Abstract
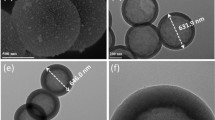
A porous nanostructured covalent-organic framework (COF) has been prepared via condensation polymerization between the two building blocks of melem and hexaketocyclohexane octahydrate (represented as M-HO-COF). Basic characterizations revealed that the M-HO-COF network was composed of C=N and highly conjugated aromatic moieties, along with a high surface area, large pore size, remarkable electrochemical activity, and strong bioaffinity toward aptamer strands. Given that the vascular endothelial growth factor 165 (VEGF165)-targeted aptamer was stably anchored over M-HO-COF via weak intermolecular forces, the prepared M-HO-COF network exhibited great potential as a sensitive and selective platform for the impedimetric VEGF165 aptasensor. Consequently, the M-HO-COF-based aptasensor displayed an ultralow limit of detection of 0.18 fg mL−1 within a wide range of VEGF165 concentrations from 1 fg mL−1 to 10 ng mL−1. Considering its strong fluorescence performance, excellent biocompatibility, and small nanosheet-like structure, the obtained COF-based aptasensor showed a superior sensing performance and regeneration capability after 7 regeneration cycles for the detection of osteosarcoma cells (K7M2 cells), which overexpressed with VEGF165, with a low limit of detection of 49 cells mL−1. For real f human serum samples, the obtained COF-based aptasensor exhibits acceptable mean apparent recoveries of 97.41% with a relative standard deviation of 4.60%. Furthermore, the proposed bifunctional aptasensor for the detection VEGF165 and K7M2 cells exhibited good stability, appropriate selectivity toward other biomarkers or normal cells, acceptable reproducibility, and applicability.
Graphical abstract

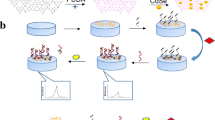
A bifunctional sensing system was constructed for detecting osteosarcoma cells (K7M2 cells) and VEGF165 based on the a porous nanostructured covalent-organic framework (M-HO-COF) via condensation polymerization between melem and hexaketocyclohexane octahydrate. The M-HO-COF-based aptasensor displayed ultralow detection limit of 0.18 fg mL−1 toward VEGF165 and 49 cell mL−1 for K7M2 cells with high selectivity, acceptable reproducibility, and good stability.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mirabello L, Troisi RJ, Savage SA (2009) International osteosarcoma incidence patterns in children and adolescents, middle ages and elderly persons. Int J Cancer 125(1):229–234. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.24320
Zhao X, Wu Q, Gong X, Liu J, Ma Y (2021) Osteosarcoma: a review of current and future therapeutic approaches. Biomed Eng Online 20(1):24–24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12938-021-00860-0
Monterde-Cruz L, Ramirez-Salazar EG, Rico-Martinez G, Miguel Linares-Gonzalez L, Guzman-Gonzalez R, Delgado-Cedillo E, Estrada-Villasenor E, Valdes-Flores M, Velazquez-Cruz R, Hidalgo-Bravo A (2020) MicroRNA expression in relation with clinical evolution of osteosarcoma. Pathol Res Pract 216:8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2020.153038
Yang S-Y, Yu H, Krygier JE, Wooley PH, Mott MP (2007) High VEGF with rapid growth and early metastasis in a mouse osteosarcoma model. Sarcoma 2007:95628–95627. https://doi.org/10.1155/2007/95628
Clark JCM, Dass CR, Choong PFM (2008) A review of clinical and molecular prognostic factors in osteosarcoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 134(3):281–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-007-0330-x
Zhang Y, Qi S, Liu Z, Shi Y, Yue W, Yi C (2016) Rapid determination of dopamine in human plasma using a gold nanoparticle-based dual-mode sensing system. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater 61:207–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.12.038
Hicklin DJ, Ellis LM (2005) Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol 23(5):1011–1027. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2005.06.081
Varey AHR, Rennel ES, Qiu Y, Bevan HS, Perrin RM, Raffy S, Dixon AR, Paraskeva C, Zaccheo O, Hassan AB, Harper SJ, Bates DO (2008) VEGF(165)b, an antiangiogenic VEGF-A isoform, binds and inhibits bevacizumab treatment in experimental colorectal carcinoma: balance of pro- and antiangiogenic VEGF-A isoforms has implications for therapy. Br J Cancer 98(8):1366–1379. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6604308
Poon RTP, Lau C, Pang R, Ng KK, Yuen J, Fan ST (2007) High serum vascular endothelial growth factor levels predict poor prognosis after radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: importance of tumor biomarker in ablative therapies. Ann Surg Oncol 14(6):1835–1845. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-007-9366-z
Azimi-Nezhad M, Stathopoulou MG, Bonnefond A, Rancier M, Saleh A, Lamont J, Fitzgerald P, Ndiaye NC, Visvikis-Siest S (2013) Associations of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) with adhesion and inflammation molecules in a healthy population. Cytokine 61(2):602–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2012.10.024
Tabrizi MA, Shamsipur M, Farzin L (2015) A high sensitive electrochemical aptasensor for the determination of VEGF(165) in serum of lung cancer patient. Biosens Bioelectron 74:764–769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.07.032
Tabrizi MA, Shamsipur M, Saber R, Sarkar S (2017) Simultaneous determination of CYC and VEGF(165) tumor markers based on immobilization of flavin adenine dinucleotide and thionine as probes on reduced graphene oxide-poly(amidoamine)/gold nanocomposite modified dual working screen-printed electrode. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 240:1174–1181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.09.108
Dehghani S, Nosrati R, Yousefi M, Nezami A, Soltani F, Taghdisi SM, Abnous K, Alibolandi M, Ramezani M (2018) Aptamer-based biosensors and nanosensors for the detection of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF): a review. Biosens Bioelectron 110:23–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.03.037
Wang B, Akiba U, J-i A (2017) Recent progress in nanomaterial-based electrochemical biosensors for cancer biomarkers: a review. Molecules 22(7):1048
Chen S, Yuan B, Liu G, Zhang D (2020) Electrochemical sensors based on covalent organic frameworks: a critical review. Front Chem 8:601044. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.601044
Kim S, Choi HC (2020) Recent advances in covalent organic frameworks for molecule-based two-dimensional materials. ACS Omega 5(2):948–958. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b03549
Babu HV, Bai MGM, Rao MR (2019) Functional π-conjugated two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(12):11029–11060. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b19087
Zhang X, Chi K-N, Li D-L, Deng Y, Ma Y-C, Xu Q-Q, Hu R, Yang Y-H (2019) 2D-porphrinic covalent organic framework-based aptasensor with enhanced photoelectrochemical response for the detection of C-reactive protein. Biosens Bioelectron 129:64–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.01.009
Tian YY, Lu QP, Guo XX, Wang SY, Gao Y, Wang LH (2020) Au nanoparticles deposited on ultrathin two-dimensional covalent organic framework nanosheets for in vitro and intracellular sensing. Nanoscale 12(14):7776–7781. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nr08220d
Wang L, Liang HH, Xu ML, Wang LY, Xie Y, Song YH (2019) Ratiometric electrochemical biosensing based on double-enzymes loaded on two-dimensional dual-pore COFETTA-TPAL. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 298:7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.126859
Xu ML, Wang LY, Xie Y, Song YH, Wang L (2019) Ratiometric electrochemical sensing and biosensing based on multiple redox-active state COFDHTA-TTA. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 281:1009–1015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.11.032
Ma XH, Pang CH, Li SH, Xiong YH, Li JP, Luo JH, Yang Y (2019) Synthesis of Zr-coordinated amide porphyrin-based two-dimensional covalent organic framework at liquid-liquid interface for electrochemical sensing of tetracycline. Biosens Bioelectron 146:9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111734
Dong J, Li X, Peh SB, Yuan YD, Wang Y, Ji D, Peng S, Liu G, Ying S, Yuan D, Jiang J, Ramakrishna S, Zhao D (2019) Restriction of molecular rotors in ultrathin two-dimensional covalent organic framework nanosheets for sensing signal amplification. Chem Mater 31(1):146–160. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b03685
Zhang X, Yadavalli VK (2010) Molecular interaction studies of vascular endothelial growth factor with RNA aptamers. Analyst 135(8):2014–2021. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0an00200c
Pan J, Guo L, Zhang S, Wang N, Jin S, Tan B (2018) Embedding carbon nitride into a covalent organic framework with enhanced photocatalysis performance. Chem-Asian J 13(13):1674–1677. https://doi.org/10.1002/asia.201800506
Thevenot DR, Toth K, Durst RA, Wilson GS (2001) Electrochemical biosensors: recommended definitions and classification. Biosens Bioelectron 16(1–2):121–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0956-5663(01)00115-4
Heo NS, Lee SU, Rethinasabapathy M, Lee EZ, Cho H-J, Oh SY, Choe SR, Kim Y, Hong WG, Krishnan G, Hong WH, Jeon T-J, Jun Y-S, Kim HJ, Huh YS (2018) Visible-light-driven dynamic cancer therapy and imaging using graphitic carbon nitride nanoparticles. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater 90:531–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2018.04.035
Kim S, Choi HC (2019) Light-promoted synthesis of highly-conjugated crystalline covalent organic framework. Commun Chem 2:60. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42004-019-0162-z
Wang M, Hu M, Liu J, Guo C, Peng D, Jia Q, He L, Zhang Z, Du M (2019) Covalent organic framework-based electrochemical aptasensors for the ultrasensitive detection of antibiotics. Biosens Bioelectron 132:8–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.02.040
Gauthier M, Carney TJ, Grimaud A, Giordano L, Pour N, Chang H-H, Fenning DP, Lux SF, Paschos O, Bauer C, Maglia F, Lupart S, Lamp P, Shao-Horn Y (2015) Electrode–electrolyte interface in Li-ion batteries: current understanding and new insights. J Phys Chem Lett 6(22):4653–4672. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.5b01727
Dahbi M, Yabuuchi N, Fukunishi M, Kubota K, Chihara K, Tokiwa K, Yu X-f, Ushiyama H, Yamashita K, Son J-Y, Cui Y-T, Oji H, Komaba S (2016) Black phosphorus as a high-capacity, high-capability negative electrode for sodium-ion batteries: investigation of the electrode/electrolyte Interface. Chem Mater 28(6):1625–1635. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.5b03524
Guan Q, Guo H, Xue R, Wang M, Wu N, Cao Y, Zhao X, Yang W (2021) Electrochemical sensing platform based on covalent organic framework materials and gold nanoparticles for high sensitivity determination of theophylline and caffeine. Microchim Acta 188(3):85–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04744-x
Zhang Y, Riduan SN, Wang J (2017) Redox active metal- and covalent organic frameworks for energy storage: balancing porosity and electrical conductivity. Chem-Eur J 23(65):16419–16431. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201702919
Jia T, Fu C, Huang C, Yang H, Jia N (2015) Highly sensitive naphthalimide-based fluorescence polarization probe for detecting cancer cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(18):10013–10021. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b02429
Wang M, Hu M, Li Z, He L, Song Y, Jia Q, Zhang Z, Du M (2019) Construction of Tb-MOF-on-Fe-MOF conjugate as a novel platform for ultrasensitive detection of carbohydrate antigen 125 and living cancer cells. Biosens Bioelectron 142:111536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111536
Li Y, Hu MY, Huang XY, Wang MH, He LH, Song YP, Jia QJ, Zhou N, Zhang ZH, Du M (2020) Multicomponent zirconium-based metal-organic frameworks for impedimetric aptasensing of living cancer cells. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 306:11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127608
Yan X, Song Y, Liu J, Zhou N, Zhang C, He L, Zhang Z, Liu Z (2019) Two-dimensional porphyrin-based covalent organic framework: a novel platform for sensitive epidermal growth factor receptor and living cancer cell detection. Biosens Bioelectron 126:734–742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.11.047
Zhang Y, Luo S, Situ B, Chai Z, Li B, Liu J, Zheng L (2018) A novel electrochemical cytosensor for selective and highly sensitive detection of cancer cells using binding-induced dual catalytic hairpin assembly. Biosens Bioelectron 102:568–573 doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.12.010
Norouzi A, Ravan H, Mohammadi A, Hosseinzadeh E, Norouzi M, Fozooni T (2018) Aptamer–integrated DNA nanoassembly: a simple and sensitive DNA framework to detect cancer cells. Anal Chim Acta 1017:26–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.02.037
Zhang Z, Ji H, Song Y, Zhang S, Wang M, Jia C, Tian J-Y, He L, Zhang X, Liu C-S (2017) Fe(III)-based metal-organic framework-derived core-shell nanostructure: sensitive electrochemical platform for high trace determination of heavy metal ions. Biosens Bioelectron 94:358–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.03.014
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82071388, 81601082, 81771329), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019 M660175), and Henan Distinguished Youth Science Fund Project (CN) (No. 202300410492).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Experimental section; Chemical structure of M-OH-COF; Analysis of cell cytotoxicity for M-OH-COF; Electrochemical performances of M-OH-COF-based aptasensor; Optimization of experimental conditions for sensing VEGF165 and K7M2 cells; Determination of real sample using the proposed aptasensors.
ESM 1
(DOCX 2190 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Liu, Y., Wang, C. et al. Determination of VEGF165 using impedimetric aptasensor based on cyclohexanehexone-melem covalent-organic framework. Microchim Acta 188, 211 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04843-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04843-9