Abstract
Objective
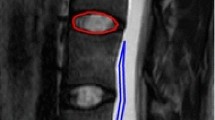
The aim of this study was to determine the relationship between the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration using diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DWI).
Materials and methods
Using a 3 T magnetic resonance scanner, DWI of the lumbar spine was assessed in 109 patients, with a total of 545 lumbar discs analyzed. Apparent diffusion coefficient values were recorded for each disc, and all discs were visually graded by two independent observers using Pfirrmann’s grading system. Apparent diffusion coefficient values of disc were tested by correlation with qualitative clinical grading of degeneration severity, patient age, and sex. Correlations were investigated using Pearson’s and Spearman’s rank correlation analysis, and multiple regression analysis.
Results
Intervertebral disc degeneration was negatively correlated with ADC values of all levels (Spearman’s correlation coefficient ranged from −0.381 to −0.604, p < 0.001). There was a significant negative association between age and ADC values at all spinal levels (Pearson’s correlation coefficient ranged from −0.353 to −0.650, p < 0.001). When stepwise regression models were analyzed, both disc degeneration and age remained negatively associated with ADC values at each lumbar level (standardized coefficients ranged from −0.231 to −0.505, p < 0.01 and standardized coefficients ranged from −0.179 to −0.523, p < 0.05 respectively).
Conclusion
Apparent diffusion coefficient values obtained using DWI can assess lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration, and the ADC values were negatively correlated with the degree of disc degeneration.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
An HS, Anderson PA, Haughton VM, Iatridis JC, Kang JD, Lotz JC et al (2004) Introduction: disc degeneration: summary. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 29(23):2677–2678
Smith LJ, Kurmis AP, Slavotinek JP, Fazzalari NL (2011) In vitro evaluation of a manganese chloride phantom-based MRI technique for quantitative determination of lumbar intervertebral disc composition and condition. Eur Spine J 20(3):434–439
Kettler A, Wilke H (2006) Review of existing grading systems for cervical or lumbar disc and facet joint degeneration. Eur Spine J 15(6):705–718
Theilmann RJ, Borders R, Trouard TP, Xia G, Outwater E, Ranger-Moore J et al (2004) Changes in water mobility measured by diffusion MRI predict response of metastatic breast cancer to chemotherapy. Neoplasia 6(6):831–837
Ohgiya Y, Oka M, Hiwatashi A, Liu X, Kakimoto N, Westesson PA et al (2007) Diffusion tensor MR imaging of the cervical spinal cord in patients with multiple sclerosis. Eur Radiol 17(10):2499–2504
Khalil C, Hancart C, Le Thuc V, Chantelot C, Chechin D, Cotton A (2008) Diffusion tensor imaging and tractography of the median nerve in carpal tunnel syndrome: preliminary results. Eur Radiol 18(10):2283–2291
Antoniou J, Demers CN, Beaudoin G, Goswami T, Mwale F, Aebi M et al (2004) Apparent diffusion coefficient of intervertebral discs related to matrix composition and integrity. Magn Reson Imaging 22(7):963–972
Beattie PF, Morgan PS, Peters D (2008) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of normal and degenerative lumbar intervertebral discs: a new method to potentially quantify the physiologic effect of physical therapy intervention. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 38(2):42–49
Kealey SM, Aho T, Delong D, Barboriak DP, Provenzale JM, Eastwood JD (2005) Assessment of apparent diffusion coefficient in normal and degenerated intervertebral lumbar disks: initial experience. Radiology 235(2):569–574
Niinimäki J, Korkiakoski A, Ojala O, Karppinen J, Ruohonen J, Haapea M et al (2009) Association between visual degeneration of intervertebral discs and the apparent diffusion coefficient. Magn Reson Imaging 27(5):641–647
Williams JR (2008) The Declaration of Helsinki and public health. Bull World Health Organ 86(8):650–652
Pfirrmann CW, Metzdorf A, Zanetti M, Hodler J, Boos N (2001) Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 26(17):1873–1878
Ichikawa T, Haradome H, Hachiya J, Nitatori T, Araki T (1999) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging with single-shot echo-planar imaging in the upper abdomen: preliminary clinical experience in 61 patients. Abdom Imaging 24(5):456–461
Urban JP, Winlove CP (2007) Pathophysiology of the intervertebral disc and the challenges for MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 25(2):419–432
Kerttula L, Kurunlahti M, Jauhiainen J, Koivula A, Oikarinen J, Tervonen O (2001) Apparent diffusion coefficients and T2 relaxation time measurements to evaluate disc degeneration: a quantitative MR study of young patients with previous vertebral fracture. Acta Radiol 42(6):585–591
Siemionow K, An H, Masuda K, Andersson G, Cs-Szabo G (2011) The Effects of age, gender, ethnicity, and spinal level on the rate of intervertebral disc degeneration. A review of 1712 intervertebral discs. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 36(17):1333–1339
Keller TS, Colloca CJ, Harrison DE, Harrison DD, Janik TJ (2005) Influence of spine morphology on intervertebral disc loads and stresses in asymptomatic adults: implications for the ideal spine. Spine J 5(3):297–309
Anderson DG, Tannoury C (2005) Molecular pathogenic factors in symptomatic disc degeneration. Spine J 5(6 Suppl):260S–266S
Roughley PJ (2004) Biology of intervertebral disc aging and degeneration: involvement of the extracellular matrix. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 29(23):2691–2699
Feng H, Danfelter M, Strömqvist B, Heinegård D (2006) Extracellular matrix in disc degeneration. J Bone Joint Surg Am 88(Suppl 2):25–29
Roberts S, Evans H, Trivedi J, Menage J (2006) Histology and pathology of the human intervertebral disc. J Bone Joint Surg Am 88(Suppl 2):10–14
Podichetty VK (2007) The aging spine: the role of inflammatory mediators in intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 53(5):4–18
Boos N, Weissbach S, Rohrbach H, Weiler C, Spratt KF, Nerlich AG (2002) Classification of age-related changes in lumbar intervertebral discs: 2002 volvo award in basic science. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 27(23):2631–2644
Antoniou J, Steffen T, Nelson F, Winterbottom N, Hollander AP, Poole RA et al (1996) The human lumbar intervertebral disc. Evidence for changes in the biosynthesis and denaturation of the extracellular matrix with growth, maturation, ageing, and degeneration. J Clin Invest 98(4):996–1003
Takatalo J, Karppinen J, Niinimäki J, Taimela S, Mutanen P, Sequeiros RB et al (2012) Association of modic changes, Schmorl’s nodes, spondylolytic defects, high-intensity zone lesions, disc herniations, and radial tears with low back symptom severity among young Finnish adults. Spine 37(14):1231–1239
Wang YX, Griffith JF (2010) Effect of menopause on lumbar disc degeneration: potential etiology. Radiology 257(2):318–320
Kim KW, Chung HN, Ha KY, Lee JS, Kim YY (2009) Senescence mechanisms of nucleus pulposus chondrocytes in human intervertebral discs. Spine J 9(8):658–666
Rodriguez AG, Slichter CK, Acosta FL, Rodriguez-Soto AE, Burghardt AJ, Majumdar S et al (2011) Human disc nucleus properties and vertebral endplate permeability. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 36(7):512–520
Rodriguez AG, Rodriguez-Soto AE, Burghardt AJ, Berven S, Majumdar S, Lotz JC (2012) Morphology of the human vertebral endplate. J Orthop Res 30(2):280–287
Miller JA, Schmatz C, Schultz AB (1988) Lumbar disc degeneration: correlation with age, sex, and spine level in 600 autopsy specimens. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 13(2):173–178
Acknowledgments
We thank Ph.D PengXue for analysis and interpretation of data (Department of Endocrinology, the Third Hospital of Hebei medical University, Shijiazhuang, Hebei 050051, China).
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has any conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Ma, X., Wang, Y. et al. Assessment of apparent diffusion coefficient in lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Eur Spine J 23, 1830–1836 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-014-3285-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-014-3285-z