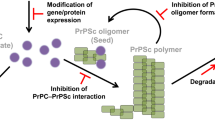
Abstract
Prions are suspected as causative agents of several neuropathogenic diseases, even though the mode of their action is still not clear. A combination of chemical and recombinant syntheses can provide suitable probes for explanation of prions role in pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. However, the prions contain several difficult sequences for synthesis by Fmoc/tBu approach. For that reason, the peptide thioesters as the key building blocks for chemical syntheses of proteins by native chemical ligation were employed. A scan of the mouse prion domain 93–231 was carried out in order to discover availability of derived thioesters as the suitable building blocks for a total chemical synthesis of the prion protein based probes. The synthesis on 2-chlorotritylchloride resin was utilized and after a deprotection of the samples for analysis, the peptide segments were purified and characterized. If the problems were detected during the synthesis, the segment was re-synthesized either using the special pseudoproline dipeptides or by splitting its molecule to two or three smaller segments, which were prepared easier. The protected segments, prepared correctly without any deletion and in sufficient amounts, were coupled either with EtSH after DIC/DMAP activation or with p-Ac-NH-Ph-SH using PyBOP activation to yield corresponding thioesters. In some special cases, the other techniques of thioester formation, like sulfonamide-safety catch and/or trimethylaluminium approach were utilized.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AA:
-
Amino acid analysis
- ACN:
-
Acetonitrile
- Asi:
-
Aspartic acid imide
- Boc:
-
tert-Butoxycarbonyl
- ClTrt:
-
2-Chlorotrityl
- DIC:
-
N,N′-Diisopropylcarbodiimide
- DCM:
-
Dichloromethane
- DIEA:
-
N,N-Diisopropylethylamine
- DMAP:
-
4-(Dimethylamino)pyridine
- Dmb:
-
Dimethylbenzyl
- DMF:
-
N,N-Dimethylformamide
- EDT:
-
1,2-Ethanedithiol
- ESI MS:
-
Electro-spray ionization mass spectrometry
- Et:
-
Ethyl
- Fmoc:
-
[(Fluoren-1-yl-methoxy]carbonyl
- HBTU:
-
O-(Benzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N’,N’-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate
- HFIP:
-
Hexafluoroisopropanol
- HOBt:
-
1-Hydroxybenzotriazole
- HPLC:
-
High performance liquid chromatography
- MALDI TOF:
-
Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time of flight
- Mpa:
-
Mercaptopropionic acid
- NMP:
-
N-Methylpyrrolidone
- PyBOP:
-
(Benzotriazol-1-yloxy)-tris(pyrrolidino)phosphonium hexafluorophosphate
- Sec:
-
Selenocysteine
- SPPS:
-
Solid-phase peptide synthesis
- tBu:
-
tert-Butyl
- TFA:
-
Trifluoroacetic acid
- THF:
-
Tetrahydrofuran
- Thz:
-
Thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid
- TIS:
-
Tri-isopropylsilane
- TMS:
-
Trimethylsilyl
References
Backes BJ, Ellman JA (1999) An alkanesulfonamide safety-catch linker for solid-phase synthesis. J Org Chem 64:2322–2330
Ball HL, King DS, Cohen FE, Prusiner SB, Baldwin MA (2001) Engineering the prion protein using chemical synthesis. J Peptide Res 58:357–374
Bang D, Kent SBH (2004) A one-pot total synthesis of crambin. Angew Chem Int Ed 43:2534–2538
Bons N, Mestre-Frances N, Belli P, Cathala F, Gajdusek DC, Brown P (1999) Natural and experimental oral infection of nonhuman primates by bovine spongiform encephalopathy agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:4046–4051
Brask J, Albericio F, Jensen KJ (2003) Fmoc solid-phase synthesis of peptide thioesters by masking as trithioortho esters. Org Lett 5:2951–2953
Bueler H, Fisher M, Lang Y, Bluethmann H, Lipp HP, DeArmond SJ, Prusiner SB, Aguet M, Weissmann C (1992) Normal development and behaviour of mice lacking the neuronal cell-surface PrP protein. Nature 356:577–582
Cardona V, Eberle I, Barthelemy S, Beythien J, Doerner B, Schneeberger P, Keyte J, White P (2008) Application of Dmb-dipeptides in the Fmoc SPPS of difficult and aspartimide-prone sequences. Int J Pept Res Therapeutics 14:285–292
Castilla J, Saá P, Hetz C, Soto C (2005) In vitro generation of infectious scrapie prions. Cell 121:195–206
Caughey B (2000) Transmissible spongiform encephalopathies, amyloidoses and yeast prions: Common threads? Nat Med 6:751–754
Cohen FE, Prusiner SB (1998) In vitro generation of infectious scrapie prions. Annu Rev Biochem 67:793–819
Come JH, Fraser PE, Lansbury PT (1993) A kinetic model for amyloid formation in the prion diseases: importance of seeding. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:5959–5963
Dawson PE, Kent SBH (2000) Synthesis of native proteins by chemical ligation. Ann Rev Biochem 69:923–960
Dawson PE, Muir TW, Clark-Lewis I, Kent SBH (1994) Synthesis of proteins by native chemical ligation. Science 266:776–779
Fields GB, Noble RL (1990) Solid phase peptide synthesis utilizing 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl amino acids. Int J Pept Protein Res 35:161–214
Forloni G, Angeretti N, Chiesa R, Monzani E, Salmona M, Bugiani O, Tagliavini F (1993) Neurotoxicity of a prion protein fragment. Nature 362:543–546
GPCRDB: Swiss-Prot entry (2011) http://www.receptors.org/Prion/seq/all/PRIO_HUMAN.SW.html
Hagenmaier H (1970) The influence of the chain length on the coupling reaction in solid phase peptide synthesis. Tetrahedron Lett 11:283–286
Huang Z, Prusiner SB, Cohen FE (1996) Scrapie prions: a three-dimensional model of an infectious fragment. Fold Des 1:13–19
Jackson GS, Hosszu LLP, Power A, Hill AF, Kenney J, Saibil H, Craven CJ, Waltho JP, Clarke AR, Collinge J (1999) Reversible conversion of monomeric human prion protein between native and fibrilogenic conformations. Science 283:1935–1937
Jarrett JT, Lansbury PT (1993) Seeding “one-dimensional crystallization” of amyloid: a pathogenic mechanism in Alzheimer's disease and scrapie? Cell 73:1055–1058
Jobling M, Barrow C, White A, Masters C, Collins S, Cappai R (1999) The synthesis and spectroscopic analysis of the neurotoxic prion peptide 106–126: Comparative use of manual Boc and Fmoc chemistry. Lett Pept Sci 6:129–134
Kaiser E, Colescott RL, Bossinger CD, Cook PI (1970) Color test for detection of free terminal amino groups in the solid-phase synthesis of peptides. Anal Biochem 34:595–598
Kaneko K, Ball HL, Wille H, Zhang H, Groth D, Torchia M, Tremblay P, Safar J, Prusiner SB, DeArmond SJ, Baldwin MA, Cohen FE (2000) A synthetic peptide initiates Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker (GSS) disease in transgenic mice. J Mol Biol 295:997–1007
Krchňák V, Vágner J, Šafář P, Lebl M (1988a) Non-invasive continuous monitoring of solid phase peptide synthesis by acid-base indicator. Coll Czech Chem Comm 53:2542–2548
Krchňák V, Vágner J, Lebl M (1988b) Noninvasive continuous monitoring of solid-phase peptide synthesis by acid-base indicator. Int J Pept Protein Res 32:415–416
Legname G, Baskakov IV, Nguyen HO, Riesner D, Cohen FE, DeArmond SJ, Prusiner SB (2004) Synthetic mammalian prions. Science 305:673–676
Milton RC, Milton SCF, Kent SBH (1992) Total chemical synthesis of a D-enzyme: the enantiomers of HIV-1 protease show demonstration of reciprocal chiral substrate specificity. Science 256:1445–1448
Pan K-M, Baldwin M, Nguyen J, Gasset M, Serban A, Groth D, Huang Z, Fletterick RJ, Cohen FE, Prusiner SB (1993) Conversion of alpha-helices into beta-sheets features in the formation of the scrapie prion proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:10962–10966
Prusiner SB (1998) Prions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:13363–13383
Sarin VK, Kent SBH, Tam JP, Merrifield RB (1981) Quantitative monitoring of solid phase peptide synthesis by the ninhydrin reaction. Anal Biochem 117:147–157
Šebestik J, Matějka P, Hlaváček J, Stibor I (2004) Solid-phase synthesis of head and tail bis-acridinylated peptides. Tetrahedron Lett 45:1203–1205
Šebestik J, Hlaváček J, Stibor I (2006) Rational design and synthesis of a double-stranded DNA-binder library. Biopolymers 84:400–407
Sewing A, Hilvert D (2001) Fmoc compatible solid-phase peptide synthesis of long C-terminal thioesters. Angew Chem Int Ed. 40:3395–3396
Spielhaupter C, Schaetzl HM (2001) PrPC directly interacts with proteins involved in signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 276:44604–44612
Supattapone S, Bosque P, Muramoto T, Wille H, Aagaard C, Peretz D, Nguyen H-OB, Heinrich C, Torchia M, Safar J, Cohen FE, DeArmond SJ, Prusiner SB, Scott M (1999) Prion protein of 106 residues creates an artificial transmission barrier for prion replication in transgenic mice. Cell 96:869–878
Vojkovský T (1995) Detection of secondary amines on solid phase. Pept Res 8:236–237
Von Eggelkraut-Gottanka R, Klose A, Beck-Sickinger AG, Beyermann M (2003) Peptide thioester formation using standard Fmoc-chemistry. Tetrahedron Lett 44:3551–3554
Wan Q, Danishefsky SJ (2007) Free-radical-based, specific desulfurization of cysteine: a powerful advance in the synthesis of polypeptides and glycopolypeptides. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:9248–9252
Weissman C (1999) Molecular genetics of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. J Biol Chem 274:3–6
White P, Keyte JW, Bailey K, Bloomberg G (2004) Expediting the Fmoc solid phase synthesis of long peptides through the application of dimethyloxazolidine dipeptides. J Pept Sci 10:18–26
Will RG, Ironside JW, Zeidler M, Cousens SN, Estibeiro K, Alperovitch A, Poser S, Pocchiari M, Hofman A, Smith PG (1996) A new variant of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in the UK. Lancet 347:921–925
Wollscheid B, Bausch-Fluck D, Henderson C, O’Brien R, Bibel M, Schiess R, Aebersold R, Watts JD (2009) Mass-spectrometric identification and relative quantification of N-linked cell surface glycoproteins. Nat Biotechnol 27:378–386
Zahariev S, Guarnaccia C, Zanuttin F, Pintar A, Esposito G, Maravic G, Krust B, Hovanessian AG, Pongor S (2005) Efficient synthesis and comparative studies of the arginine and Nω, Nω-dimethylarginine forms of the human nucleolin glycine/arginine rich domain. J Pept Sci 11:17–28
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant of Czech Science Foundation (GA CR) No. 203/07/1517 and Research Project Z40550506. We greatly thanks to Miroslava Blechová and Alexandrina Prychodska for assembly of peptide sequences on automated peptide synthesizer; and to Lenka Monincová for some ESI-MS measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The nomenclature and symbols of the amino acids follow the Recommendations of the IUPAC/IUB Joint Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature. Eur J Biochem (1984) 138:9–37.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Šebestík, J., Zawada, Z., Šafařík, M. et al. Comparative syntheses of peptides and peptide thioesters derived from mouse and human prion proteins. Amino Acids 43, 1297–1309 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-1203-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-1203-9