Abstract
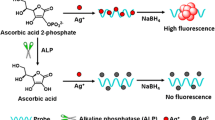
The authors describe a sensitive fluorometric method for the determination of the activity of alkaline phosphatase (ALP). It is based on the use of a composite prepared consisting of flower-like cobalt oxyhydroxide (CoOOH) and copper nanoclusters (CuNCs). On formation of the CuNC-CoOOH aggregates, the fluorescence of the CuNCs is quenched by the CoOOH sheets. If, however, the CoOOH sheets are reduced to Co(II) ions in the presence of ascorbic acid (AA), fluorescence recovers. AA is formed in-situ by hydrolysis of the substrate ascorbic acid 2-phosphate (AA2P) as catalyzed by ALP. Thus, the ALP activity can be detected indirectly by kinetic monitoring of the increase in fluorescence, best at excitation/emission wavelengths of 335/410 nm. The assay allows ALP to be determined in 0.5 to 150 mU·mL−1 activity range and with a 0.1 mU·mL−1 detection limit. The method was successfully applied to the determination of ALP activity in (spiked) human serum samples. The assay has attractive features in being of the off-on type and immune against false positive results.

A fluorescent bioassay is reported for the determination of the activity of alkaline phosphatase (ALP). It is exploiting the ascorbic acid (AA)-induced decomposition of nanoclusters composed of flower-like cobalt oxyhydroxide and copper nanoclusters. ALP catalyzes hydrolysis of ascorbic acid 2-phosphate (AA2P) and dephosphorylation to form AA.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yuan J, Cen Y, Kong XJ, Wu S, Liu CL, Yu RQ, Chu X (2015) MnO2-nanosheet-modified upconversion nanosystem for sensitive turn-on fluorescence detection of H2O2 and glucose in blood. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:10548–10555
Li N, Li YH, Han YY, Pan W, Zhang TT, Tang B (2014) A highly selective and instantaneous nanoprobe for detection and imaging of ascorbic acid in living cells and in vivo. Anal Chem 86:3924–3930
Li LB, Wang C, Liu KY, Wang YH, Liu K, Lin YQ (2015) Hexagonal cobalt oxyhydroxide-carbon dots hybridized surface: high sensitive fluorescence turn-on probe for monitoring of ascorbic acid in rat brain following brain ischemia. Anal Chem 87:3404–3411
Li GL, Kong WH, Zhao M, Lu SM, Gong PW, Chen G, Xia L, Wang H, You JM, Wu YN (2016) A fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) based “Turn-On” nanofluorescence sensor using a nitrogen-doped carbon dot-hexagonal cobalt oxyhydroxide nanosheet architecture and application to α-glucosidase inhibitor screening. Biosens Bioelectron 79:728–735
Cen Y, Tang J, Kong XJ, Wu S, Yuan J, Yu RQ, Chu X (2015) A cobalt oxyhydroxide-modified upconversion nanosystem for sensitive fluorescence sensing of ascorbic acid in human plasma. Nanoscale 7:13951–13957
Meng HM, Zhang XB, Yang C, Kuai HL, Mao GJ, Gong L, Zhang WH, Feng SL, Chang JB (2016) Efficient two-photon fluorescence nanoprobe for turn-on detection and imaging of ascorbic acid in living cells and tissues. Anal Chem 88:6057–6063
Cen Y, Yang Y, Yu RQ, Chen TT, Chu X (2016) A cobalt oxyhydroxide nanoflake-based nanoprobe for the sensitive fluorescence detection of T4 polynucleotide kinase activity and inhibition. Nanoscale 8:8202–8209
Yang Y, Cen Y, Deng WJ, Yu RQ, Chen TT, Chu X (2016) An aptasensor based on cobalt oxyhydroxide nanosheets for the detection of thrombin. Anal Methods 8:7199–7203
Chang YQ, Zhang Z, Liu HQ, Wang N, Tang JL (2016) Cobalt oxyhydroxide nanoflake based fluorescence sensing platform for label-free detection of DNA. Analyst 141:4719–4724
Coleman JE (2003) Structure and mechanism of alkaline phosphatase. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 21:441–483
Hausamen TU, Helger R, Rick W, Gross W (1967) Optimal conditions for the determination of serum alkaline phosphatase by a new kinetic method. Clin Chim Acta 15:241–245
Chen L, Li X, Zheng Z, Lu X, Lin M, Pan C, Liu J (2014) A novel ATP7B gene mutation in a liver failure patient with normal ceruloplasmin and low serum alkaline phosphatase. Gene 538:204–206
Christenson RH (1998) Biochemical markers of bone metabolism: an overview. Clin Biochem 30:573–593
Ooi K, Shiraki K, Morishita Y, Nobori T (2007) High-molecular intestinal alkaline phosphatase in chronic liver diseases. J Clin Lab Anal 21:133–139
Wolf PL (1994) Clinical significance of serum high-molecular-mass alkaline phosphatase, alkaline phosphatase-lipoprotein-X complex, and intestinal variant alkaline phosphatase. J Clin Lab Anal 8:172–176
Yang J, Zheng L, Wang Y, Li W, Zhang J, Gu J, Fu Y (2016) Guanine-rich DNA-based peroxidase mimetics for colorimetric assays of alkaline phosphatase. Biosens Bioelectron 77:549–556
Hu Q, He MH, Mei YQ, Feng WJ, Jing S, Kong JM, Zhang XJ (2017) Sensitive and selective colorimetric assay of alkaline phosphatase activity with Cu(II)-phenanthroline complex. Talanta 163:146–152
Jiang H, Wang X (2012) Alkaline phosphatase-responsive anodic electrochemiluminescence of CdSe nanoparticles. Anal Chem 84:6986–6993
Ingram A, Moore BD, Graham D (2009) Simultaneous detection of alkaline phosphatase and beta-galactosidase activity using SERRS. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19:1569–1571
Shen CC, Li XZ, Rasooly A, Guo LY, Zhang KN, Yang MH (2016) A single electrochemical biosensor for detecting the activity and inhibition of both protein kinase and alkaline phosphatase based on phosphate ions induced deposition of redox precipitates. Biosens Bioelectron 85:220–225
Kong RM, Fu T, Sun NN, Qu FL, Zhang SF, Zhang XB (2013) Pyrophosphate-regulated Zn(2+)-dependent DNAzyme activity: an amplified fluorescence sensing strategy for alkaline phosphatase. Biosens Bioelectron 50:351–355
Mao ZQ, Hu L, Zhong C, Zhang H, Liu BF, Liu ZH (2015) A dual-mechanism strategy to design a wide-range pH probe with multicolor fluorescence. Sens Actuators B Chem 219:179–184
Jin LY, Dong YM, Wu XM, Cao GX, Wang GL (2015) Versatile and amplified biosensing through enzymatic cascade reaction by coupling alkaline phosphatase in situ generation of photoresponsive nanozyme. Anal Chem 87:10429–10436
Guo LY, Chen DL, Yang MH (2017) DNA-templated silver nanoclusters for fluorometric determination of the activity and inhibition of alkaline phosphatase. Microchim Acta 184:2165–2170
Xiang MH, Liu JW, Li N, Tang H, Yu RQ, Jiang JH (2016) A fluorescent graphitic carbon nitride nanosheet biosensor for highly sensitive, label-free detection of alkaline phosphatase. Nanoscale 8:4727–4732
Jia L, Xu JP, Li D, Pang SP, Fang Y, Song ZG, Ji J (2010) Fluorescence detection of alkaline phosphatase activity with β-cyclodextrin-modified quantum dots. Chem Commun 46:7166–7168
Liu Y, Schanze KS (2008) Conjugated polyelectrolyte-based real-time fluorescence assay for alkaline phosphatase with pyrophosphate as substrate. Anal Chem 80:8605–8612
Nutiu R, Yu JMY, Li Y (2004) Signaling aptamers for monitoring enzymatic activity and for inhibitor screening. Chem Bio Chem 5:1139–1144
Wang HB, Chen Y, Li Y, Liu YM (2016) A sensitive fluorescence sensor for glutathione detection based on MnO2 nanosheets-copper nanoclusters composites. RSC Adv 6:79526–79532
Wang HB, Chen Y, Li N, Liu YM (2017) A fluorescent glucose bioassay based on the hydrogen peroxide-induced decomposition of a quencher system composed of MnO2 nanosheets and copper nanoclusters. Microchim Acta 184:515–523
Chen J, Ge J, Zhang L, Li ZH, Li JJ, Sun YH, Qu LB (2016) Reduced graphene oxide nanosheets functionalized with poly(styrene sulfonate) as a peroxidase mimetic in a colorimetric assay for ascorbic acid. Microchim Acta 183:1847–1853
Rao HB, Ge HW, Lu ZW, Liu W, Chen ZQ, Zhang ZY, Wang XX, Zou P, Wang YY, He H, Zeng XY (2016) Copper nanoclusters as an on-off-on fluorescent probe for ascorbic acid. Microchim Acta 183:1651–1657
Huang S, Qiu HN, Zhu FW, Lu SY, Xiao Q (2015) Graphene quantum dots as on-off-on fluorescent probes for chromium(VI) and ascorbic acid. Microchim Acta 182:1723–1731
Zhang LF, Hou T, Li HY, Li F (2015) A highly sensitive homogeneous electrochemical assay for alkaline phosphatase activity based on single molecular beacon-initiated T7 exonuclease-mediated signal amplification. Analyst 140:4030–4036
Kang WJ, Ding YY, Zhou H, Liao QY, Yang X, Yang YG, Jiang JS, Yang MH (2015) Monitoring the activity and inhibition of alkaline phosphatase via quenching and restoration of the fluorescence of carbon dots. Microchim Acta 182:1161–1167
Zhang LL, Zhao JJ, Duan M, Zhang H, Jiang JH, Yu RQ (2013) Inhibition of dsDNA-templated copper nanoparticles by pyrophosphate as a label-free fluorescent strategy for alkaline phosphatase assay. Anal Chem 85:3797–3801
Liu XG, Xing XJ, Li B, Guo YM, Zhang YZ, Yang Y, Zhang LF (2016) Fluorescent assay for alkaline phosphatase activity based on graphene oxide integrating with λ exonuclease. Biosens Bioelectron 81:460–464
Qu FL, Pei HM, Kong RM, Zhu SY, Xia L (2017) Novel turn-on fluorescent detection of alkaline phosphatase based on green synthesized carbon dots and MnO2 nanosheets. Talanta 165:136–142
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U1704153, 21305119), Plan for Young Excellent Teachers in Universities of Henan Province (No. 2017GGJS), Nanhu Scholars Program for Young Scholars of XYNU, Plan for Scientific Innovation Talent of Henan Province (No. 2017JR0016), the Science & Technology Innovation Talents in Universities of Henan Province (No. 16HASTIT004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 9840 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, HB., Li, Y., Chen, Y. et al. Determination of the activity of alkaline phosphatase by using nanoclusters composed of flower-like cobalt oxyhydroxide and copper nanoclusters as fluorescent probes. Microchim Acta 185, 102 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2622-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2622-4