Abstract
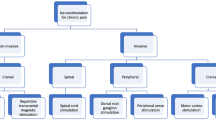
The goal of this narrative review was to give an up-to-date overview of the peripheral and central neurostimulation methods that can be used to treat chronic pain. Special focus has been given to three pain conditions: neuropathic pain, nociplastic pain and primary headaches. Both non-invasive and invasive techniques are briefly presented together with their pain relief potentials. For non-invasive stimulation techniques, data concerning transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS), remote electrical neuromodulation (REN) and vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) are provided. Concerning invasive stimulation techniques, occipital nerve stimulation (ONS), vagus nerve stimulation (VNS), epidural motor cortex stimulation (EMCS), spinal cord stimulation (SCS) and deep brain stimulation (DBS) are presented. The action mode of all these techniques is only partly understood but can be very different from one technique to the other. Patients’ selection is still a challenge. Recent consensus-based guidelines for clinical practice are presented when available. The development of closed-loop devices could be of interest in the future, although the clinical benefit over open loop is not proven yet.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahdab R, Ayache SS, Brugières P et al (2010) Comparison of “standard” and “navigated” procedures of TMS coil positioning over motor, premotor and prefrontal targets in patients with chronic pain and depression. Neurophysiol Clin Clin Neurophysiol 40:27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucli.2010.01.001
Akram H, Miller S, Lagrata S et al (2017) Optimal deep brain stimulation site and target connectivity for chronic cluster headache. Neurology 89:2083–2091. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000004646
Ambrosini A, Coppola G, Iezzi E et al (2017) Reliability and repeatability of testing visual evoked potential habituation in migraine: a blinded case-control study. Cephalalgia Int J Headache 37:418–422. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102416648656
Andre-Obadia N, Magnin M, Simon E, Garcia-Larrea L (2018) Somatotopic effects of rTMS in neuropathic pain? A comparison between stimulation over hand and face motor areas. Eur J Pain Lond Engl 22:707–715. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejp.1156
André-Obadia N, Mertens P, Gueguen A et al (2008) Pain relief by rTMS: differential effect of current flow but no specific action on pain subtypes. Neurology 71:833–840. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000325481.61471.f0
André-Obadia N, Mertens P, Lelekov-Boissard T et al (2014) Is life better after motor cortex stimulation for pain control? Results at long-term and their prediction by preoperative rTMS. Pain Physician 17:53–62
Andreou AP, Holland PR, Akerman S et al (2016) Transcranial magnetic stimulation and potential cortical and trigeminothalamic mechanisms in migraine. Brain J Neurol 139:2002–2014. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/aww118
Ansarinia M, Rezai A, Tepper SJ et al (2010) Electrical stimulation of sphenopalatine ganglion for acute treatment of cluster headaches. Headache 50:1164–1174. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1526-4610.2010.01661.x
Antal A, Alekseichuk I, Bikson M et al (2017) Low intensity transcranial electric stimulation: safety, ethical, legal regulatory and application guidelines. Clin Neurophysiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2017.06.001
Assaf AT, Hillerup S, Rostgaard J et al (2016) Technical and surgical aspects of the sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG) microstimulator insertion procedure. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 45:245–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2015.09.023
Attal N, Ayache SS, Ciampi De Andrade D et al (2016) Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation and transcranial direct-current stimulation in neuropathic pain due to radiculopathy: a randomized sham-controlled comparative study. Pain 157:1224–1231. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000510
Ayache SS, Palm U, Chalah MA et al (2016) Prefrontal tDCS decreases pain in patients with multiple sclerosis. Front Neurosci 10:147. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2016.00147
Baptista AF, Fernandes AMBL, Sá KN et al (2019) Latin American and Caribbean consensus on noninvasive central nervous system neuromodulation for chronic pain management (LAC2-NIN-CP). Pain Rep 4:e692. https://doi.org/10.1097/PR9.0000000000000692
Bhola R, Kinsella E, Giffin N et al (2015) Single-pulse transcranial magnetic stimulation (sTMS) for the acute treatment of migraine: evaluation of outcome data for the UK post market pilot program. J Headache Pain 16:535. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10194-015-0535-3
Bittar RG, Kar-Purkayastha I, Owen SL et al (2005) Deep brain stimulation for pain relief: a meta-analysis. J Clin Neurosci 12:515–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2004.10.005
Blumberger DM, Vila-Rodriguez F, Thorpe KE et al (2018) Effectiveness of theta burst versus high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in patients with depression (THREE-D): a randomised non-inferiority trial. Lancet Lond Engl 391:1683–1692. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30295-2
Bouhassira D, Lantéri-Minet M, Attal N et al (2008) Prevalence of chronic pain with neuropathic characteristics in the general population. Pain 136:380–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2007.08.013
Boyer L, Dousset A, Roussel P et al (2014) rTMS in fibromyalgia: a randomized trial evaluating QoL and its brain metabolic substrate. Neurology 82:1231–1238. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000000280
Breivik H, Collett B, Ventafridda V et al (2006) Survey of chronic pain in Europe: prevalence, impact on daily life, and treatment. Eur J Pain Lond Engl 10:287–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpain.2005.06.009
Buse DC, Manack AN, Fanning KM et al (2012) Chronic migraine prevalence, disability, and sociodemographic factors: results from the American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention Study. Headache 52:1456–1470. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1526-4610.2012.02223.x
Buvanendran A, Lubenow TJ (2008) Efficacy of transverse tripolar spinal cord stimulator for the relief of chronic low back pain from failed back surgery. Pain Physician 11:333–338
Castillo-Saavedra L, Gebodh N, Bikson M et al (2016) Clinically effective treatment of fibromyalgia pain with high-definition transcranial direct current stimulation: phase II open-label dose optimization. J Pain 17:14–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2015.09.009
Cervigni M, Onesti E, Ceccanti M et al (2018) Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for chronic neuropathic pain in patients with bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis. Neurourol Urodyn. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.23718
Chen SP, Ay I, de Morais AL, Qin T, Zheng Y, Sadeghian H, Oka F, Simon B, Eikermann-Haerter K, Ayata C (2016) Vagus nerve stimulation inhibits cortical spreading depression. Pain 157(4):797–805. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000437
Chou DE, Shnayderman Yugrakh M, Winegarner D et al (2019) Acute migraine therapy with external trigeminal neurostimulation (ACME): a randomized controlled trial. Cephalalgia Int J Headache 39:3–14. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102418811573
Ciampi de Andrade D, Galhardoni R, Pinto LF et al (2012) Into the Island: a new technique of non-invasive cortical stimulation of the insula. Neurophysiol Clin 42:363–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucli.2012.08.003
Ciampi de Andrade D, Mhalla A, Adam F et al (2014) Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation induced analgesia depends on N-methyl-D-aspartate glutamate receptors. Pain 155:598–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2013.12.022
Coffey RJ (2001) Deep brain stimulation for chronic pain: results of two multicenter trials and a structured review. Pain Med Malden Mass 2:183–192. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1526-4637.2001.01029.x
Coppola G, Di Lorenzo C, Schoenen J, Pierelli F (2013) Habituation and sensitization in primary headaches. J Headache Pain 14:65. https://doi.org/10.1186/1129-2377-14-65
Cruccu G, Aziz TZ, Garcia-Larrea L et al (2007) EFNS guidelines on neurostimulation therapy for neuropathic pain. Eur J Neurol 14:952–970. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2007.01916.x
Cruccu G, Garcia-Larrea L, Hansson P et al (2016) EAN guidelines on central neurostimulation therapy in chronic pain conditions. Eur J Neurol 23:1489–1499. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.13103
Dailey DL, Rakel BA, Vance CGT et al (2013) Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation reduces pain, fatigue and hyperalgesia while restoring central inhibition in primary fibromyalgia. Pain 154:2554–2562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2013.07.043
DaSilva AF, Truong DQ, DosSantos MF et al (2015) State-of-art neuroanatomical target analysis of high-definition and conventional tDCS montages used for migraine and pain control. Front Neuroanat 9:89. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2015.00089
de Andrade DC, Mhalla A, Adam F et al (2011) Neuropharmacological basis of rTMS-induced analgesia: the role of endogenous opioids. Pain 152:320–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2010.10.032
de Vos CC, Rajan V, Steenbergen W et al (2009) Effect and safety of spinal cord stimulation for treatment of chronic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy. J Diabetes Complications 23:40–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2007.08.002
Deer TR, Levy RM, Kramer J et al (2017) Dorsal root ganglion stimulation yielded higher treatment success rate for complex regional pain syndrome and causalgia at 3 and 12 months: a randomized comparative trial. Pain 158:669–681. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000814
Deer T, Slavin KV, Amirdelfan K et al (2018) Success using neuromodulation with BURST (SUNBURST) study: results from a prospective, randomized controlled trial using a novel burst waveform. Neuromodulation 21:56–66. https://doi.org/10.1111/ner.12698
Deng Z-D, Lisanby SH, Peterchev AV (2013) Electric field depth-focality tradeoff in transcranial magnetic stimulation: simulation comparison of 50 coil designs. Brain Stimulat 6:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2012.02.005
Dodick DW, Silberstein SD, Reed KL et al (2015) Safety and efficacy of peripheral nerve stimulation of the occipital nerves for the management of chronic migraine: long-term results from a randomized, multicenter, double-blinded, controlled study. Cephalalgia Int J Headache 35:344–358. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102414543331
Donnell A, Nascimento DT, Lawrence M et al (2015) High-definition and non-invasive brain modulation of pain and motor dysfunction in chronic TMD. Brain Stimulat 8:1085–1092. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2015.06.008
Dostrovsky JO (2000) Role of thalamus in pain. Prog Brain Res 129:245–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6123(00)29018-3
Fayaz A, Croft P, Langford RM et al (2016) Prevalence of chronic pain in the UK: a systematic review and meta-analysis of population studies. BMJ Open 6:e010364. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2015-010364
Ferrari MD, Klever RR, Terwindt GM et al (2015) Migraine pathophysiology: lessons from mouse models and human genetics. Lancet Neurol 14:65–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70220-0
Fontaine D, Bruneto JL, El Fakir H et al (2009a) Short-term restoration of facial sensory loss by motor cortex stimulation in peripheral post-traumatic neuropathic pain. J Headache Pain 10:203–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10194-009-0115-5
Fontaine D, Hamani C, Lozano A (2009b) Efficacy and safety of motor cortex stimulation for chronic neuropathic pain: critical review of the literature. J Neurosurg 110:251–256. https://doi.org/10.3171/2008.6.17602
Fontaine D, Lanteri-Minet M, Ouchchane L et al (2010a) Anatomical location of effective deep brain stimulation electrodes in chronic cluster headache. Brain J Neurol 133:1214–1223. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awq041
Fontaine D, Lazorthes Y, Mertens P et al (2010b) Safety and efficacy of deep brain stimulation in refractory cluster headache: a randomized placebo-controlled double-blind trial followed by a 1-year open extension. J Headache Pain 11:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10194-009-0169-4
Fontaine D, Blond S, Lucas C et al (2017) Occipital nerve stimulation improves the quality of life in medically-intractable chronic cluster headache: results of an observational prospective study. Cephalalgia Int J Headache 37:1173–1179. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102416673206
Fontaine D, Santucci S, Lanteri-Minet M (2018) Managing cluster headache with sphenopalatine ganglion stimulation: a review. J Pain Res 11:375–381. https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S129641
Fregni F, Boggio PS, Lima MC et al (2006) A sham-controlled, phase II trial of transcranial direct current stimulation for the treatment of central pain in traumatic spinal cord injury. Pain 122:197–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2006.02.023
Galhardoni R, Aparecida da Silva V, García-Larrea L et al (2019) Insular and anterior cingulate cortex deep stimulation for central neuropathic pain: disassembling the percept of pain. Neurology 92:e2165–e2175. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000007396
GBD (2016) Headache collaborators (2018) global, regional, and national burden of migraine and tension-type headache, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2016. Lancet Neurol 17:954–976. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30322-3
Gibson W, Wand BM, O’Connell NE (2017) Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) for neuropathic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst 9:CD011976. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD011976.pub2
Goadsby PJ (2002) Pathophysiology of cluster headache: a trigeminal autonomic cephalgia. Lancet Neurol 1:251–257
Goadsby PJ, Bartsch T, Dodick DW (2008) Occipital nerve stimulation for headache: mechanisms and efficacy. Headache 48:313–318. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1526-4610.2007.01022.x
Gybels J, Erdine S, Maeyaert J et al (1998) Neuromodulation of pain. A consensus statement prepared in Brussels 16–18 January 1998 by the following task force of the European Federation of IASP Chapters (EFIC). Eur J Pain Lond Engl 2:203–209
Heidari F, Afshari M, Moosazadeh M (2017) Prevalence of fibromyalgia in general population and patients, a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatol Int 37:1527–1539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-017-3725-2
Hodaj H, Alibeu J-P, Payen J-F, Lefaucheur J-P (2015) Treatment of chronic facial pain including cluster headache by repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the motor cortex with maintenance sessions: a naturalistic study. Brain Stimulat 8:801–807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2015.01.416
Hodaj H, Payen J-F, Lefaucheur J-P (2018) Therapeutic impact of motor cortex rTMS in patients with chronic neuropathic pain even in the absence of an analgesic response. A case report. Neurophysiol Clin. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucli.2018.05.039
Hoelscher C, Riley J, Wu C, Sharan A (2017) Cost-effectiveness data regarding spinal cord stimulation for low back pain. Spine 42(Suppl 14):S72–S79. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0000000000002194
Hosobuchi Y, Adams JE, Linchitz R (1977) Pain relief by electrical stimulation of the central gray matter in humans and its reversal by naloxone. Science 197:183–186. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.301658
Jin Y, Xing G, Li G et al (2015) High frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy for chronic neuropathic pain: a meta-analysis. Pain Physician 18:E1029–E1046
Johnson MI, Claydon LS, Herbison GP et al (2017) Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) for fibromyalgia in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 10:CD012172. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD012172.pub2
Kapural L, Yu C, Doust MW et al (2016) Comparison of 10-kHz high-frequency and traditional low-frequency spinal cord stimulation for the treatment of chronic back and leg pain: 24-month results from a multicenter, randomized, controlled pivotal trial. Neurosurgery 79:667–677. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000001418
Kemler MA, Barendse GA, van Kleef M et al (2000) Spinal cord stimulation in patients with chronic reflex sympathetic dystrophy. N Engl J Med 343:618–624. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM200008313430904
Kim YJ, Ku J, Kim HJ et al (2013) Randomized, sham controlled trial of transcranial direct current stimulation for painful diabetic polyneuropathy. Ann Rehabil Med 37:766–776. https://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2013.37.6.766
Kinfe TM, Pintea B, Link C et al (2016) High frequency (10 kHz) or burst spinal cord stimulation in failed back surgery syndrome patients with predominant back pain: preliminary data from a prospective observational study. Neuromodulation 19:268–275. https://doi.org/10.1111/ner.12379
Kobayashi M, Pascual-Leone A (2003) Transcranial magnetic stimulation in neurology. Lancet Neurol 2:145–156
Koopmeiners AS, Mueller S, Kramer J, Hogan QH (2013) Effect of electrical field stimulation on dorsal root ganglion neuronal function. Neuromodulation 16:304–311. https://doi.org/10.1111/ner.12028(Discussion 310–311)
Krames ES (2015) The dorsal root ganglion in chronic pain and as a target for neuromodulation: a review. Neuromodulation 18:24–32. https://doi.org/10.1111/ner.12247(Discussion 32)
Kumar K, Taylor RS, Jacques L et al (2007) Spinal cord stimulation versus conventional medical management for neuropathic pain: a multicentre randomised controlled trial in patients with failed back surgery syndrome. Pain 132:179–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2007.07.028
Kumar K, Taylor RS, Jacques L et al (2008) The effects of spinal cord stimulation in neuropathic pain are sustained: a 24-month follow-up of the prospective randomized controlled multicenter trial of the effectiveness of spinal cord stimulation. Neurosurgery 63:762–770. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000325731.46702.D9(Discussion 770)
Lantéri-Minet M, Valade D, Géraud G et al (2005) Migraine and probable migraine–results of FRAMIG 3, a French nationwide survey carried out according to the 2004 IHS classification. Cephalalgia 25:1146–1158. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2982.2005.00977.x
Lefaucheur J-P (2008) Principles of therapeutic use of transcranial and epidural cortical stimulation. Clin Neurophysiol 119:2179–2184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2008.07.007
Lefaucheur J-P (2009) Methods of therapeutic cortical stimulation. Neurophysiol Clin 39:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucli.2008.11.001
Lefaucheur J-P (2010) Why image-guided navigation becomes essential in the practice of transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neurophysiol Clin 40:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucli.2009.10.004
Lefaucheur J-P (2012) Neurophysiology of cortical stimulation. Int Rev Neurobiol 107:57–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-404706-8.00005-X
Lefaucheur J-P (2016) A comprehensive database of published tDCS clinical trials (2005–2016). Neurophysiol Clin 46:319–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucli.2016.10.002
Lefaucheur JP, Drouot X, Nguyen JP (2001) Interventional neurophysiology for pain control: duration of pain relief following repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the motor cortex. Neurophysiol Clin 31:247–252
Lefaucheur JP, Drouot X, Ménard-Lefaucheur I et al (2006a) Motor cortex rTMS restores defective intracortical inhibition in chronic neuropathic pain. Neurology 67:1568–1574. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000242731.10074.3c
Lefaucheur JP, Hatem S, Nineb A et al (2006b) Somatotopic organization of the analgesic effects of motor cortex rTMS in neuropathic pain. Neurology 67:1998–2004. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000247138.85330.88
Lefaucheur J-P, Antal A, Ahdab R et al (2008) The use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) and transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) to relieve pain. Brain Stimulat 1:337–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2008.07.003
Lefaucheur J-P, Drouot X, Cunin P et al (2009) Motor cortex stimulation for the treatment of refractory peripheral neuropathic pain. Brain J Neurol 132:1463–1471. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awp035
Lefaucheur J-P, Ménard-Lefaucheur I, Goujon C et al (2011) Predictive value of rTMS in the identification of responders to epidural motor cortex stimulation therapy for pain. J Pain 12:1102–1111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2011.05.004
Lefaucheur J-P, André-Obadia N, Antal A et al (2014) Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS). Clin Neurophysiol 125:2150–2206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2014.05.021
Lefaucheur J-P, Antal A, Ayache SS et al (2017) Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS). Clin Neurophysiol 128:56–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2016.10.087
Lenaerts ME, Oommen KJ, Couch JR, Skaggs V (2008) Can vagus nerve stimulation help migraine? Cephalalgia 28:392–395. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01538.x
Leone M, Franzini A, Bussone G (2001) Stereotactic stimulation of posterior hypothalamic gray matter in a patient with intractable cluster headache. N Engl J Med 345:1428–1429. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM200111083451915
Leone M, May A, Franzini A et al (2004) Deep brain stimulation for intractable chronic cluster headache: proposals for patient selection. Cephalalgia 24:934–937. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2982.2004.00742.x
Leung A, Donohue M, Xu R et al (2009) rTMS for suppressing neuropathic pain: a meta-analysis. J Pain 10:1205–1216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2009.03.010
Levy R, Deer TR, Poree L et al (2019) Multicenter, randomized, double-blind study protocol using human spinal cord recording comparing safety, efficacy, and neurophysiological responses between patients being treated with evoked compound action potential-controlled closed-loop spinal cord stimulation or open-loop spinal cord stimulation (the Evoke Study). Neuromodulation J 22:317–326. https://doi.org/10.1111/ner.12932
Liem L, Russo M, Huygen FJPM et al (2013) A multicenter, prospective trial to assess the safety and performance of the spinal modulation dorsal root ganglion neurostimulator system in the treatment of chronic pain. Neuromodulation 16:471–482. https://doi.org/10.1111/ner.12072(Discussion 482)
Lipton RB, Goadsby PJ, Cady RK et al (2009) PRISM study: occipital nerve stimulation for treatment-refractory migraine. Cephalalgia Int J Headache 29(Suppl 1):1–166
Lipton RB, Dodick DW, Silberstein SD et al (2010) Single-pulse transcranial magnetic stimulation for acute treatment of migraine with aura: a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, sham-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 9:373–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70054-5
Maarrawi J, Peyron R, Mertens P et al (2007) Motor cortex stimulation for pain control induces changes in the endogenous opioid system. Neurology 69:827–834. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000269783.86997.37
Magis D, Schoenen J (2012) Advances and challenges in neurostimulation for headaches. Lancet Neurol 11:708–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70139-4
Magis D, Bruno M-A, Fumal A et al (2011) Central modulation in cluster headache patients treated with occipital nerve stimulation: an FDG-PET study. BMC Neurol 11:25. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2377-11-25
Magis D, D’Ostilio K, Thibaut A et al (2017) Cerebral metabolism before and after external trigeminal nerve stimulation in episodic migraine. Cephalalgia Int J Headache 37:881–891. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102416656118
Mansouri F, Fettes P, Schulze L et al (2018) A Real-Time Phase-Locking System for Non-invasive Brain Stimulation. Front Neurosci 12:877. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00877
Marin J, Giffin N, Consiglio E et al (2018) Non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation for treatment of cluster headache: early UK clinical experience. J Headache Pain 19:114. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10194-018-0936-1
Martelletti P, Jensen RH, Antal A et al (2013) Neuromodulation of chronic headaches: position statement from the European Headache Federation. J Headache Pain 14:86. https://doi.org/10.1186/1129-2377-14-86
Matharu MS, Bartsch T, Ward N et al (2004) Central neuromodulation in chronic migraine patients with suboccipital stimulators: a PET study. Brain J Neurol 127:220–230. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awh022
May A, Bahra A, Büchel C et al (1998) Hypothalamic activation in cluster headache attacks. Lancet Lond Engl 352:275–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(98)02470-2
May A, Ashburner J, Büchel C et al (1999) Correlation between structural and functional changes in brain in an idiopathic headache syndrome. Nat Med 5:836–838. https://doi.org/10.1038/10561
Melzack R, Wall PD (1965) Pain mechanisms: a new theory. Science 150:971–979. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.150.3699.971
Meyerson BA, Linderoth B (2006) Mode of action of spinal cord stimulation in neuropathic pain. J Pain Symptom Manage 31:S6–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2005.12.009
Mhalla A, Baudic S, Ciampi de Andrade D et al (2011) Long-term maintenance of the analgesic effects of transcranial magnetic stimulation in fibromyalgia. Pain 152:1478–1485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2011.01.034
Moisset X, Lefaucheur J-P (2018) Non pharmacological treatment for neuropathic pain: invasive and non-invasive cortical stimulation. Rev Neurol (Paris). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurol.2018.09.014
Moisset X, Goudeau S, Poindessous-Jazat F et al (2015) Prolonged continuous theta-burst stimulation is more analgesic than “classical” high frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Brain Stimulat 8:135–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2014.10.006
Moisset X, de Andrade DC, Bouhassira D (2016) From pulses to pain relief: an update on the mechanisms of rTMS-induced analgesic effects. Eur J Pain Lond Engl 20:689–700. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejp.811
Moran F, Leonard T, Hawthorne S et al (2011) Hypoalgesia in response to transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) depends on stimulation intensity. J Pain 12:929–935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2011.02.352
Nesbitt AD, Marin JCA, Tompkins E et al (2015) Initial use of a novel noninvasive vagus nerve stimulator for cluster headache treatment. Neurology 84:1249–1253. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000001394
Nguyen J-P, Nizard J, Keravel Y, Lefaucheur J-P (2011) Invasive brain stimulation for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Nat Rev Neurol 7:699–709. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2011.138
Nguyen J-P, Nizard J, Kuhn E et al (2016) A good preoperative response to transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation predicts a better therapeutic effect of implanted occipital nerve stimulation in pharmacologically intractable headaches. Neurophysiol Clin 46:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucli.2015.12.002
Nizard J, Lefaucheur J-P, Helbert M et al (2012) Non-invasive stimulation therapies for the treatment of refractory pain. Discov Med 14:21–31
North RB, Kidd DH, Farrokhi F, Piantadosi SA (2005) Spinal cord stimulation versus repeated lumbosacral spine surgery for chronic pain: a randomized, controlled trial. Neurosurgery 56:98–106. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000144839.65524.e0(Discussion 106–107)
O’Connell NE, Marston L, Spencer S et al (2018) Non-invasive brain stimulation techniques for chronic pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD008208.pub4
Onesti E, Gabriele M, Cambieri C et al (2013) H-coil repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for pain relief in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Eur J Pain Lond Engl 17:1347–1356. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1532-2149.2013.00320.x
Oshinsky ML, Murphy AL, Hekierski H Jr, Cooper M, Simon BJ (2014) Noninvasive vagus nerve stimulation as treatment for trigeminal allodynia. Pain 155(5):1037–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2014.02.009
Palm U, Chalah MA, Padberg F et al (2016) Effects of transcranial random noise stimulation (tRNS) on affect, pain and attention in multiple sclerosis. Restor Neurol Neurosci 34:189–199. https://doi.org/10.3233/RNN-150557
Passard A, Attal N, Benadhira R et al (2007) Effects of unilateral repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the motor cortex on chronic widespread pain in fibromyalgia. Brain J Neurol 130:2661–2670. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awm189
Pérez-Borrego YA, Campolo M, Soto-León V et al (2014) Pain treatment using tDCS in a single patient: tele-medicine approach in non-invasive brain simulation. Brain Stimulat 7:334–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brs.2013.11.008
Peyron R, Faillenot I, Mertens P et al (2007) Motor cortex stimulation in neuropathic pain. Correlations between analgesic effect and hemodynamic changes in the brain. A PET study. NeuroImage 34:310–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.08.037
Piquet M, Balestra C, Sava SL, Schoenen JE (2011) Supraorbital transcutaneous neurostimulation has sedative effects in healthy subjects. BMC Neurol 11:135. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2377-11-135
Pommier B, Créac’h C, Beauvieux V et al (2016) Robot-guided neuronavigated rTMS as an alternative therapy for central (neuropathic) pain: clinical experience and long-term follow-up. Eur J Pain Lond Engl 20:907–916. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejp.815
Pommier B, Quesada C, Fauchon C et al (2018) Added value of multiple versus single sessions of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in predicting motor cortex stimulation efficacy for refractory neuropathic pain. J Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.12.JNS171333
Quesada C, Pommier B, Fauchon C et al (2018) Robot-guided neuronavigated repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) in central neuropathic pain. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2018.04.013
Rossi S, Hallett M, Rossini PM et al (2009) Safety, ethical considerations, and application guidelines for the use of transcranial magnetic stimulation in clinical practice and research. Clin Neurophysiol 120:2008–2039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2009.08.016
Saper JR, Dodick DW, Silberstein SD et al (2011) Occipital nerve stimulation for the treatment of intractable chronic migraine headache: ONSTIM feasibility study. Cephalalgia 31:271–285. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102410381142
Schoenen J, Jensen RH, Lantéri-Minet M et al (2013a) Stimulation of the sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG) for cluster headache treatment. Pathway CH-1: a randomized, sham-controlled study. Cephalalgia 33:816–830. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102412473667
Schoenen J, Vandersmissen B, Jeangette S et al (2013b) Migraine prevention with a supraorbital transcutaneous stimulator: a randomized controlled trial. Neurology 80:697–704. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182825055
Schytz HW, Barløse M, Guo S et al (2013) Experimental activation of the sphenopalatine ganglion provokes cluster-like attacks in humans. Cephalalgia 33:831–841. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102413476370
Shealy CN, Mortimer JT, Reswick JB (1967) Electrical inhibition of pain by stimulation of the dorsal columns: preliminary clinical report. Anesth Analg 46:489–491
Shimizu T, Hosomi K, Maruo T et al (2017) Efficacy of deep rTMS for neuropathic pain in the lower limb: a randomized, double-blind crossover trial of an H-coil and figure-8 coil. J Neurosurg 127:1172–1180. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.9.JNS16815
Silberstein SD, Dodick DW, Saper J et al (2012) Safety and efficacy of peripheral nerve stimulation of the occipital nerves for the management of chronic migraine: results from a randomized, multicenter, double-blinded, controlled study. Cephalalgia 32:1165–1179. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102412462642
Silberstein SD, Calhoun AH, Lipton RB et al (2016a) Chronic migraine headache prevention with noninvasive vagus nerve stimulation: the EVENT study. Neurology 87:529–538. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000002918
Silberstein SD, Mechtler LL, Kudrow DB et al (2016b) Non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation for the acute treatment of cluster headache: findings from the randomized, double-blind, sham-controlled ACT1 study. Headache 56:1317–1332. https://doi.org/10.1111/head.12896
Sluka KA, Walsh D (2003) Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation: basic science mechanisms and clinical effectiveness. J Pain 4:109–121
Smitherman TA, Burch R, Sheikh H, Loder E (2013) The prevalence, impact, and treatment of migraine and severe headaches in the United States: a review of statistics from national surveillance studies. Headache 53:427–436. https://doi.org/10.1111/head.12074
Starling AJ, Tepper SJ, Marmura MJ et al (2018) A multicenter, prospective, single arm, open label, observational study of sTMS for migraine prevention (ESPOUSE Study). Cephalalgia 38:1038–1048. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102418762525
Stilling JM, Monchi O, Amoozegar F, Debert CT (2019) Transcranial magnetic and direct current stimulation (TMS/tDCS) for the treatment of headache: a systematic review. Headache 59:339–357. https://doi.org/10.1111/head.13479
Tassorelli C, Grazzi L, de Tommaso M et al (2018) Noninvasive vagus nerve stimulation as acute therapy for migraine: the randomized PRESTO study. Neurology 91:e364–e373. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000005857
Tsubokawa T, Katayama Y, Yamamoto T et al (1991) Chronic motor cortex stimulation for the treatment of central pain. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 52:137–139
Turner JA, Loeser JD, Deyo RA, Sanders SB (2004) Spinal cord stimulation for patients with failed back surgery syndrome or complex regional pain syndrome: a systematic review of effectiveness and complications. Pain 108:137–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2003.12.016
Valle A, Roizenblatt S, Botte S et al (2009) Efficacy of anodal transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for the treatment of fibromyalgia: results of a randomized, sham-controlled longitudinal clinical trial. J Pain Manag 2:353–361
Voigt J, Carpenter L, Leuchter A (2017) Cost effectiveness analysis comparing repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation to antidepressant medications after a first treatment failure for major depressive disorder in newly diagnosed patients–A lifetime analysis. PLoS One 12:e0186950. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0186950
Weiner RL, Reed KL (1999) Peripheral neurostimulation for control of intractable occipital neuralgia. Neuromodulation 2:217–221. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1525-1403.1999.00217.x
Wilbrink LA, Teernstra OPM, Haan J et al (2013) Occipital nerve stimulation in medically intractable, chronic cluster headache. The ICON study: rationale and protocol of a randomised trial. Cephalalgia 33:1238–1247. https://doi.org/10.1177/0333102413490351
Yarnitsky D (2010) Conditioned pain modulation (the diffuse noxious inhibitory control-like effect): its relevance for acute and chronic pain states. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 23:611–615. https://doi.org/10.1097/ACO.0b013e32833c348b
Yarnitsky D, Volokh L, Ironi A et al (2017) Nonpainful remote electrical stimulation alleviates episodic migraine pain. Neurology 88:1250–1255. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000003760
Yarnitsky D, Dodick DW, Grosberg BM et al (2019) Remote electrical neuromodulation (REN) relieves acute migraine: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Headache. https://doi.org/10.1111/head.13551
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
X Moisset has received personal fees from Teva, Novartis, Roche, Biogen, Sanofi-Genzyme and Merck-Serono, and non-financial support from SOS oxygene, Boehringer, Bristol Myers Squibb, not related to the submitted work. M. Lanteri-Minet received grants and honoraria for advisory boards, speaker panels or investigation studies from Allergan, Amgen, Astellas, ATI, BMS, Boehringer, Boston Scientific, CoLucid, Convergence, GlaxoSmithKline, Grunenthal, Eli Lilly, Medtronic, Menarini, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Reckitt Benckiser, Saint-Jude-Abbott, Sanofi-Aventis, Teva Pharmaceuticals, UCB, and Zambon. D Fontaine has received personal fees from Boston Scientific, Medtronic and Saint-Jude-Abbott. Boston Scientific, Medtronic and Saint-Jude-Abbott are in the field of neuromodulation.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moisset, X., Lanteri-Minet, M. & Fontaine, D. Neurostimulation methods in the treatment of chronic pain. J Neural Transm 127, 673–686 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-019-02092-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-019-02092-y