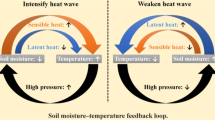
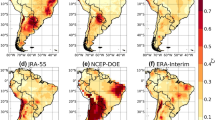
Abstract
Land-atmosphere coupling over the south Asian monsoon region is examined using a regional climate model. For this purpose, the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model with a resolution of 45 km was used. In the control experiment (CTL), the model was integrated from the year 2000 to 2011 and allowed the soil moisture interaction with the atmosphere using a coupled land surface model. In the second experiment (CSM), the soil moisture evolution at each time step was replaced with the climatology of soil moisture taken from the control run. The results reveal that land-atmosphere coupling plays a critical role in influencing the south Asian monsoon climate variability. Soil moisture is found to have stronger impacts on daily maximum temperature compared to minimum temperature. Soil moisture also makes a significant contribution to monsoon rainfall variability over the monsoon region. The coupling strength for large-scale rainfall is found to be higher compared to that of cumulus rainfall. Soil moisture is found more strongly coupled to sensible heat flux over most of the monsoon region.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asharaf S, Dobler A, Ahrens B (2012) Soil moisture–precipitation feedback processes in the Indian summer monsoon season. J Hydrometeorol 13(5):1461–1474
Bellon G (2010) Monsoon intraseasonal oscillation and land–atmosphere interaction in an idealized model. Clim Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-010-0893-0
Betts AK (1986) A new convective adjustment scheme. Part I. Observational and theoretic basis. Quart J Roy Meteor Soc 112:677–691
Betts AK (2004) Understanding hydrometeorology using global models. B Am Meteorol Soc 85(11):1673–1688
Betts AK, Miller MJ (1986) A new convective adjustment scheme. Part II: single column tests using GATE wave, BOMEX, ATEX and Arctic air-mass data sets. QJRMS 112(473):693–709 July 1986
Bhate J, Unnikrishnan CK, Rajeevan M (2012) Regional climate model simulations of the 2009 Indian summer monsoon. Indian J Radio Space Phys 41:488–500
Chang H-I, Niyogi D, Kumar A, Kishtawal CM, Dudhia J, Chen F, Mohanty UC, Shepherd M (2009) Possible relation between land surface feedback and the post-landfall structure of monsoon depressions. Geophys Res Let 36:L15826. doi:10.1029/2009GL037781
Charney JG, Shukla J (1981) In: Lighthill J, Pearce RP (eds) Predictability of monsoons, in monsoon dynamics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp. 99–108
Chen F, Dudhia J (2001) Coupling an advanced land surface hydrology model with the Penn State–NCAR MM5 modeling system. Part I: model implementation and sensitivity. Mon Wea Rev 129:569–585
Delworth T, Manabe S (1989) The influence of soil wetness on near-surface atmospheric variability. J Clim 2:1147–1462
Dirmeyer PA, Koster RD, Guo Z (2006) Do global models properly represent the feedback between land and atmosphere?. J Hydrometeor 7:1177–1198
Douville H (2002) Influence of soil moisture on the Asian and African monsoons. Part II: interannual variability. J Climate 15:701–720. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2002)015<0701:IOSMOT>2.0.CO;2
Douville H (2010) Relative contribution of soil moisture and snow mass to seasonal climate predictability: a pilot study. Clim Dyn 34–6:797–818
Douville H, Chauvin F, Broqua H (2001) Influence of soil moisture on the Asian and African monsoons. Part I: mean monsoon and daily precipitation. J Climate 14:2381–2403. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2001)014<2381:IOSMOT>2.0.CO;2
Dudhia J (1989) Numerical study of convection observed during the winter monsoon experiment using a mesoscale two-dimensional model. J Atmos Sci 46,:3077–3107
Fan Y, van den Dool H (2008) A global monthly land surface air temperature analysis for 1948–present. J Geophys Res 113:D01103. doi:10.1029/2007JD008470
Fennessy M, Shukla J (1999) Impact of initial soil wetness on seasonal atmospheric prediction. J Clim 12:3167–3180. doi:10.1175/15200442(1999)012<3167:IOISWO>2.0.CO;2
Ferranti L, Slingo JM, Palmer TN, Hoskins BJ (1999) The effect of land-surface feedbacks on the monsoon circulation. QJRMS 125(557):1473–1912
Gadgil S, Rajeevan M, Francis PA (2007) Monsoon variability: links to major oscillations over the equatorial Pacific and Indian oceans. Curr Sci 93(2):182–194
Guo Z et al. (2006) GLACE: the global land–atmosphere coupling experiment. Part II: analysis. J Hydrometeor 7:611–625
Guo Z, Dirmeyer PA, DelSole T (2011) Land surface impacts on subseasonal and seasonal predictability. Geophys Res Lett 38:L24812. doi:10.1029/2011GL049945
Guo Z, Dirmeyer PA, DelSole T, Koster RD (2012) Rebound in atmospheric predictability and the role of the land surface. J Climate 25:4744–4749. doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00651.1
Hong, S.-Y, and J. Dudhia, 2003, Testing of a new non-local boundary layer vertical diffusion scheme in numerical weather prediction applications, 20th Conference on Weather Analysis and Forecasting/16th Conference on Numerical Weather Prediction, Seattle, WA, https://ams.confex.com/ams/pdfpapers/72744.pdf)
Huffman G, Adler R, Bolvin D, Gu G, Nelkin E, Bowman K, Hong Y, Stocker E, Wolff D (2007) The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis, TCMA: quasi-global, multiyear, combined sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J Hydrometeorol 8:38–55. doi:10.1175/JHM560.1
Janjic ZI (1994) The step-mountain Eta coordinate model: further developments of the convection, viscous sublayer, and turbulence closure schemes. Mon. Wea. Rev. 122:927–945
Joshi MK, Rai A, Pandey AC (2012) Validation of TMPA and GPCP 1DD against the ground truth rain-gauge data for Indian region, online published. Int J. Clim. doi:10.1002/joc.3612
Kim JE, Hong SY (2007) Impact of soil moisture anomalies on summer rainfall over East Asia: a regional climate model study. J. Climate 20:5732–5743
Koster RD, Suarez MJ (2003) Impact of land surface initialization on seasonal precipitation and temperature prediction. J Hydrometeorol 4(2):408–423
Koster RD, Suarez MJ, Heiser M (2000) Variance and predictability of precipitation at seasonal-tointerannual timescales. J Hydrometeorol 1:26–46. doi:10.1175/1525-7541
Koster RD et al. (2004) Regions of strong coupling between soil moisture and precipitation. Science 305:1138–1140
Koster RD et al. (2006) GLACE: the global land–atmosphere coupling experiment. Part I: overview. J. Hydrometeor. 7:590–610
Koster RD et al. (2010) Contribution of land surface initialization to subseasonal forecast skill: first results from a multi-model experiment. Geophys Res Lett 37:L02402. doi:10.1029/2009GL041677
Koster RD et al. (2011) The second phase of the global land–atmosphere coupling experiment: soil moisture contributions to subseasonal forecast skill. J Hydrometeor 12:805–822
Lin YL, Farley RD, Orville HD (1983) Bulk parameterization of the snow field in a cloud model. J Clim Appl Meteorol 22:1065–1092
Meehl GA (1994) Influence of the land surface in the Asian summer monsoon: external conditions versus internal feedbacks. J Climate 7:1033–1049. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(1994)007<1033:IOTLSI>2.0.CO;2
Miller DA, White RA (1998) A conterminous United States multilayer soil characteristics data set for regional climate and hydrology modeling. Earth Interact 2:1–26
Mlawer EJ, Taubman SJ, Brown PD, Iacono MJ, Clough SA (1997) Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmospheres: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the longwave. J Geophys Res 102:16663–16682
Monin AS, Obukhov AM (1954) Basic laws of turbulent mixing in the surface layer of the atmosphere (in Russian). Contrib Geophys Inst Acad Sci USSR 151:63–187
Mukhopadhyay P, Taraphdar S, Goswami BN, Krishnakumar K (2010) Indian summer monsoon precipitation climatology in a high-resolution regional climate model: impacts of convective parameterization on systematic biases. Wea Forecast 25:369–387. doi:10.1175/2009WAF2222320.1
Rasmusson EM, Carpenter TH (1983) The relationship between eastern equatorial Pacific sea surface temperature and rainfall over India and Sri Lanka. Mon Weather Rev 111:517–528
Saha SK, Halder S, Kumar KK, Goswami BN (2011) Pre-onset land surface processes and ‘internal’ interannual variabilities of the Indian summer monsoon. Clim Dyn 36:2077–2089
Saha SK, Halder S, Rao ASA, Goswami BN (2012) Modulation of ISOs by land-atmosphere feedback and contribution to the interannual variability of Indian summer monsoon. J Geophys Res. doi:10.1029/2011JD017291
Seneviratne SI, Luthi D, Litschi M, Scha r C (2006) Land-atmosphere coupling and climate change in Europe. Nature 443:205–209
Shukla J (1981) Dynamical predictability of monthly means. J Atmos Sci 38:2547–2572
Shukla J, Mintz Y (1982) The influence of land surface evapotranspiration on the earth’s climate. Science 214:1498–1501
Sijikumar S, Liji J, Manjusha K (2013) Sensitivity study on the role of Western Ghats in simulating the Asian summer monsoon characteristics. Meteorog Atmos Phys 120(1–2):53–60
Sikka DR (1980) Some aspects of the large scale fluctuations of summer monsoon rainfall over India in relation to fluctuations in the planetary and regional scale circulation parameters. Proc Indian Acad Sci Earth Planet Sci 89:179–195
Srinivas CV, Hariprasad D, Bhaskar Rao DV, Anjaneyulu Y, Baskaran R, Venkatraman B (2013) Simulation of the Indian summer monsoon regional climate using advanced research WRF model. Int J Climatol 33:1195–1210. doi:10.1002/joc.3505
Steiner AL, Pal JS, Rauscher SA, Bell JL, Diffenbaugh NS, Boone A, Sloan LC, Giorgi F (2009) Land surface coupling in regional climate simulations of the West African monsoon. Clim Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-009-0543-6
Takata K, Saitoa K, Yasunari T (2009) Changes in the Asian monsoon climate during 1700–1850 induced by preindustrial cultivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:9586–9589. doi:10.1073/pnas.0807346106
Taylor CM et al. (2011) New perspectives on land–atmosphere feedbacks from the African monsoon multidisciplinary analysis. Atmospheric Science Letters 12(1):38–44
van den Hurk B et al. (2012) Soil moisture effects on seasonal temperature and precipitation forecast scores in Europe. Clim Dyn 38:349–362. doi:10.1007/s00382-010-0956-2v
Wagner W, Dorigo W, de Jeu R, Fernandez D, Benveniste J, Haas E, Ertl M (2012) Fusion of active and passive microwave observations to create an essential climate variable data record on soil moisture. ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences (ISPRS Annals), volume I-7, XXII ISPRS Congress, Melbourne. Australia:315–321
Webster PJ (1983) Mechanisms of low-frequency variability: surface hydrological effects. J Atmos Sci 40:2110–2124
Webster PJ, Yang S (1992) Monsoon and ENSO: selectively interactive systems. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society. 118(507):877–926
Yeh TC, Wetherald RT, Manabe S (1984) The effect of soil moisture on the short-term climate and hydrology change-A numerical experiment. Mon Weather Rev 112:474–490
Yihui Ding, and D. R. Sikka, 2006, Synoptic systems and weather. The Asian Monsoon Springer Praxis Books 2006. pp 131–201
Zhang J, Wang WC, Leung LR (2008) Contribution of land atmosphere coupling to summer climate variability over the contiguous United States. J Geophys Res 113:D22109. doi:10.1029/2008JD010136
Zhang J, Wu L, Dong W (2011) Land atmosphere coupling and summer climate variability over East Asia. J Geophys Res 116:D05117. doi:10.1029/2010JD014714
Acknowledgments
We thank the Director, National Atmospheric Research Laboratory, Gadanki, India for providing support and encouragement to carry out this study. We would like to thank Dr. Zhang, the Center for Monsoon System Research, Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences for useful discussions on the subject. The TRMM rainfall data used in this study were produced with the Giovanni online data system, developed and maintained by the NASA GES DISK. ECMWF ERA-Interim data used in this study project have been provided by ECMWF have been obtained from the ECMWF data server. Authors thank the editor and anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments, which helped to improve the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Unnikrishnan, C.K., Rajeevan, M. & Vijaya Bhaskara Rao, S. A study on the role of land-atmosphere coupling on the south Asian monsoon climate variability using a regional climate model. Theor Appl Climatol 127, 949–964 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-015-1680-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-015-1680-y