Abstract
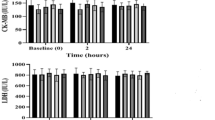
The aim of this study was to document sedation and analgesic effects, electrocardiographic (ECG) parameters, and some physiologic variable and serum concentrations of electrolytes after intravenous (IV) administration of detomidine in camels. Five healthy female dromedary camels (Camelus dromedarius) aged 2 years and average weight of 200 ± 20 kg were used. Data were recorded before and 3, 5, 10, 15, 30, 45, 60, and 90 min after IV administration of detomidine (50 μg kg−1). Sedation and antinociception response were recorded. The ECG was attached as a bipolar base-apex lead, and indices measured and analyzed were P, QRS, and T wave amplitude, duration and configuration, and duration of P-R, Q-T, and R-R intervals. Venous blood was collected for the measurement of sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), chloride (Cl−), calcium (Ca2+), magnesium (Mg2+), and phosphorus (P−) concentrations. Posture and behavioral observed after detomidine administration were depression, swaying, tremors, muscular weakness, nasal discharge, drooling, drooping of head and lower lip, hind limb ataxia, anorexia, frequent urination, staggering, snoring, and nystagmus. Significantly increased in sedation scores and antinociception grades were seen. Heart rate (HR) was significantly decreased. Amplitude of P, QRS, and T waves, and P-R interval durations were not significantly changed from baseline during sedation. Durations of Q-T and R-R intervals were significantly prolonged after detomidine injection (p < 0.05). Sinus arrhythmia and bradycardia were recorded in five out of five camels from 3 to 60 min after detomidine administration. ECG waves configurations were not changed during sedation. Serum concentrations of all electrolytes were not changed after detomidine injection (p > 0.05). Detomidine produced a rapid and reliable sedation and antinociception, and could be used for a variety of diagnostic and surgical procedures in C. dromedarius without cardiopulmonary disease in the field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali BH, Sanhouri AA, Musa BE (1989) Some clinical, hematological and biochemical effects of four tranquilizer in camels (Camelus dromedarius). Reselev Med Vet Pays Trop 42:13–17
Alshara MA, Somro H, Memon MA, Kalhoro AB (2000) Effect of xylazine on the blood glucose levels in young male buffaloes. Pak Vet J 20:200–202
Azari O, Molaei MM, Emadi L, Sakhaee E, Sharifi H, Mehdizadeh S (2012) Hematological and biochemical alterations caused by epidural and intramuscular administration of xylazine hydrochloride in dromedary camels (Camelus dromedarius). Vet Ital 48:313–321
Berton JJ, Horspool JIL (2004) Equine clinical pharmacology, 1st edn. WB Saunders, London, pp 267–306
Bogin E (2000) Clinical pathology of Camelides: present and future. Revue Med Vet 151:563–568
Cardoso CG, Marques DR, Silva TH, Mattos-junior E (2014) Cardiorespiratory, sedative and antinociceptive effects of dexmedetomidine alone or in combination with methadone, morphine or tramadol in dogs. Vet Anaesth Analg 41:636–643
Cebra C, Cebra M (2002) Diseases of the cardiovascular system. In: Sheep and goat medicine, 1st edn. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 393–396
Duke-Novakovski T, Palacios-Jimenez C, Wetzel T, Rymes L, Sanches-Teran AF (2015) Cardiopulmonary effects of dexmedetomidine and ketamine infusions with either propofol infusion or isoflurane for anesthesia in horses. Vet Anaesth Analg 42:39–49
El-Maghraby HM, Al-qudah K (2005) Sedative and analgesic effects of detomidine in camels (Camelus dromedarius). J Camel Pract Res 12:41–45
Escudero A, Gonzalez JR, Benedito JL, Prieto FR, Ayala I (2009) Electrocardiographic parameters in the clinically healthy Zamorano-leones donkey. Res Vet Sci 87:458–461
Garcia-Villar R, Toutain PL, Alvinerie M, Ruckebusch Y (1981) The pharmacokinetics of xylazine hydrochloride: an inter specific study. J Vet pharm Ther 4:87–92
Hall LW, Clark KW (1991) Veterinary anesthesia, 9th edn. Bailliere Tindal, Philadelphia, pp 51–71
Jam JS, Kaihoro AB, Somro J, Memon MA, Buriro R, Qureshsi TA (2005) Effects of xylazine on hematological parameters in indigenous sheep. Abstracts 2nd National Conference on Agriculture and Animal Sciences, Tandojam, p 37–38
Jochle W, Moore JN, Brown J, Lowe JE, Moore JN, Watking JP, Reeves MJ, White NA, Funbini S (1989) Comparison of detomidine, butorphanol, flunixin meglumine and xylazine in clinical cases of equine colic. Equine Vet J 7:111–116
Khan MA, Ashraf M, Pervez K, Hashmi HA, Mahmood AK (2003) Effects of detomidine on blood chemistry and electrolyte profile in buffalo calves. Int J Agri Biol 5:308–310
Latimer KS, Mahaffey EA, Prasse KW (2003) Duncan and Prasse’s veterinary laboratory medicine, 4th edn. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 3–45
Marais AL, Van Der Walt JG, Skinner JD (1991) The effect of xylazine and fentanyl on various hormones and metabolites in karakul sheep and a blesbok. J S Afr Vet Assoc 62:17–19
Plumb DC (2002) Veterinary drug handbook, 4th edn. Iowa state university press, IA, pp 400–402
Pourjafar M, Badiei K, Chalmeh A, Naghib M, Pourmirzaei H, Abdolhoseinzadeh M (2011) Prevalence of cardiac arrhythmias in normal Camelus dromedarius. Online J Vet Med 15:297–303
Radostits OM, Gay CC, Hinchcliff KW, Constable PD (2007) Veterinary medicine: a text book of the diseases of cattle, horses, sheep, pigs and goats, 10th edn. Elsevier, London, pp 399–438
Rezakhani A, Szabuniewicz M (1977) The electrocardiogram of the camel (Camelus dromedarius). Zbl Vet Med A 24:277–286
Rezakhani A, Papahn AA, Shekarfroush S (2004) Analysis of base apex lead electrocardiograms of normal dairy cows. Vet Arhiv 74:351–358
Ringer SK, Schwarzwald CC, Portier K, Mauch J, Ritter A, Bettschart-Wolfensberger R (2013) Blood glucose, acid–base and electrolyte changes during loading doses of alpha2-adrenergic agonists followed by constant rate infusions in horses. Vet J 198:684–689
Shah Z, Kalhore AB, Kachiwal AB, Ahmad I, Sattar H, Khan MA, Rehman ZU, Khan FA, Hussain T, Ullah HA (2013) Comparative studies on sedative and analgesic effects of xylazine and detomidine in goats. J Anim Plant Sci 23:39–42
Shekidef MH, Saleh SY (2011) Effects of epidural administration of ketamine/xylazine and ketamine/medetomidine combinations in dromedary camels (Camelus dromedarius). J Camel Pract Res 18:319–329
Short CE (1992) Alpha2-agonists in animals: sedation, analgesia and anesthesia, 1st edn. Veterinary practice publishing company, California, pp 23–81
Tajik J, Sazmand AR, Rasooli A, Mohammadzadeh YA (2015) Serum concentration of some ions in clinically healthy camels (Camelus dromedaries). Euroasian J Vet Sci 31:204–208
Tunio AN, Kalhoro AB, Kathio IH (2003) Sedative and analgesic effects of detomidine hydrochloride in goats. Pak Vet J 23:143–149
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samimi, A.S., Azari, O. The effect of detomidine on clinical signs, serum electrolytes, electrocardiographic indices, and cardiac arrhythmias in Camelus dromedarius . Comp Clin Pathol 26, 707–712 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-017-2441-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-017-2441-3