Abstract
Screening serum for the presence of prostate specific antigen (PSA) belongs to the most common approach for the detection of prostate cancer. This review (with 156 refs.) addresses recent developments in PSA detection based on the use of various kinds of nanomaterials. It starts with an introduction into the field, the significance of testing for PSA, and on current limitations. A first main section treats electrochemical biosensors for PSA, with subsections on methods based on the use of gold electrodes, graphene or graphene-oxide, carbon nanotubes, hybrid nanoparticles, and other types of nanoparticles. It also covers electrochemical methods based on the enzyme-like activity of PSA, on DNA-, aptamer- and biofuel cell-based methods, and on the detection of PSA via its glycan part. The next main section covers optical biosensors, with subsections on methods making use of surface plasmon resonance (SPR), localized SPR and plasmonic ELISA-like schemes. This is followed by subsections on methods based on the use of fiber optics, fluorescence, chemiluminescence, Raman scattering and SERS, electrochemiluminescence and cantilever-based methods. The most sensitive biosensors are the electrochemical ones, with lowest limits of detection (down to attomolar concentrations), followed by mass cantilever sensing and electrochemilumenescent strategies. Optical biosensors show lower performance, but are still more sensitive compared to standard ELISA. The most commonly applied nanomaterials are metal and carbon-based ones and their hybrid composites used for different amplification strategies. The most attractive sensing schemes are summarized in a Table. The review ends with a section on conclusions and perspectives.

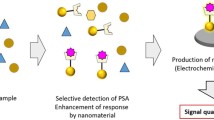
Schematic representation of nanostructure-based biosensors for detection of prostate specific antigen using various detection schemes and biorecognition elements such as antibodies (Abs), aptamers (APT), lectins (LEC), and molecularly imprinted polymers (MIP).









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Steliarova-Foucher E, Lortet-Tieulent J, Rosso S, Coebergh JWW, Comber H, Forman D, Bray F (2013) Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: Estimates for 40 countries in 2012. Eur J Cancer 49(6):1374–1403
Bray F, Kiemeney LA (2017) Epidemiology of Prostate Cancer in Europe: Patterns, Trends and Determinants. In: Management of Prostate Cancer. Springer, pp 1–27
Mokdad AH, Dwyer-Lindgren L, Fitzmaurice C, Stubbs RW, Bertozzi-Villa A, Morozoff C, Charara R, Allen C, Naghavi M, Murray CJ (2017) Trends and patterns of disparities in cancer mortality among US counties, 1980-2014. JAMA 317(4):388–406
Prostate cancer (2015). http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Cancer-of-the-prostate/Pages/Introduction.aspx
Miller DC, Hafez KS, Stewart A, Montie JE, Wei JT (2003) Prostate carcinoma presentation, diagnosis, and staging: an update form the National Cancer Data Base. Cancer 98(6):1169–1178
Mottet N, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Briers E, Cumberbatch MG, De Santis M, Fossati N, Gross T, Henry AM, Joniau S, Lam TB, Mason MD, Matveev VB, Moldovan PC, van den Bergh RCN, Van den Broeck T, van der Poel HG, van der Kwast TH, Rouvière O, Schoots IG, Wiegel T, Cornford P (2017) EAU-ESTRO-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer. Part 1: Screening, Diagnosis, and Local Treatment with Curative Intent. Eur Urol 71(4):618–629
Parpart S, Rudis A, Schreck A, Dewan N, Warren P (2007) Sensitivity and specificity in prostate cancer screening methods and strategies. J Young Invest http://www.jyi.org/issue/sensitivity-and-specificity-in-prostate-cancer-screening-methods-and-strategies/
Wolf AM, Wender RC, Etzioni RB, Thompson IM, D'Amico AV, Volk RJ, Brooks DD, Dash C, Guessous I, Andrews K, DeSantis C, Smith RA (2010) American Cancer Society guideline for the early detection of prostate cancer: update 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 60(2):70–98
Stamey TA, Yang N, Hay AR, McNeal JE, Freiha FS, Redwine E (1987) Prostate-specific antigen as a serum marker for adenocarcinoma of the prostate. N Engl J Med 317(15):909–916
Hara M, Inoue T, Koyanagi Y, Fukuyama T, Iki H (1969) Immunochemical characteristics of human specific component “γ-Sm”. Nippon Hoigaku Zasshi 23:333
Oesterling JE (1991) Prostate specific antigen: a critical assessment of the most useful tumor marker for adenocarcinoma of the prostate. J Urol 145(5):907–923
Yousef GM, Diamandis EP (2001) The new human tissue kallikrein gene family: structure, function, and association to disease. Endocr Rev 22(2):184–204
Jolly P, Tamboli V, Harniman RL, Estrela P, Allender CJ, Bowen JL (2016) Aptamer–MIP hybrid receptor for highly sensitive electrochemical detection of prostate specific antigen. Biosens Bioelectron 75:188–195
Oesterling JE, Jacobsen SJ, Chute CG, Guess HA, Girman CJ, Panser LA, Lieber MM (1993) Serum prostate-specific antigen in a community-based population of healthy men. Establishment of age-specific reference ranges. JAMA 270(7):860–864
Ito K, Yamamoto T, Ohi M, Kurokawa K, Suzuki K, Yamanaka H (2003) Free/total PSA ratio is a powerful predictor of future prostate cancer morbidity in men with initial PSA levels of 4.1 to 10.0 ng/mL. Urology 61(4):760–764
Catalona WJ, Partin AW, Slawin KM, Brawer MK, Flanigan RC, Patel A, Richie JP, deKernion JB, Walsh PC, Scardino PT, Lange PH, Subong EN, Parson RE, Gasior GH, Loveland KG, Southwick PC (1998) Use of the percentage of free prostate-specific antigen to enhance differentiation of prostate cancer from benign prostatic disease: a prospective multicenter clinical trial. JAMA 279(19):1542–1547
Velonas VM, Woo HH, dos Remedios CG, Assinder SJ (2013) Current Status of Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer. Int J Mol Sci 14(6):11034–11060
Sharma S, Zapatero-Rodríguez J, O'Kennedy R (2017) Prostate cancer diagnostics: Clinical challenges and the ongoing need for disruptive and effective diagnostic tools. Biotechnol Adv 35(2):135–149
Shan J, Ma Z (2017) A review on amperometric immunoassays for tumor markers based on the use of hybrid materials consisting of conducting polymers and noble metal nanomaterials. Microchim Acta 184:969–979
Paleček E, Tkáč J, Bartošík M, Ts B, Ostatná V, Paleček J (2015) Electrochemistry of Nonconjugated Proteins and Glycoproteins. Toward Sensors for Biomedicine and Glycomics. Chem Rev 115(5):2045–2108
Labib M, Sargent EH, Kelley SO (2016) Electrochemical Methods for the Analysis of Clinically Relevant Biomolecules. Chem Rev 116(16):9001–9090
Rackus DG, Shamsi MH, Wheeler AR (2015) Electrochemistry, biosensors and microfluidics: a convergence of fields. Chem Soc Rev 44(15):5320–5340
Grieshaber D, MacKenzie R, Vörös J, Reimhult E (2008) Electrochemical Biosensors - Sensor Principles and Architectures. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland) 8(3):1400–1458
Uludag Y, Narter F, Sağlam E, Köktürk G, Gök MY, Akgün M, Barut S, Budak S (2016) An integrated lab-on-a-chip-based electrochemical biosensor for rapid and sensitive detection of cancer biomarkers. Anal Bioanal Chem 408(27):7775–7783
Schumacher S, Nestler J, Otto T, Wegener M, Ehrentreich-Forster E, Michel D, Wunderlich K, Palzer S, Sohn K, Weber A, Burgard M, Grzesiak A, Teichert A, Brandenburg A, Koger B, Albers J, Nebling E, Bier FF (2012) Highly-integrated lab-on-chip system for point-of-care multiparameter analysis. Lab Chip 12(3):464–473
Pandey B, Demchenko AV, Stine KJ (2012) Nanoporous gold as a solid support for protein immobilization and development of an electrochemical immunoassay for prostate specific antigen and carcinoembryonic antigen. Microchim Acta 179(1):71–81
Tian J, Huang J, Zhao Y, Zhao S (2012) Electrochemical immunosensor for prostate-specific antigen using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a nanocomposite containing gold nanoparticles supported with starch-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Microchim Acta 178(1):81–88
Yang J, Wen W, Zhang X, Wang S (2015) Electrochemical immunosensor for the prostate specific antigen detection based on carbon nanotube and gold nanoparticle amplification strategy. Microchim Acta 182(9):1855–1861
Uludag Y, Köktürk G (2015) Determination of prostate-specific antigen in serum samples using gold nanoparticle based amplification and lab-on-a-chip based amperometric detection. Microchim Acta 182(9):1685–1691
Wang Y, Qu Y, Liu G, Hou X, Huang Y, Wu W, Wu K, Li C (2015) Electrochemical immunoassay for the prostate specific antigen using a reduced graphene oxide functionalized with a high molecular-weight silk peptide. Microchim Acta 182(11):2061–2067
Zhao J, Guo Z, Feng D, Guo J, Wang J, Zhang Y (2015) Simultaneous electrochemical immunosensing of alpha-fetoprotein and prostate specific antigen using a glassy carbon electrode modified with gold nanoparticle-coated silica nanospheres and decorated with Azure A or ferrocenecarboxylic acid. Microchim Acta 182(15):2435–2442
Gutiérrez-Zúñiga GG, Hernández-López JL (2016) Sensitivity improvement of a sandwich-type ELISA immunosensor for the detection of different prostate-specific antigen isoforms in human serum using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and an ordered and hierarchically organized interfacial supramolecular architecture. Anal Chim Acta 902:97–106
Liu B, Lu L, Hua E, Jiang S, Xie G (2012) Detection of the human prostate-specific antigen using an aptasensor with gold nanoparticles encapsulated by graphitized mesoporous carbon. Microchim Acta 178(1):163–170
Shin KS, Ji JH, Hwang KS, Jun SC, Kang JY (2016) Sensitivity Enhancement of Bead-based Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (BEIS) biosensor by electric field-focusing in microwells. Biosens Bioelectron 85:16–24
Çevik E, Bahar Ö, Şenel M, Abasıyanık MF (2016) Construction of novel electrochemical immunosensor for detection of prostate specific antigen using ferrocene-PAMAM dendrimers. Biosens Bioelectron 86:1074–1079
Novoselov KS, Geim AK, Morozov SV, Jiang D, Zhang Y, Dubonos SV, Grigorieva IV, Firsov AA (2004) Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 306(5696):666–669
Yan M, Zang D, Ge S, Ge L, Yu J (2012) A disposable electrochemical immunosensor based on carbon screen-printed electrodes for the detection of prostate specific antigen. Biosens Bioelectron 38(1):355–361
Mao K, Wu D, Li Y, Ma H, Ni Z, Yu H, Luo C, Wei Q, Du B (2012) Label-free electrochemical immunosensor based on graphene/methylene blue nanocomposite. Anal Biochem 422(1):22–27
Salimi A, Kavosi B, Fathi F, Hallaj R (2013) Highly sensitive immunosensing of prostate-specific antigen based on ionic liquid–carbon nanotubes modified electrode: Application as cancer biomarker for prostatebiopsies. Biosens Bioelectron 42:439–446
Kavosi B, Salimi A, Hallaj R, Amani K (2014) A highly sensitive prostate-specific antigen immunosensor based on gold nanoparticles/PAMAM dendrimer loaded on MWCNTS/chitosan/ionic liquid nanocomposite. Biosens Bioelectron 52:20–28
Feng J, Li Y, Li M, Li F, Han J, Dong Y, Chen Z, Wang P, Liu H, Wei Q (2017) A novel sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor for PSA detection based on PtCu bimetallic hybrid (2D/2D) rGO/g-C3N4. Biosens Bioelectron 91:441–448
Ding L-L, Ge J-P, Zhou W-Q, Gao J-P, Zhang Z-Y, Xiong Y (2016) Nanogold-functionalized g-C3N4 nanohybrids for sensitive impedimetric immunoassay of prostate-specific antigen using enzymatic biocatalytic precipitation. Biosens Bioelectron 85:212–219
Liu L, Li Y, Tian L, Wei Q, Cao W (2016) Ultrasensitive sandwich-type prostate specific antigen immunosensor based on Ag overgrowth in Pd nano-octahedrons heterodimers decorated on amino functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Sensors Actuators B Chem 237:733–739
Akter R, Rahman MA, Rhee CK (2012) Amplified Electrochemical Detection of a Cancer Biomarker by Enhanced Precipitation Using Horseradish Peroxidase Attached on Carbon Nanotubes. Anal Chem 84(15):6407–6415
Li Y, Khan MS, Tian L, Liu L, Hu L, Fan D, Cao W, Wei Q (2017) An ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensor for the detection of prostate-specific antigen based on conductivity nanocomposite with halloysite nanotubes. Anal Bioanal Chem: 1–7
Wang H, Zhang Y, Yu H, Wu D, Ma H, Li H, Du B, Wei Q (2013) Label-free electrochemical immunosensor for prostate-specific antigen based on silver hybridized mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Anal Biochem 434(1):123–127
Fan D, Li N, Ma H, Li Y, Hu L, Du B, Wei Q (2016) Electrochemical immunosensor for detection of prostate specific antigen based on an acid cleavable linker into MSN-based controlled release system. Biosens Bioelectron 85:580–586
Jang HD, Kim SK, Chang H, Choi J-W (2015) 3D label-free prostate specific antigen (PSA) immunosensor based on graphene–gold composites. Biosens Bioelectron 63:546–551
Han L, Liu C-M, Dong S-L, Du C-X, Zhang X-Y, Li L-H, Wei Y (2017) Enhanced conductivity of rGO/Ag NPs composites for electrochemical immunoassay of prostate-specific antigen. Biosens Bioelectron 87:466–472
Hong W, Lee S, Jae Kim E, Lee M, Cho Y (2016) A reusable electrochemical immunosensor fabricated using a temperature-responsive polymer for cancer biomarker proteins. Biosens Bioelectron 78:181–186
Pan L-H, Kuo S-H, Lin T-Y, Lin C-W, Fang P-Y, Yang H-W (2017) An electrochemical biosensor to simultaneously detect VEGF and PSA for early prostate cancer diagnosis based on graphene oxide/ssDNA/PLLA nanoparticles. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 89(Part 1):598–605
Sharafeldin M, Bishop GW, Bhakta S, El-Sawy A, Suib SL, Rusling JF (2017) Fe3O4 nanoparticles on graphene oxide sheets for isolation and ultrasensitive amperometric detection of cancer biomarker proteins. Biosens Bioelectron 91:359–366
Chuah K, Lai LMH, Goon IY, Parker SG, Amal R, Justin Gooding J (2012) Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) using gold-coated magnetic nanoparticles as 'dispersible electrodes'. Chem Commun 48(29):3503–3505
Ma H, Li Y, Wang Y, Hu L, Zhang Y, Fan D, Yan T, Wei Q (2016) Cubic Cu2O nanoframes with a unique edge-truncated structure and a good electrocatalytic activity for immunosensor application. Biosens Bioelectron 78:167–173
Jiao L, Mu Z, Miao L, Du W, Wei Q, Li H (2017) Enhanced amperometric immunoassay for the prostate specific antigen using Pt-Cu hierarchical trigonal bipyramid nanoframes as a label. Microchim Acta 184(2):423–429
Bhardwaj SK, Sharma AL, Bhardwaj N, Kukkar M, Gill AAS, Kim K-H, Deep A (2017) TCNQ-doped Cu-metal organic framework as a novel conductometric immunosensing platform for the quantification of prostate cancer antigen. Sens Actuat B: Chem 240:10–17
Hong W, Lee S, Cho Y (2016) Dual-responsive immunosensor that combines colorimetric recognition and electrochemical response for ultrasensitive detection of cancer biomarkers. Biosens Bioelectron 86:920–926
Li F, Li Y, Feng J, Dong Y, Wang P, Chen L, Chen Z, Liu H, Wei Q (2017) Ultrasensitive amperometric immunosensor for PSA detection based on Cu2O@CeO2-Au nanocomposites as integrated triple signal amplification strategy. Biosens Bioelectron 87:630–637
Duangkaew P, Wutikhun T, Laocharoensuk R (2017) Triple signal amplification strategy based on size and shape transformation of ultrasmall sub-10 nm gold nanoparticles tag towards sensitivity improvement of electrochemical immunosensors. Sensors Actuators B Chem 239:430–437
Kavosi B, Salimi A, Hallaj R, Moradi F (2015) Ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensor for PSA biomarker detection in prostate cancer cells using gold nanoparticles/PAMAM dendrimer loaded with enzyme linked aptamer as integrated triple signal amplification strategy. Biosens Bioelectron 74:915–923
Zhao L, Ma Z (2017) New immunoprobes based on bovine serum albumin-stabilized copper nanoclusters with triple signal amplification for ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensing for tumor marker. Sensors Actuators B Chem 241:849–854
Klukova L, Bertok T, Petrikova M, Sediva A, Mislovicova D, Katrlik J, Vikartovska A, Filip J, Kasak P, Andicsová-Eckstein A (2015) Glycoprofiling as a novel tool in serological assays of systemic sclerosis: A comparative study with three bioanalytical methods. Anal Chim Acta 853:555–562
Tang Z, Wang L, Ma Z (2017) Triple sensitivity amplification for ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of prostate specific antigen. Biosens Bioelectron 92:577–582
Zhu Y, Wang H, Wang L, Zhu J, Jiang W (2016) Cascade Signal Amplification Based on Copper Nanoparticle-Reported Rolling Circle Amplification for Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Detection of the Prostate Cancer Biomarker. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(4):2573–2581
Strzemińska I, Sainte Rose Fanchine S, Anquetin G, Reisberg S, Noël V, Pham MC, Piro B (2016) Grafting of a peptide probe for Prostate-Specific Antigen detection using diazonium electroreduction and click chemistry. Biosens Bioelectron 81:131–137
Parnsubsakul A, Safitri RE, Rijiravanich P, Surareungchai W (2017) Electrochemical assay of proteolytically active prostate specific antigen based on anodic stripping voltammetry of silver enhanced gold nanoparticle labels. J Electroanal Chem 785:125–130
Heydari-Bafrooei E, Shamszadeh NS (2017) Electrochemical bioassay development for ultrasensitive aptasensing of prostate specific antigen. Biosens Bioelectron 91:284–292
Tahmasebi F, Noorbakhsh A (2016) Sensitive Electrochemical Prostate Specific Antigen Aptasensor: Effect of Carboxylic Acid Functionalized Carbon Nanotube and Glutaraldehyde Linker. Electroanalysis 28(5):1134–1145
Rahi A, Sattarahmady N, Heli H (2016) Label-free electrochemical aptasensing of the human prostate-specific antigen using gold nanospears. Talanta 156–157:218–224
Jolly P, Formisano N, Tkáč J, Kasák P, Frost CG, Estrela P (2015) Label-free impedimetric aptasensor with antifouling surface chemistry: A prostate specific antigen case study. Sensors Actuators B Chem 209:306–312
Tzouvadaki I, Jolly P, Lu X, Ingebrandt S, de Micheli G, Estrela P, Carrara S (2016) Label-Free Ultrasensitive Memristive Aptasensor. Nano Lett 16(7):4472–4476
Deng H, Li J, Zhang Y, Pan H, Xu G (2016) A new strategy for label-free electrochemical immunoassay based on “gate-effect” of β-cyclodextrin modified electrode. Anal Chim Acta 926:48–54
Xie S, Zhang J, Yuan Y, Chai Y, Yuan R (2015) An electrochemical peptide cleavage-based biosensor for prostate specific antigen detection via host-guest interaction between ferrocene and [small beta]-cyclodextrin. Chem Commun 51(16):3387–3390
Gao C, Zhang L, Wang Y, Yu J, Song X (2016) Visible-light driven biofuel cell based on hierarchically branched titanium dioxide nanorods photoanode for tumor marker detection. Biosens Bioelectron 83:327–333
Pihíková D, Belicky Š, Kasák P, Bertok T, Tkac J (2016) Sensitive detection and glycoprofiling of a prostate specific antigen using impedimetric assays. Analyst 141(3):1044–1051
Pihikova D, Pakanova Z, Nemcovic M, Barath P, Belicky S, Bertok T, Kasak P, Mucha J, Tkac J (2016) Sweet characterisation of prostate specific antigen using electrochemical lectin-based immunosensor assay and MALDI TOF/TOF analysis: Focus on sialic acid. Proteomics 16(24):3085–3095
Pihikova D, Kasak P, Kubanikova P, Sokol R, Tkac J (2016) Aberrant sialylation of a prostate-specific antigen: Electrochemical label-free glycoprofiling in prostate cancer serum samples. Anal Chim Acta 934:72–79
Xia N, Deng D, Zhang L, Yuan B, Jing M, Du J, Liu L (2013) Sandwich-type electrochemical biosensor for glycoproteins detection based on dual-amplification of boronic acid-gold nanoparticles and dopamine-gold nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 43:155–159
Cao Y, Yuan R, Chai Y, Mao L, Niu H, Liu H, Zhuo Y (2012) Ultrasensitive luminol electrochemiluminescence for protein detection based on in situ generated hydrogen peroxide as coreactant with glucose oxidase anchored AuNPs@MWCNTs labeling. Biosens Bioelectron 31(1):305–309
Xu Y, Liu J, Gao C, Wang E (2014) Applications of carbon quantum dots in electrochemiluminescence: A mini review. Electrochem Commun 48:151–154
Jiao T, Leca-Bouvier BD, Boullanger P, Blum LJ, Girard-Egrot AP (2008) Electrochemiluminescent detection of hydrogen peroxide using amphiphilic luminol derivatives in solution. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 321 (1–3):143-146
Liu D-Y, Xin Y-Y, He X-W, Yin X-B (2011) A sensitive, non-damaging electrochemiluminescent aptasensor via a low potential approach at DNA-modified gold electrodes. Analyst 136(3):479–485
Parveen S, Aslam MS, Hu L, Xu G (2013) Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence: Protocols and Applications. Springer
Zhang F, Mao L, Zhu M (2014) Ultrasensitive immunoassay for free prostate-specific antigen based on ferrocenecarboxylate enhanced cathodic electrochemiluminescence of peroxydisulfate. Microchim Acta 181(11):1285–1291
Xu X (2016) Sensitive Electrochemiluminescence Immunosensor for Determination of Tumor Biomarker PSA Based on Multifunctionalized Pt/Ag@BSA Core–Shell Nanoparticles. Bull Kor Chem Soc 37(4):452–457
Ge S, Yu J, Jiao X, Chen D (2013) Ultrasensitive Electrochemiluminescence Immunoassay for Protein Specific Detection Based on Dendrimer-Encapsulated Gold Nanoparticles Labels. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 23(5):1113–1121
Sardesai NP, Kadimisetty K, Faria R, Rusling JF (2013) A microfluidic electrochemiluminescent device for detecting cancer biomarker proteins. Anal Bioanal Chem 405(11):3831–3838
Kadimisetty K, Malla S, Sardesai NP, Joshi AA, Faria RC, Lee NH, Rusling JF (2015) Automated multiplexed ECL Immunoarrays for cancer biomarker proteins. Anal Chem 87(8):4472–4478
Deng W, Chu C, Ge S, Yu J, Yan M, Song X (2015) Electrochemiluminescence PSA assay using an ITO electrode modified with gold and palladium, and flower-like titanium dioxide microparticles as ECL labels. Microchim Acta 182(5):1009–1016
Li W, Dai W, Ge L, Ge S, Yan M, Yu J (2013) Electropolymerized Poly(3,4-ethylendioxythiophene)/Graphene Composite Film and its Application in Quantum Dots Electrochemiluminescence Immunoassay. J Inorg Organomet Polym Mater 23(3):719–725
Ma H, Li X, Yan T, Li Y, Zhang Y, Wu D, Wei Q, Du B (2016) Electrochemiluminescent immunosensing of prostate-specific antigen based on silver nanoparticles-doped Pb (II) metal-organic framework. Biosens Bioelectron 79:379–385
Wu D, Liu Y, Wang Y, Hu L, Ma H, Wang G, Wei Q (2016) Label-free Electrochemiluminescent Immunosensor for Detection of Prostate Specific Antigen based on Aminated Graphene Quantum Dots and Carboxyl Graphene Quantum Dots. Sci Rep 6:20511
Zhao Y, Wang Q, Li J, Ma H, Zhang Y, Wu D, Du B, Wei Q (2016) A CeO2-matrical enhancing ECL sensing platform based on the Bi2S3-labeled inverted quenching mechanism for PSA detection. J Mater Chem B 4(17):2963–2971
Tian CY, Zhao WW, Wang J, Xu JJ, Chen HY (2012) Amplified quenching of electrochemiluminescence from CdS sensitized TiO2 nanotubes by CdTe-carbon nanotube composite for detection of prostate protein antigen in serum. Analyst 137(13):3070–3075
Ma H, Zhou J, Li Y, Han T, Zhang Y, Hu L, Du B, Wei Q (2016) A label-free electrochemiluminescence immunosensor based on EuPO4 nanowire for the ultrasensitive detection of Prostate specific antigen. Biosens Bioelectron 80:352–358
Yang J-J, Cao J-T, Wang H, Liu Y-M, Ren S-W (2017) Ferrocene-graphene sheets for high-efficiency quenching of electrochemiluminescence from Au nanoparticles functionalized cadmium sulfide flower-like three dimensional assemblies and sensitive detection of prostate specific antigen. Talanta 167:325–332
He Y, Chai Y, Yuan R, Wang H, Bai L, Liao N (2014) A supersandwich electrochemiluminescence immunosensor based on mimic-intramolecular interaction for sensitive detection of proteins. Analyst 139(20):5209–5214
Damborský P, Švitel J, Katrlík J (2016) Optical biosensors. Essays Biochem 60(1):91–100
Vigneshvar S, Sudhakumari CC, Senthilkumaran B, Prakash H (2016) Recent Advances in Biosensor Technology for Potential Applications – An Overview. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 4:11
Esseghaier C, Suaifan GARY, Ng A, Zourob M (2014) One-Step Assay for Optical Prostate Specific Antigen Detection Using Magnetically Engineered Responsive Thin Film. J Biomed Nanotechnol 10(6):1123–1129
Berthuy OI, Blum LJ, Marquette CA (2015) Cancer-cells on a chip for label-free optic detection of secreted molecules. In: Baldini F, Homola J, Lieberman RA (eds) Optical Sensors 2015, vol 9506. Proceedings of SPIE. pp 950615–950615-950618. doi:10.1117/12.2179883
Damborský P, Madaboosi N, Chu V, Conde JP, Katrlík J (2015) Surface plasmon resonance application in prostate cancer biomarker research. Chem Pap 69(1):143–149
Soelberg SD, Stevens RC, Limaye AP, Furlong CE (2009) Surface Plasmon Resonance Detection Using Antibody-Linked Magnetic Nanoparticles for Analyte Capture, Purification, Concentration, and Signal Amplification. Anal Chem 81(6):2357–2363
Lyon LA, Musick MD, Natan MJ (1998) Colloidal Au-Enhanced Surface Plasmon Resonance Immunosensing. Anal Chem 70(24):5177–5183
Uludag Y, Tothill IE (2012) Cancer Biomarker Detection in Serum Samples Using Surface Plasmon Resonance and Quartz Crystal Microbalance Sensors with Nanoparticle Signal Amplification. Anal Chem 84(14):5898–5904
Ertürk G, Özen H, Tümer MA, Mattiasson B, Denizli A (2016) Microcontact imprinting based surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensor for real-time and ultrasensitive detection of prostate specific antigen (PSA) from clinical samples. Sens Actuat B: Chem 224:823–832
Stephenson-Brown A, Acton AL, Preece JA, Fossey JS, Mendes PM (2015) Selective glycoprotein detection through covalent templating and allosteric click-imprinting. Chem Sci 6(9):5114–5119
Hong Y, Huh Y-M, Yoon DS, Yang J (2012) Nanobiosensors Based on Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance for Biomarker Detection. J Nanomater 2012:13
Aćimović SS, Ortega MA, Sanz V, Berthelot J, Garcia-Cordero JL, Renger J, Maerkl SJ, Kreuzer MP, Quidant R (2014) LSPR Chip for Parallel, Rapid, and Sensitive Detection of Cancer Markers in Serum. Nano Lett 14(5):2636–2641
Hwang WS, Truong PL, Sim SJ (2012) Size-dependent plasmonic responses of single gold nanoparticles for analysis of biorecognition. Anal Biochem 421(1):213–218
Xuan Z, Li M, Rong P, Wang W, Li Y, Liu D (2016) Plasmonic ELISA based on the controlled growth of silver nanoparticles. Nano 8(39):17271–17277
De La Rica R, Stevens MM (2012) Plasmonic ELISA for the ultrasensitive detection of disease biomarkers with the naked eye. Nat Nanotechnol 7(12):821–824
De La Rica R, Stevens MM (2013) Plasmonic ELISA for the detection of analytes at ultralow concentrations with the naked eye. Nat Protoc 8(9):1759–1764
Howes PD, Rana S, Stevens MM (2014) Plasmonic nanomaterials for biodiagnostics. Chem Soc Rev 43(11):3835–3853
Liang J, Yao C, Li X, Wu Z, Huang C, Fu Q, Lan C, Cao D, Tang Y (2015) Silver nanoprism etching-based plasmonic ELISA for the high sensitive detection of prostate-specific antigen. Biosens Bioelectron 69:128–134
Xia Y, Ye J, Tan K, Wang J, Yang G (2013) Colorimetric Visualization of Glucose at the Submicromole Level in Serum by a Homogenous Silver Nanoprism–Glucose Oxidase System. Anal Chem 85(13):6241–6247
Liu D, Yang J, Wang H-F, Wang Z, Huang X, Wang Z, Niu G, Hight Walker AR, Chen X (2014) Glucose Oxidase-Catalyzed Growth of Gold Nanoparticles Enables Quantitative Detection of Attomolar Cancer Biomarkers. Anal Chem 86(12):5800–5806
Mullett WM, Lai EP, Yeung JM (2000) Surface plasmon resonance-based immunoassays. Methods 22(1):77–91
Sanders M, Lin Y, Wei J, Bono T, Lindquist RG (2014) An enhanced LSPR fiber-optic nanoprobe for ultrasensitive detection of protein biomarkers. Biosens Bioelectron 61:95–101
Uh M, Kim JS, Park JH, Jeong DH, Lee HY, Lee SM, Lee SK (2017) Fabrication of localized surface plasmon resonance sensor based on optical fiber and micro fluidic channel. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 17(2):1083–1091
Uh M, Kang S-K, Park J-H, Jeong DH, Lee H-Y, Lee S-M, Lee S-K (2016) Analysis and Optimization of Antibody Immobilization for Immunoassay Using Fiber-Optic Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensors. Nanosci Nanotechnol Lett 8(1):8–12
Jeong HH, Erdene N, Park JH, Jeong DH, Lee HY, Lee SK (2013) Real-time label-free immunoassay of interferon-gamma and prostate-specific antigen using a Fiber-Optic Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance sensor. Biosens Bioelectron 39(1):346–351
Breault-Turcot J, Poirier-Richard HP, Couture M, Pelechacz D, Masson JF (2015) Single chip SPR and fluorescent ELISA assay of prostate specific antigen. Lab Chip 15(23):4433–4440
Xu DD, Deng YL, Li CY, Lin Y, Tang HW (2017) Metal-enhanced fluorescent dye-doped silica nanoparticles and magnetic separation: A sensitive platform for one-step fluorescence detection of prostate specific antigen. Biosens Bioelectron 87:881–887
Zhang Q, Wu L, Wong TI, Zhang J, Liu X, Zhou X, Bai P, Liedberg B, Wang Y (2017) Surface plasmon-enhanced fluorescence on Au nanohole array for prostate-specific antigen detection. Int J Nanomedicine 12:2307–2314
Wang J, Mountziaris TJ (2013) Homogeneous immunoassays based on fluorescence emission intensity variations of zinc selenide quantum dot sensors. Biosens Bioelectron 41:143–149
Pei H, Zhu S, Yang M, Kong R, Zheng Y, Qu F (2015) Graphene oxide quantum dots@silver core–shell nanocrystals as turn-on fluorescent nanoprobe for ultrasensitive detection of prostate specific antigen. Biosens Bioelectron 74:909–914
Ming T, Zhao L, Yang Z, Chen H, Sun L, Wang J, Yan C (2009) Strong polarization dependence of plasmon-enhanced fluorescence on single gold nanorods. Nano Lett 9(11):3896–3903
Ma H, Li B, Zhang L, Han D, Zhu G (2015) Targeted synthesis of core-shell porous aromatic frameworks for selective detection of nitro aromatic explosives via fluorescence two-dimensional response. J Mater Chem A 3(38):19346–19352
Song HY, Wong TI, Sadovoy A, Wu L, Bai P, Deng J, Guo S, Wang Y, Knoll W, Zhou X (2015) Imprinted gold 2D nanoarray for highly sensitive and convenient PSA detection via plasmon excited quantum dots. Lab Chip 15(1):253–263
Frascione N, Gooch J, Abbate V, Daniel B (2015) Fluorogenic displacement biosensors for PSA detection using antibody-functionalised quantum dot nanoparticles. RSC Adv 5(9):6595–6598
Liu D, Huang X, Wang Z, Jin A, Sun X, Zhu L, Wang F, Ma Y, Niu G, HightWalker AR, Chen X (2013) Gold Nanoparticle Based Activatable Probe for Sensing Ultra-Low Levels of Prostate Specific Antigen. ACS Nano 7(6):5568–5576
Lee S, Hosokawa K, Kim S, Jeong OC, Lilja H, Laurell T, Maeda M (2016) Porous silicon microarray for simultaneous fluorometric immunoassay of the biomarkers prostate-specific antigen and human glandular kallikrein 2. Microchim Acta 183(12):3321–3327
Kong R-M, Ding L, Wang Z, You J, Qu F (2015) A novel aptamer-functionalized MoS2 nanosheet fluorescent biosensor for sensitive detection of prostate specific antigen. Anal Bioanal Chem 407(2):369–377
Barbosa AI, Gehlot P, Sidapra K, Edwards AD, Reis NM (2015) Portable smartphone quantitation of prostate specific antigen (PSA) in a fluoropolymer microfluidic device. Biosens Bioelectron 70:5–14
Tsunoda M, Imai K (2005) Analytical applications of peroxyoxalate chemiluminescence. Anal Chim Acta 541(1–2):13–23
Liu R, Wang C, Jiang Q, Zhang W, Yue Z, Liu G (2013) Magnetic-particle-based, ultrasensitive chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for free prostate-specific antigen. Anal Chim Acta 801:91–96
Xie X, Ohnishi N, Takahashi Y, Kondo A (2009) Application of magnetic nanoparticles in full-automated chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay. J Magn Magn Mater 321(10):1686–1688
Cha T, Cho S, Kim YT, Lee JH (2014) Rapid aptasensor capable of simply diagnosing prostate cancer. Biosens Bioelectron 62:31–37
Porter MD, Lipert RJ, Siperko LM, Wang G, Narayanan R (2008) SERS as a bioassay platform: fundamentals, design, and applications. Chem Soc Rev 37(5):1001–1011
Gao R, Cheng Z, deMello AJ, Choo J (2016) Wash-free magnetic immunoassay of the PSA cancer marker using SERS and droplet microfluidics. Lab Chip 16(6):1022–1029
Yang A-q, Wang D, Wang X, Han Y, X-b K, Wang H-j, Zhou X, Ren L (2015) Rational design of Au nanorods assemblies for highly sensitive and selective SERS detection of prostate specific antigen. RSC Adv 5(48):38354–38360
Koukouvinos G, Petrou PS, Misiakos K, Drygiannakis D, Raptis I, Goustouridis D, Kakabakos SE (2015) A label-free flow-through immunosensor for determination of total- and free-PSA in human serum samples based on white-light reflectance spectroscopy. Sens Actuat B: Chem 209:1041–1048
Alzghoul S, Hailat M, Zivanovic S, Que L, Shah GV (2016) Measurement of serum prostate cancer markers using a nanopore thin film based optofluidic chip. Biosens Bioelectron 77:491–498
Kumar A (2000) Biosensors based on piezoelectric crystal detectors: theory and application. JOM-e 52(10):1–6
Jokerst JV, Chen Z, Xu L, Nolley R, Chang E, Mitchell B, Brooks JD, Gambhir SS (2015) A Magnetic Bead-Based Sensor for the Quantification of Multiple Prostate Cancer Biomarkers. PLoS One 10(9):e0139484
Kosaka PM, PiniV, Ruz JJ, da Silva RA, González MU, RamosD, CallejaM, TamayoJ (2014) Detection of cancer biomarkers in serum using a hybrid mechanical and optoplasmonic nanosensor. Nat Nano 9 (12):1047-1053
Arlett JL, Myers EB, Roukes ML (2011) Comparative advantages of mechanical biosensors. Nat Nano 6(4):203–215
Lee H-J, Lee J-H, Moon H-S, Jang I-S, Choi J-S, Yook J-G, Jung H-I (2012) A planar split-ring resonator-based microwave biosensor for label-free detection of biomolecules. Sens Actuat B: Chem 169:26–31
Moser HO, Casse BDF, Wilhelmi O, Saw BT (2005) Terahertz Response of a Microfabricated Rod\char21{}Split-Ring-Resonator Electromagnetic Metamaterial. Phys Rev Lett 94(6):063901
Zhang F, Li S, Cao K, Wang P, Su Y, Zhu X, Wan Y (2015) A Microfluidic Love-Wave Biosensing Device for PSA Detection Based on an Aptamer Beacon Probe. Sensors 15(6)
Lange K, Rapp BE, Rapp M (2008) Surface acoustic wave biosensors: a review. Anal Bioanal Chem 391(5):1509–1519
Sun X, Lei C, Guo L, Zhou Y (2016) Sandwich immunoassay for the prostate specific antigen using a micro-fluxgate and magnetic bead labels. Microchim Acta 183(8):2385–2393
Lei J, Wang T, Lei C, Zhou Y (2013) Detection of Dynabeads using a micro-electro-mechanical-systems fluxgate sensor. Appl Phys Lett 102(2):022413
Sun X, Zhi S, Lei C, Zhou Y (2016) Investigation of contactless detection using a giant magnetoresistance sensor for detecting prostate specific antigen. Biomed Microdevices 18(4):60
Jiang X, Cheng S, Chen W, Wang L, Shi F, Zhu C (2012) Comparison of oligonucleotide-labeled antibody probe assays for prostate-specific antigen detection. Anal Biochem 424(1):1–7
Acknowledgements
The financial support received from the Slovak Scientific Grant Agency VEGA 2/0162/14 and the Slovak Research and Development Agency APVV-14-0753 is acknowledged. The research leading to these results received funding from the European Research Council under the European Union’s Seventh Framework Program (FP/2007-2013)/ERC grant agreement number 311532. This publication was made possible by NPRP grant number 6-381-1-078 from the Qatar National Research Fund (a member of the Qatar Foundation). The statements made herein are solely the responsibility of the authors. This publication is the result of the project implementation: Centre for materials, layers and systems for applications and chemical processes under extreme conditions – Stage I, ITMS No.: 26240120007, supported by the Research & Development Operational Program funded by the ERDF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Damborska, D., Bertok, T., Dosekova, E. et al. Nanomaterial-based biosensors for detection of prostate specific antigen. Microchim Acta 184, 3049–3067 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2410-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2410-1