Abstract
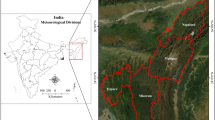
Agriculture in India is highly sensitive to climatic variations particularly to rainfall and temperature; therefore, any change in rainfall and temperature will influence crop yields. An understanding of the spatial and temporal distribution and changing patterns in climatic variables is important for planning and management of natural resources. Time series analysis of climate data can be a very valuable tool to investigate its variability pattern and, maybe, even to predict short- and long-term changes in the series. In this study, the sub-divisional rainfall data of India during the period 1871 to 2016 has been investigated. One of the widely used powerful nonparametric techniques namely wavelet analysis was used to decompose and de-noise the series into time–frequency component in order to study the local as well as global variation over different scales and time epochs. On the decomposed series, autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) and artificial neural network (ANN) models were applied and by means of inverse wavelet transform, the prediction of rainfall for different sub-divisions was obtained. To this end, empirical comparison was carried out toward forecast performance of the approaches namely Wavelet-ANN, Wavelet-ARIMA, and ARIMA. It is reported that Wavelet-ANN and Wavelet-ARIMA approach outperforms the usual ARIMA model for forecasting of rainfall for the data under consideration.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almasri A, Locking H, Shukur G (2008) Testing for climate warming in Sweden during 1850–1999, using wavelets analysis. J Appl Stat 35:431–443. https://doi.org/10.1080/02664760701835011
Aminghafari M, Poggi JM (2007) Forecasting time series using wavelets. Int J Wavelets Multiresolution Inf Process 5:709–724
Aminghafari M, Poggi JM (2012) Nonstationary Time series forecasting using wavelets and kernel smoothing. Commun Stat- Theory Methods 41:485–499. https://doi.org/10.1080/03610926.2010.529532
Antoniadis A (1997) Wavelets in statistics: a review. J Ital Stat Soc 6:97–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03178905
Box GEP, Jenkins GM and Reinsel GC. 2007. Time-series analysis: forecasting and control. 3rd ed. Pearson Education, India.
Daubechies I (1992) Ten lectures on wavelets. SIAM, Philadelphia
Fryzlewicz P, Bellegem SV, von Sachs R (2003) Forecasting non-stationary time series by wavelet process modeling. Ann Inst Stat Math 55:737–764. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02523391
Ghosh H, Paul RK and Prajneshu 2010. Wavelet frequency domain approach for statistical modeling of rainfall time-series data. J Stat Theory Pract, 4, 813-825, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/15598608.2010.10412020.
Kakatkar R, Gnanaseelan C, Chowdary JS, Parekh A, Deepa JS (2017) Indian summer monsoon rainfall variability during 2014 and 2015 and associated Indo-Pacific upper ocean temperature patterns. Theor Appl Climatol 131:1235–1247
Kisi O (2010) Wavelet regression model for short-term stream flow forecasting. J Hydrol 389:344–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.06.013
Kisi O (2011) Wavelet regression model as an alternative to neural networks for river stage forecasting. Water Resour Manag 25(2):579–600. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9715-8
Meena HM, Machiwal D, Santra P (2019) Trends and homogeneity of monthly, seasonal, and annual rainfall over arid region of Rajasthan, India. Theor Appl Climatol 136:795–811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2510-9
Ogden T (1997) Essential wavelets for statistical applications and data analysis. Birkhauser, Boston. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0031182097001868
Parthasarathy B, Munot AA, Kothawale DR (1995) All India monthly and seasonal rainfall series: 1871–1993. Theor Appl Climatol 49:217–224
Paul RK (2017) Modeling long memory in maximum and minimum temperature series in India. Mausam 68(2):317–326
Paul RK. 2019. WaveletANN: wavelet ANN model. R package version 0.1.0. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=WaveletANN
Paul RK, Anjoy P (2018) Modeling fractionally integrated maximum temperature series in India in presence of structural break. Theor Appl Climatol 134(1&2):241–249
Paul RK, Birthal PS (2015) Investigating rainfall trend over India using wavelet technique. J Water Climate Chang 7(2):365–378
Paul RK and Samanata S. 2018. WaveletArima: wavelet ARIMA model. R package version 0.1.0. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=WaveletArima
Paul RK, Prajneshu, Ghosh H (2011) Wavelet methodology for estimation of trend in Indian monsoon rainfall time-series data. Indian J Agric Sci 81:96–98
Paul RK, Prajneshu, Ghosh H (2013) Wavelet frequency domain approach for modeling and forecasting of Indian monsoon rainfall time-series data. J Indian Soc Agric Stat 67(3):319–327
Paul RK, Birthal PS, Paul AK, Gurung B (2015) Temperature trend in different agro-climatic zones in India. Mausam 66(4):841–846
Paul RK, Sarkar S, Mitra D, Panwar S, Paul AK and Bhar LM. 2019. Wavelets based estimation of trend in sub-divisional rainfall in India. Mausam (Accepted)
Percival DB, Mofjeld HO (1997) Analysis of subtidal coastal sea level fluctuations using wavelets. J Am Stat Assoc 92:868–880
Percival DB, Walden AT (2000) Wavelet methods for time-series analysis. Cambridge Univ, Press, U.K.
Rajeevan M, Pai DS, Dikshit SK, Kelkar RR (2004) IMD’s new operational models for long-range forecast of southwest monsoon rainfall over India and their verification for 2003. Curr Sci 86:422–431
Renaud O, Stark JL, Murtagh F (2003) Prediction based on a multiscale decomposition. Int J Wavelets Multiresolution Inf Process 1:217–232
Sunilkumar G and Prajneshu 2004. Modeling and forecasting meteorological subdivisions rainfall data using wavelet thresholding approach. Calcutta Stat Assoc Bull, 54, 255-268.
Venkata Ramana R, Krishna B, Kumar SR (2013) Monthly rainfall prediction using wavelet neural network analysis. Water Resour Manag 27:3697–3711. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-013-0374-4
Vidakovic B (1999) Statistical modeling by wavelets. John Wiley, New York
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere thanks to the anonymous reviewers and the editor for their valuable suggestions that helped us a lot in improving this manuscript. We also acknowledge Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology for providing sub-divisional rainfall data of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paul, R.K., Paul, A.K. & Bhar, L.M. Wavelet-based combination approach for modeling sub-divisional rainfall in India. Theor Appl Climatol 139, 949–963 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-019-03026-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-019-03026-0