Abstract
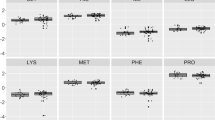
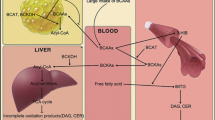
Amino acids are one of the main metabolites in the body, and provide energy for the body and brain. The purpose of this study is to provide a profile of amino acid changes in the serum of patients with Moyamoya disease (MMD) and identify potential disease biomarkers. In this paper, we quantitatively determined the serum amino acid metabolic profiles of 43 MMD patients and 42 healthy controls (HCs). T test, multivariate statistical analysis, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis were used to identify candidate markers. Thirty-nine amino acids were quantified, and 12 amino acid levels differed significantly between the MMD patients and HCs. Moreover, based on ROC curve analysis, four amino acid (l-methionine, l-glutamic acid, β-alanine and o-phosphoserine) biomarkers showed high sensitivity and specificity (AUC > 0.90), and showed the best sensitivity and specificity in MetaboAnalyst 5.0 using binary logistic regression analysis. We have provided serum amino acid metabolic profiles of MMD patients, and identified four potential biomarkers which may both provide clinicians with an objective diagnostic method for early detection of MMD and further our understanding of MMD pathogenesis.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Amantea D, Bagetta G (2017) Excitatory and inhibitory amino acid neurotransmitters in stroke: from neurotoxicity to ischemic tolerance. Curr Opin Pharmacol 35:111–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coph.2017.07.014
Araki Y, Yoshikawa K, Okamoto S, Sumitomo M, Maruwaka M, Wakabayashi T (2010) Identification of novel biomarker candidates by proteomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid from patients with moyamoya disease using SELDI-TOF-MS. BMC Neurol 10:112. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2377-10-112
Aune D, Ursin G, Veierod MB (2009) Meat consumption and the risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Diabetologia 52(11):2277–2287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-009-1481-x
Cai HL, Li HD, Yan XZ, Sun B, Zhang Q, Yan M et al (2012) Metabolomic analysis of biochemical changes in the plasma and urine of first-episode neuroleptic-naive schizophrenia patients after treatment with risperidone. J Proteome Res 11(8):4338–4350. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr300459d
Castilho JC, Perry JC, Andreatini R, Vital MA (2004) Phosphatidylserine: an antidepressive or a cognitive enhancer? Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 28(4):731–738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2004.05.013
Chen X, Liu L, Palacios G, Gao J, Zhang N, Li G et al (2010) Plasma metabolomics reveals biomarkers of the atherosclerosis. J Sci 33(17–18):2776–2783. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201000395
Claro FT, Patti CL, Abílio VC, Frussa-Filho R, Silva RH (2006) Bovine brain phosphatidylserine attenuates scopolamine induced amnesia in mice. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 30(5):881–886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2006.01.013
Duan X, Ni P, Zhao L, Ni R, Wei J, Ma X et al (2020) Correlation between altered levels of neurotransmitters in the frontal lobe and hippocampus and behavioral abnormalities in a Clock mutant mice modeling bipolar manic disorder. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi 37(9):991–996. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.cn511374-20191014-00526
Engel RR, Satzger W, Günther W, Kathmann N, Bove D, Gerke S et al (1992) Double-blind cross-over study of phosphatidylserine vs. placebo in patients with early dementia of the Alzheimer type. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2(2):149–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/0924-977x(92)90025-4
Fujimura M, Sonobe S, Nishijima Y, Niizuma K, Sakata H, Kure S et al (2014) Genetics and biomarkers of moyamoya disease: significance of RNF213 as a susceptibility gene. J Stroke 16(2):65–72. https://doi.org/10.5853/jos.2014.16.2.65
Garlick PJ (2006) Toxicity of methionine in humans. J Nutr 136:1722S-1725S. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/136.6.1722S
Geng C, Cui C, Guo Y, Wang C, Zhang J, Han W et al (2020) Metabolomic profiling revealed potential biomarkers in patients with moyamoya disease. Front Neurosci 14:308. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.00308
Hameed A, Mojsak P, Buczynska A, Suleria HAR, Kretowski A, Ciborowski M (2020) Altered metabolome of lipids and amino acids species: a source of early signature biomarkers of T2DM. J Clin Med 9(7):2257. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9072257
Jeon JP, Yun T, Jin X, Cho WS, Son YJ, Bang JS et al (2015) 1H-NMR-based metabolomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid from adult bilateral moyamoya disease: comparison with unilateral moyamoya disease and atherosclerotic stenosis. Medicine 94(17):e629. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000000629
Kim YK, Kim OY, Song J (2020) Alleviation of depression by glucagon-like peptide 1 through the regulation of neuroinflammation, neurotransmitters, neurogenesis, and synaptic function. Front Pharmacol 11:1270. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.01270
Kuroda S, Houkin K (2008) Moyamoya disease: current concepts and future perspectives. Lancet Neurol 7(11):1056–1066. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(08)70240-0
Lee JH, Youn TJ, Yoon YE, Park JJ, Hong SJ, Chun EJ et al (2013) Coronary artery stenosis in moyamoya disease: tissue characterization by 256-slice multi-detector CT and virtual histology. Circulation 127(20):2063–2065. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.136473
Li R, He H, Fang S, Hua Y, Yang X, Yuan Y et al (2019) Time series characteristics of serum branched-chain amino acids for early diagnosis of chronic heart failure. J Proteome Res 18(5):2121–2128. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.9b00002
Nuru M, Muradashvili N, Kalani A, Lominadze D, Tyagi N (2018) High methionine, low folate and low vitamin B6/B12 (HM-LF-LV) diet causes neurodegeneration and subsequent short-term memory loss. Metab Brain Dis 33(6):1923–1934. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0298-z
Pandey R, Caflisch L, Lodi A, Brenner AJ, Tiziani S (2017) Metabolomic signature of brain cancer. Mol Carcinog 56(11):2355–2371. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.22694
Roque W, Romero F (2021) Cellular metabolomics of pulmonary fibrosis, from amino acids to lipids. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 320(5):c689–c695. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00586.2020
Sale C, Saunders B, Harris RC (2010) Effect of beta-alanine supplementation on muscle carnosine concentrations and exercise performance. Amino Acids 39(2):321–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-009-0443-4
Tiedje KE, Stevens K, Barnes S, Weaver DF (2010) Beta-alanine as a small molecule neurotransmitter. Neurochem Int 57(3):177–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2010.06.001
Turer AT, Stevens RD, Bain JR, Muehlbauer MJ, van der Westhuizen J, Mathew JP et al (2009) Metabolomic profiling reveals distinct patterns of myocardial substrate use in humans with coronary artery disease or left ventricular dysfunction during surgical ischemia/reperfusion. Circulation 119(13):1736–1746. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.816116
Varanoske AN, Wells AJ, Boffey D, Harat I, Frosti CL, Kozlowski GJ et al (2021) Effects of high-dose, short-duration β-alanine supplementation on cognitive function, mood, and circulating brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF) in recreationally-active males before simulated military operational stress. J Diet Suppl 18(2):147–168. https://doi.org/10.1080/19390211.2020.1733730
Wu G (2009) Amino acids: metabolism, functions, and nutrition. Amino Acids 37(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-009-0269-0
Yoo SH, Chang YH (2016) Volatile compound, physicochemical, and antioxidant properties of beany flavor-removed soy protein isolate hydrolyzates obtained from combined high temperature pre-treatment and enzymatic hydrolysis. Prev Nutr Food Sci 21(4):338–347. https://doi.org/10.3746/pnf.2016.21.4.338
Zhou Y, Zhang X, Chen R, Han S, Liu Y, Liu X et al (2020) Serum amino acid metabolic profiles of ankylosing spondylitis by targeted metabolomics analysis. Clin Rheumatol 39(8):2325–2336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-04974-z
Acknowledgements
We appreciate all the participants and the staffs of the Department of Clinical Translational Medicine, Jining Life Science Center for their invaluable support and assistance.
Funding
Our work was supported by Ph.D. Research Foundation of the Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University (no. 2021-BS-014), the Taishan Scholar Project of Shandong Province (no. tsqn201812159), the Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81602846; no. 81901954), and the Key Research and Development Program of Jining Science and Technology (no. 2019SMNS012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PJ and CC conceptualized the research and designed the study. CW, SZ, and SH collected and collated the data. XL, FJ, and PJ analyzed and interpreted the data. XL, FJ, and SZ performed statistical analyses. XL drafted the manuscript. PJ and CC critically revised the manuscript, and all authors read and approved the final manuscript. PJ is the guarantor of this work and as such had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
Our work was based on the Declaration of Helsinki and was agreed upon by all participants, with written informed consent. In addition, this study was approved by the Ethics Committee of The Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University (Jining, China) (Approval No. 2017C036).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from the all patients.
Additional information
Handling editor: S. Broer.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Jin, F., Wang, C. et al. Targeted metabolomics analysis of serum amino acid profiles in patients with Moyamoya disease. Amino Acids 54, 137–146 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-021-03100-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-021-03100-w