and quantum cost. We found 37.5% garbage minimization is achieved compared to NFT, which is utmost minimization of garbage ever reported in QCA literature. Thirteen three variable standard Boolean functions are considered as logic benchmarks to guesstimate the capability and efficiency of proposed URLG in QCA circuit implementation and synthesizing logic gates. In average, our proposed U2 achieved 36.66% improvement in energy dissipation for different kink energy ratios over early reported work.

























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abutaleb MM (2018) QCAPUF: QCA-based physically unclonable function as a hardware security primitive. Semicond Sci Technol 33(4):045011. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6641/aab458
Bennett CH (1973) Logical reversibility of computation. IBM J Res Dev 17:525–532
Das K, De D (2010) Novel approach to design a testable conservative logic gate for QCA implementation. In: Advance computing conference (IACC), 2010 IEEE 2nd International. IEEE, pp 82–87
Das JC, De D (2016) User authentication based on quantum-dot cellular automata using reversible logic for secure nanocommunication. Arab J Sci Eng 41(3):773–784
Das JC, De D (2017) Operational efficiency of novel SISO shift register under thermal randomness in quantum-dot cellular automata design. Microsyst Technol 23(9):4155–4168
Feynman R (1985) Quantum mechanical computers. Opt News 11:11–20
Fredkin E, Toffoli T (1982) Conservative logic. Int J Theor Phys 21:219–253
Gadim MR, Navimipour NJ (2018) A new three-level fault tolerance arithmetic and logic unit based on quantum dot cellular automata. Microsyst Technol 24(2):1295–1305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-017-3502-x
Haghparast M, Navi K (2008) A novel fault tolerance reversible gate for nanotechnology based system. Am J Appl Sci 5(5):519–523
Haghparast M et al (2008) Design of a novel reversible multiplier circuit using HNG gate in nanotechnology. World Appl Sci 3(6):974–978
Huang J, Momenzadeh M, Schiano L, Lombardi F (2005) Simulation based design of modular QCA circuits. In: Proceedings of IEEE conference on nanotechnology, Nagoya
Kakali D, Mukhopadhyay D, Dutta P (2017) Comprehensive study on the performance comparison of logically reversible and irreversible parity generator and checker designs using two-dimensional two-dot one-electron QCA. Microsyst Technol 25:1659–1667
Kelsey J, Schneier B, Wagner D, Hall C (1998) Side channel cryptanalysis of product ciphers. In: Quisquater J-J, Deswarte Y, Meadows C, Gollmann D (eds) ESORICS 1998, vol 1485. LNCS. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 97–110
Kocher P, Jaffe J, Jun B (1999) Differential power analysis. In: Wiener M (ed) CRYPTO 1999, vol 1666. LNCS. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 388–397
Landauer R (1961) Irreversibility and heat generation in the computing process. IBM J Res Dev 5(3):183–191
Lent CS, Taugaw PD, Porod W, Bernstein GH (1993) Quantum cellular automata. Nanotechnology 4:49–57
Liu W, Srivastava S, O’Neill M, Swartzlander EE (2014) Security issues in QCA circuit design-power analysis attacks. In: Field-coupled nanocomputing. Springer, Berlin, pp 194–222
Ma X, Huang J, Metra C, Lombardi F (2008) Reversible gates and testability of one dimensional arrays of molecular QCA. Springer J Electron Test 24(1–3):297–311
Maslov D, Dueck GW (2004) Reversible cascades with minimal garbage. IEEE Trans CAD 23(11):1497–1509
Momenzadeh M, Huang J, Tahoori MB, Lombardi F (2005) Characterization, test, and logic synthesis of and-or-inverter (AOI) gate design for QCA implementation. In: IEEE Trans. on aided design of integrated circuits and systems, vol 24, pp 1881–1893
Pain P, Das K et al (2019) Novel true random number generator based hardware cryptographic architecture using quantum-dot cellular automata. Int J Theor Phys. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-019-04189-2
Peres A (1985) Reversible logic and quantum computers. Phys Rev A 32(6):3266–3276. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.32.3266
Sadhu A, Das K, De D, Kanjilal MR (2019) SSTRNG: self starved feedback SRAM based true random number generator using quantum cellular automata. Microsyst Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-019-04525-w
Sen B, Sikdar BK (2007) Characterization of universal NAND-NOR-inverter QCA gate. In: 11th IEEE VLSI design and test symposium, Kolkata, August 8–11
Sen B, Dutta M, Some S, Sikdar BK (2014) Realizing reversible computing in QCA framework resulting in efficient design of testable ALU. ACM J Emerg Technol Comput Syst (JETC) 11(3):30
Srivastava S, Asthana A, Bhanja S, Sarkar S (2011) QCAPro—an error-power estimation tool for QCA circuit design. IEEE Int Symp Circ Syst (ISCAS) 2011:2377–2380. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISCAS.2011.5938081
Thapliyal H, Ranganathan N (2008) Testable reversible latches for molecular QCA. In: Nanotechnology, 2008. NANO ‘08. 8th IEEE conference, pp 699–702
Thapliyal H, Ranganathan N (2009) Design of efficient reversible binary subtractors based on a new reversible gate. In: VLSI, 2009. ISVLSI ‘09. IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on 13–15 May 2009, pp 229–234
Thapliyal H, Ranganathan N (2010) Reversible logic-based concurrently testable latches for molecular QCA. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 9(1):62–69. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNANO.2009.2025038
Thapliyal H, Zwolinski M (2006) Reversible logic to cryptographic hardware: a new paradigm. In: 49th IEEE international Midwest symposium on circuits and systems, 2006. MWSCAS’06, vol 1, pp 342–346. IEEE
Thoori MB, Huang J, Momenzadeh M, Lombardi F (2004) Testing of quantum Cell automata. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 3(4):432–442
Toffoli T (1980) Reversible computing. Tech Memo MIT/LCS/TM-151, MIT Lab for Computer Science
Walus K et al (2002) ATIPS laboratory QCADesigner. ATIPS Laboratory, University of Calgary, Canada. http://www.qcadesigner.ca
Wang W, Zhang R, Walus K, Jullien GA (2004) A method of majority logic reduction for quantum cellular automata. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 3(4):443–450
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Science and Engineering Research Board (DST-SERB), Govt. of India, for providing with the grant for the accomplishment of the project under the Project File No. ECR/2016/000613.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pain, P., Das, K., Sadhu, A. et al. Power analysis attack resistable hardware cryptographical circuit design using reversible logic gate in quantum cellular automata. Microsyst Technol 28, 779–791 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-019-04581-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-019-04581-2