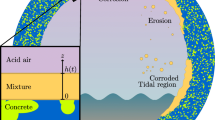
Abstract
Here mixture theory is used to capture the changes in cement concrete exposed to sodium sulfate till cracks develop. Toward this, the mixture is assumed to be made of eleven constituents of which the sodium sulfate and water move relative to themselves and the remaining nine solid constituents. The nine solid constituents constrained to move together are the eight relevant chemical constituents in concrete that react with sodium sulfate and all the other remaining chemical constituents of concrete that do not react with sulfates. Constitutive assumptions needed to be made within this mixture theory framework are the same as those reported by Gouder and Saravanan (Acta Mech 227(11):3123–3146, 2016). Within this framework of mixture theory, the radial ingress and reaction of sodium sulfate solution with the concrete cylinder sealed at top and bottom, exposed to a constant concentration of sodium sulfate at its outer surface, are formulated. The resulting nonlinear governing differential equations are converted into a system of nonlinear algebraic equations using a forward finite difference scheme in space and a backward difference in time. The nonlinear algebraic equations are solved simultaneously using constrained minimization technique till the water reaches the center of the cylinder. The results obtained for ingress without chemical reactions agree with those predicted by Fick’s equation. The axial expansion of the cylinder and the increase in the value of Young’s modulus of the part of concrete which reacted with sulfates agree qualitatively with the experiments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson, A., Hearne, J.A.: Mechanistic model for the durability of concrete barriers exposed to sulfate-bearing groundwaters. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 176, 149–156 (1990)
Bary, B.: Simplified coupled chemo-mechanical modeling of cement pastes behavior subjected to combined leaching and external sulfate attack. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 32, 1791–1816 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/nag
Basista, M., Weglewski, W.: Micromechanical modelling of sulphate corrosion in concrete: influence of ettringite forming reaction. Theoret. Appl. Mech. 35(1–3), 29–52 (2008)
Chatterji, S.: On the applicability of Fick’s second law to chloride ion migration through portland cement concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 25(2), 299–303 (1995)
Clifton, J.R., Pommersheim, J.M.: Sulfate attack of cementitious materials: volumetric relations and expansions. NISTIR 5390, National Institute of Standards and Technology p. 22 (1994)
Cohen, M.D., Mather, B.: Sulfate attack on concrete—research needs. ACI Mater. J. 88(1), 62–69 (1991)
Ferraris, C., Clifton, J., Stutzman, P., Garbocz, E.: Mechanisms of degradation of portland cement based systems by sulfate attack. In: Scrivener, K., Young, J. (eds.) Mechanisms of Chemical Degradation of Cement Based Systems, pp. 185–192. CRC Press, Boca Raton (1997)
Gouder, C.: Modeling sulfate attack on cement concrete using mixture theory. Ph.D. thesis, Indian Institute of Technology Madras (2017)
Gouder, C., Saravanan, U.: Modeling diffusion of sulfate through concrete using mixture theory. Acta Mech. 227(11), 3123–3146 (2016)
Haecker, C.J., Garboczi, E.J., Bullard, J.W., Bohn, R.B., Sun, Z., Shah, S.P., Voigt, T.: Modeling the linear elastic properties of Portland cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 35(10), 1948–1960 (2005)
Hewlett, P.: Lea’s Chemistry of Cement and Concrete. Elsever Science and Technology Books (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-7506-6256-7.50031-X
Hutter, K., Jhnk, K., Svendsen, B.: On interfacial transition conditions in two phase gravity flow. ZAMP Zeitschrift für angewandte Mathematik und Physik 45(5), 746–762 (1994)
Krajcinovic, D., Basista, M., Mallick, K., Sumarac, D.: Chemo-micromechanics of brittle solids. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 40(5), 965–990 (1992)
Marchand, J., Odler, I., Skalny, J.: Sulfate Attack on Concrete. Spon Press, London (2002)
Morland, L., Sellers, S.: Multiphase mixtures and singular surfaces. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 36(1), 131–146 (2001)
Neville, A.: The confused world of sulfate attack on concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 34(8), 1275–1296 (2004)
NIST: Virtual cement and concrete testing laboratory (2014). http://www.nist.gov/el/building_materials/evcctl.cfm
Ouyang, C.: A damage model for sulfate attack of cement mortars. Cem. Concr. Aggreg. 11(2), 92–99 (1989)
Ouyang, C., Nanni, A., Chang, W.F.: Internal and external sources of sulfate ions in Portland cement mortar: two types of chemical attack. Cem. Concr. Res. 18(5), 699–709 (1988)
Ping, X., Beaudoin, J.J.: Mechanism of sulphate expansion I. Thermodynamic principle of crystallization pressure. Cem. Concr. Res. 22(1), 631–640 (1992)
Santhanam, M.: Studies on sulfate attack: Mechanisms, test methods and modeling. Ph.D. thesis, Purdue University (2001)
Santhanam, M., Cohen, M.D., Olek, J.: Mechanism of sulfate attack: a fresh look: part 1: summary of experimental results. Cem. Concr. Res. 32(6), 915–921 (2002)
Sarkar, S., Mahadevan, S., Meeussen, J., van der Sloot, H., Kosson, D.: Numerical simulation of cementitious materials degradation under external sulfate attack. Cement Concr. Compos. 32(3), 241–252 (2010)
Shazali, M.A., Baluch, M.H., Al-Gadhib, A.H.: Predicting residual strength in unsaturated concrete exposed to sulfate attack. ASCE J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 18(June), 343–354 (2006)
Sun, C., Chen, J., Zhu, J., Zhang, M., Ye, J.: A new diffusion model of sulfate ions in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 39, 39–45 (2013)
Taylor, H.F.: Cement Chemistry. Thomas Telford Publishing, London (1997)
Tian, B., Cohen, M.D.: Expansion of alite paste caused by gypsum formation during sulfate attack. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 12(1), 24–25 (2000)
Tixier, R., Mobasher, B.: Modeling of damage in cement-based materials subjected to external sulfate attack. I: formulation. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. ASCE 15(4), 305–313 (2003)
Tixier, R., Mobasher, B.: Modeling of damage in cement-based materials subjected to external sulfate attack. II: Comparison with experiments. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. ASCE 15(4), 314–322 (2003)
Truesdell, C.: Mechanical basis of diffusion. J. Chem. Phys. 37(10), 2336 (1962)
Tumidajski, P.J., Chan, G.W., Philipose, K.E.: An effective diffusivity for sulfate transport into concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 25(6), 1159–1163 (1995)
Xi, Y., Bazant, Z.P., Molina, L., Jennings, H.M.: Moisture diffusion in cementitious materials. Adv. Cem. Based Mater. 1(6), 258–266 (1994)
Xiong, L., Yu, L.: Mechanical properties of cement mortar in sodium sulfate and sodium chloride solutions. J. Cent. South Univ. 22(3), 1096–1103 (2015)
Zhang, J., Sun, M., Hou, D., Li, Z.: External sulfate attack to reinforced concrete under drying-wetting cycles and loading condition: numerical simulation and experimental validation by ultrasonic array method. Constr. Build. Mater. 139, 365–373 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gouder, C., Saravanan, U. Modeling diffusion and reaction of sulfates with cement concrete using mixture theory. Acta Mech 229, 1353–1385 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-017-2035-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-017-2035-9