Abstract
A highly sensitive electrochemical sensor for the simultaneous determination of catechol (CC) and hydroquinone (HQ) was fabricated by electrodeposition of gold nanoparticles onto carbon nanofiber film pre-cast on an Au electrode. Both CC and HQ cause a pair of quasi-reversible and well-defined redox peaks at the modified electrode in pH 7.0 solution. Simultaneously, the oxidation peak potentials of CC and HQ become separated by 112 mV. When simultaneously changing the concentrations of both CC and HQ, the response is linear between 9.0 μM and 1.50 mM. In the presence of 0.15 mM of the respective isomer, the electrode gives a linear response in the range from 5.0 to 350 μM, and from 9.0 to 500 μM for CC and HQ, respectively, and detection limits are 0.36 and 0.86 μM. The method was successfully examined for real sample analysis with high selectivity and sensitivity.

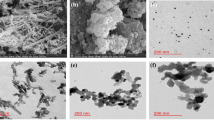
Highly sensitive and simultaneous determination of catechol and hydroquinone was realized at the GNPs/CNF/Au electrode (d), and its peak currents had nearly two times higher than that of the CNF/Au electrode(c), while only one oxidation peak was observed for both analytes at the bare Au electrode (a) and GNPs/Au electrode (b)





Similar content being viewed by others

References
Terashima C, Rao TN, Sarada BV, Tryk DA, Fujishima A (2002) Electrochemical oxidation of chlorphenols at a boron-doped diamond electrode and their determination by high-performance liquid chromatography with amperometric detection. Anal Chem 74:895–902
Xiao WX, Dan X (2007) Aminopyrene functionalized mesoporous silica for the selective determination of resorcinol. Talanta 72:1288–1292
Xie TY, Liu QW, Shi YR, Liu QY (2006) Simultaneous determination of positional isomers of benzenediols by capilary zone electrophoresis with square wave amperometric detection. J Chromatogr A 1109:317–321
Cui H, He CX, Zhao GW (1999) Determination of polyphenols by high-performance liquid chromatography with inhibited chemiluminescence detection. J Chromatogr A 855:171–179
Garcia-Mesa JA, Mateos R (2007) Direct automatic determination of bitterness and total phenolic compounds in virgin olive oil using a pH-based flow-injection analysis system. J Agric Food Chem 55:3863–3868
Pistonesi MF, Nezio MSD, Centurión ME, Palomeque ME, Lista AG, Band BSF (2006) Determination of phenol, resorcinol and hydroquinone in air samples by synchronous fluorescence using partial least-squares (PLS). Talanta 69:1265–1268
Qi HL, Zhang CX (2005) Simultaneous determination of hydroquinone and catechol at a glassy carbon electrode modified with multiwall carbon nanotubes. Electroanalysis 17:832–838
Zhao DM, Zhang XH, Feng LJ, Li J, Wang SF (2009) Simultaneous determination of hydroquinone and catechol at PASA/MWNTs composite film modified glassy carbon electrode. Colloids Surf, B 74:317–321
Zhang H, Zhao JS, Liu HT, Liu RM, Wang HS, Liu JF (2010) Electrochemical determinationof diphenols and their mixtures at the multiwall carbon nanotubes/poly (3-methylthiophene) modified glassy carbon electrode. Microchim Acta 169:277–282
Wang L, Huang P, Bai J, Wang H, Zhang L, Zhao Y (2007) Direct simultaneous electrochemical determination of hydroquinone and catechol at a poly(glutamic acid) modified glassy carbon electrode. Int J Electrochem Sci 2:123–132
Wang L, Huang PF, Bai JY, Wang HJ, Zhang LY, Zhao YQ (2007) Covalent modification of a glassy carbon electrode with penicillamine for simultaneous determination of hydroquinone and catechol. Microchim Acta 158:151–157
Wang L, Huang PF, Wang HJ, Bai JY, Zhang LY, Zhao YQ (2007) Covalent modification of glassy carbon electrode with aspartic acid for simultaneous determination of hydroquinone and catechol. Ann Chim 97:395–404
Ghanem MA (2007) Electrocatalytic activity and simultaneous determination of catechol and hydroquinone at mesoporous platinum electrode. Electrochem Commun 9:2501–2506
Yu JJ, Du W, Zhao FQ, Zeng BZ (2009) High sensitive simultaneous determination of catechol and hydroquinone at mesoporous carbon CMK-3 electrode in comparison with multi-walled carbon nanotubes and Vulcan XC-72 carbon electrodes. Electrochim Acta 54:984–988
Ahammad AJS, Sarker S, Rahman MA, Leea J-J (2010) Simultaneous determination of hydroquinone and catechol at an activated glassy carbon electrode. Electroanalysis 22:694–700
Zhang MG, Gorski W (2005) Electrochemical sensing based on redox mediation at carbon nanotubes. Anal Chem 77:3960–3965
Banks CE, Compton RG (2005) Exploring the electrocatalytic sites of carbon nanotubes for NADH detection: an edge plane pyrolytic graphite electrode study. Analyst 130:1232–1239
Weeks ML, Rahman T, Frymier PD, Islam SK, McKnight TE (2008) A reagentless enzymatic amperometric biosensor using vertically aligned carbon nanofibers (VACNF). Sensor Actuator B 133:53–59
Werner P, Verdejo R, Wöllecke F, Altstädt V, Sandler JKW, Shaffer MSP (2005) Carbon nanofibers allow foaming of semicrystalline poly(ether ether ketone). Adv Mater 17:2864–2869
Arvinte A, Valentini F, Radoi A, Arduini F, Tamburri E, Rotariu L, Palleschi G, Bala C (2007) The NADH electrochemical detection performed at carbon nanofibers modified glassy carbon electrode. Electroanalysis 19:1455–1459
Rassaei L, Sillanpaa M, Bonne MJ, Marken F (2007) Carbon nanofiber–polystyrene composite electrodes for electroanalytical processes. Electroanalysis 19:1461–1466
Daniel MC, Astruc D (2004) Gold nanoparticles:assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem Rev 104:293–346
Li HQ, Liu RL, Zhao DY, Xia YY (2007) Electrochemical properties of an ordered mesoporous carbon prepared by direct tri-constituent co-assembly. Carbon 45:2628–2635
Harvey D (2000) Modern analytical chemistry, 1st edn. Mc Graw-Hill, New York, p 151
Ding YP, Liu WL, Wu QS, Wang XG (2005) Direct simultaneous determination of dihydroxybenzene isomers at C-nanotube-modified electrodes by derivative voltammetry. J Electroanal Chem 575:275–280
Li MG, Ni F, Wang YL, Xu SD, Zhang DD, Chen SH, Wang L (2009) Sensitive and facile determination of catechol and hydroquinone simultaneously under coexistence of resorcinol with a Zn/Al layered double hydroxide film modified glassy carbon electrode. Electroanalysis 21:1521–1526
Acknowledgments
We greatly appreciate the supports of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 20775047).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
The molecule structures of catechol and hydroquinone). (DOC 30.5 kb)
Fig. S2
CV of CC in 0.1 M phosphate buffer solution (pH 7.0) containing 4 mM analyte at bare Au electrode (a), GNPs/Au electrode (b), CNF/Au electrode (c) and GNPs/CNF/Au electrode (d). (DOC 95 kb)
Fig. S3
CV of HQ in 0.1 M phosphate buffer solution (pH 7.0) containing 4 mM analyte at bare Au electrode (a), GNPs/Au electrode (b), CNF/Au electrode (c) and GNPs/CNF/Au electrode (d). (DOC 93 kb)
Fig. S4
DPV of increasing concentrations of CC and HQ in phosphate buffer solution (pH 7.0): (a) 9.0, (b) 50, (c) 150, (d) 250, (e) 550, (f) 820, (g) 1500 μM. (DOC 111 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huo, Z., Zhou, Y., Liu, Q. et al. Sensitive simultaneous determination of catechol and hydroquinone using a gold electrode modified with carbon nanofibers and gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 173, 119–125 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-010-0530-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-010-0530-y