Abstract
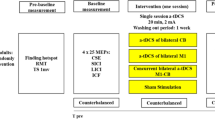
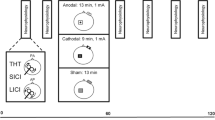
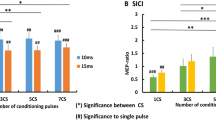
Weak cathodal transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) of the human hand area modulates corticospinal excitability with a suppression of motor-evoked potentials (MEPs) evoked by transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). The changes in excitability persist beyond the time of stimulation if tDCS is given for several minutes and can remain stable for an hour or more. The aim of present study was to evaluate whether a long-lasting suppression of cortical excitability could be induced by prolonged cathodal tDCS (20 min of stimulation). We also explored the impact of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene polymorphisms, on tDCS after-effects. Cortical excitability to single and paired-pulse TMS was evaluated both for the stimulated and contralateral hemisphere, before and up to 24 h after 20 min of cathodal tDCS. We evaluated threshold and amplitude of MEPs, short interval intracortical inhibition (SICI), and intracortical facilitation (ICF). tDCS produced a pronounced suppression of MEP amplitude that was still significant at 3 h after the end of stimulation. The BDNF genotype had not influence on tDCS after-effects. Thresholds for MEPs, SICI and ICF were not affected. No significant effect was observed in the contralateral hemisphere. Twenty minutes of cathodal tDCS is capable of inducing a long-lasting suppression of the excitability of the human motor cortex.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antal A, Chaieb L, Moliadze V, Monte-Silva K, Poreisz C, Thirugnanasambandam N, Nitsche MA, Shoukier M, Ludwig H, Paulus W (2010a) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene polymorphisms shape cortical plasticity in humans. Brain Stimul 3(4):230–237
Antal A, Terney D, Kuhnl S, Paulus W (2010b) Anodal transcranial direct current stimulation of the motor cortex ameliorates chronic pain and reduces short intracortical inhibition. J Pain Symptom Manag 39(5):890–903
Benninger DH, Lomarev M, Lopez G, Wassermann EM, Li X, Considine E, Hallett M (2010) Transcranial direct current stimulation for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 81(10):1105–1111
Boggio PS, Valasek CA, Campanha C, Giglio AC, Baptista NI, Lapenta OM, Fregni F (2011) Non-invasive brain stimulation to assess and modulate neuroplasticity in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychol Rehabil 21(5):703–716
Cheeran B, Talelli P, Mori F, Koch G, Suppa A, Edwards M, Houlden H, Bhatia K, Greenwood R, Rothwell JC (2008) A common polymorphism in the brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene (BDNF) modulates human cortical plasticity and the response to rTMS. J Physiol 586(Pt 23):5717–5725
Chen R, Cros D, Curra A, Di Lazzaro V, Lefaucheur JP, Magistris MR, Mills K, Rosler KM, Triggs WJ, Ugawa Y, Ziemann U (2008) The clinical diagnostic utility of transcranial magnetic stimulation: report of an IFCN committee. Clin Neurophysiol 119(3):504–532
Di Lazzaro V, Dileone M, Pilato F, Capone F, Musumeci G, Ranieri F, Ricci V, Bria P, Di Iorio R, de Waure C, Pasqualetti P, Profice P (2011) Modulation of motor cortex neuronal networks by rTMS: comparison of local and remote effects of six different protocols of stimulation. J Neurophysiol 105(5):2150–2156
Fritsch B, Reis J, Martinowich K, Schambra HM, Ji Y, Cohen LG, Lu B (2010) Direct current stimulation promotes BDNF-dependent synaptic plasticity: potential implications for motor learning. Neuron 66(2):198–204
Hummel F, Celnik P, Giraux P, Floel A, Wu WH, Gerloff C, Cohen LG (2005) Effects of non-invasive cortical stimulation on skilled motor function in chronic stroke. Brain 128(Pt 3):490–499
Kujirai T, Caramia MD, Rothwell JC, Day BL, Thompson PD, Ferbert A, Wroe S, Asselman P, Marsden CD (1993) Corticocortical inhibition in human motor cortex. J Physiol 471:501–519
Lang N, Nitsche MA, Paulus W, Rothwell JC, Lemon RN (2004) Effects of transcranial direct current stimulation over the human motor cortex on corticospinal and transcallosal excitability. Exp Brain Res. Experimentelle Hirnforschung 156(4):439–443
Lang N, Siebner HR, Ward NS, Lee L, Nitsche MA, Paulus W, Rothwell JC, Lemon RN, Frackowiak RS (2005) How does transcranial DC stimulation of the primary motor cortex alter regional neuronal activity in the human brain? Eur J Neurosci 22(2):495–504
Lang N, Nitsche MA, Dileone M, Mazzone P, De Andres-Ares J, Diaz-Jara L, Paulus W, Di Lazzaro V, Oliviero A (2011) Transcranial direct current stimulation effects on I-wave activity in humans. J Neurophysiol 105(6):2802–2810
Liebetanz D, Nitsche MA, Tergau F, Paulus W (2002) Pharmacological approach to the mechanisms of transcranial DC-stimulation-induced after-effects of human motor cortex excitability. Brain 125(Pt 10):2238–2247
Monte-Silva K, Kuo MF, Liebetanz D, Paulus W, Nitsche MA (2010) Shaping the optimal repetition interval for cathodal transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS). J Neurophysiol 103(4):1735–1740
Nitsche MA, Paulus W (2000) Excitability changes induced in the human motor cortex by weak transcranial direct current stimulation. J Physiol 527(Pt 3):633–639
Nitsche MA, Paulus W (2001) Sustained excitability elevations induced by transcranial DC motor cortex stimulation in humans. Neurology 57(10):1899–1901
Nitsche MA, Paulus W (2009) Noninvasive brain stimulation protocols in the treatment of epilepsy: current state and perspectives. Neurotherapeutics 6(2):244–250
Nitsche MA, Fricke K, Henschke U, Schlitterlau A, Liebetanz D, Lang N, Henning S, Tergau F, Paulus W (2003a) Pharmacological modulation of cortical excitability shifts induced by transcranial direct current stimulation in humans. J Physiol 553(Pt 1):293–301
Nitsche MA, Nitsche MS, Klein CC, Tergau F, Rothwell JC, Paulus W (2003b) Level of action of cathodal DC polarisation induced inhibition of the human motor cortex. Clin Neurophysiol 114(4):600–604
Nitsche MA, Seeber A, Frommann K, Klein CC, Rochford C, Nitsche MS, Fricke K, Liebetanz D, Lang N, Antal A, Paulus W, Tergau F (2005) Modulating parameters of excitability during and after transcranial direct current stimulation of the human motor cortex. J Physiol 568(Pt 1):291–303
Nitsche MA, Cohen LG, Wassermann EM, Priori A, Lang N, Antal A, Paulus W, Hummel F, Boggio PS, Fregni F, Pascual-Leone A (2008) Transcranial direct current stimulation: state of the art. Brain Stimul 1(3):206–223
Nitsche MA, Boggio PS, Fregni F, Pascual-Leone A (2009) Treatment of depression with transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS): a review. Exp Neurol 219(1):14–19
Oldfield RC (1971) The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 9(1):97–113
Paulus W, Classen J, Cohen Leonardo G, Large Charles H, Di Lazzaro V, Nitsche M, Pascual-Leone Alvaro, Rosenow F, Rothwell John C, Ulf Z (2008) State of the art: Pharmacologic effects on cortical excitability measures tested by transcranial magnetic stimulation. 1(3):151–163
Priori A, Berardelli A, Rona S, Accornero N, Manfredi M (1998) Polarization of the human motor cortex through the scalp. NeuroReport 9(10):2257–2260
Ranieri F, Podda MV, Riccardi E, Frisullo G, Dileone M, Profice P, Pilato F, Di Lazzaro V, Grassi C (2012) Modulation of Ltp at rat hippocampal Ca3-Ca1 synapses by direct current stimulation. J Neurophysiol 107(7):1868–1880
Ridding MC, Taylor JL, Rothwell JC (1995) The effect of voluntary contraction on cortico-cortical inhibition in human motor cortex. J Physiol 487(Pt 2):541–548
Schade S, Moliadze V, Paulus W, Antal A (2012) Modulating neuronal excitability in the motor cortex with tDCS shows moderate hemispheric asymmetry due to subjects’ handedness: a pilot study. Restor Neurol Neurosci 30(3):191–198
Siebner HR, Lang N, Rizzo V, Nitsche MA, Paulus W, Lemon RN, Rothwell JC (2004) Preconditioning of low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation with transcranial direct current stimulation: evidence for homeostatic plasticity in the human motor cortex. J Neurosci 24(13):3379–3385
Williams JA, Imamura M, Fregni F (2009) Updates on the use of non-invasive brain stimulation in physical and rehabilitation medicine. J Rehabil Med 41(5):305–311
Williams JA, Pascual-Leone A, Fregni F (2010) Interhemispheric modulation induced by cortical stimulation and motor training. Phys Ther 90(3):398–410
Zaghi S, Acar M, Hultgren B, Boggio PS, Fregni F (2010) Noninvasive brain stimulation with low-intensity electrical currents: putative mechanisms of action for direct and alternating current stimulation. Neuroscientist 16(3):285–307
Zaghi S, Thiele B, Pimentel D, Pimentel T, Fregni F (2011) Assessment and treatment of pain with non-invasive cortical stimulation. Restor Neurol Neurosci 29(6):439–451
Acknowledgments
The present study was supported by a Grant from the Italian Ministry of Health (Ricerca Finalizzata Bando 2007-Project Number RF-ABR-2007-631680).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di Lazzaro, V., Manganelli, F., Dileone, M. et al. The effects of prolonged cathodal direct current stimulation on the excitatory and inhibitory circuits of the ipsilateral and contralateral motor cortex. J Neural Transm 119, 1499–1506 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-012-0845-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-012-0845-4