Abstract
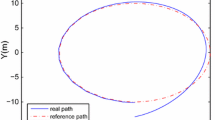
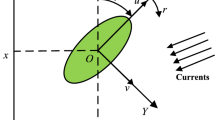
In this paper, a robust adaptive control scheme is proposed for the trajectory tracking control of underactuated surface vessels (USVs) subject to unknown dynamics, external disturbances and input saturation. First, a coordinate transformation is introduced to deal with the underactuation problem of the USV. A Gaussian error function and an adaptive neural network (NN) are adopted to approximate the saturation function and the unknown dynamics, respectively. Then, an adaptive robust integral of the sign of the error (RISE) feedback term is introduced in feedback control design to compensate the NN and saturation approximation residual errors and unknown external disturbances. On the basis of the above, a robust adaptive trajectory tracking control law is proposed incorporating a coordinate transformation, Gaussian error function and NN into RISE method. In addition, the adjustable-online adaptive feedback gain reduces the conservativeness of the control design. The theoretical analysis indicates that the designed robust adaptive control law can force USVs to track the desired trajectory while guaranteeing the asymptotic tracking performance. Simulation results verify the effectiveness of the novel robust adaptive trajectory tracking control scheme.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pettersen KY, Nijmeijer H (1999) Global practical stabilization and tracking for an underactuated ship—a combined averaging and backstepping approach. Model Identif Control 20(4):189–200
Ashrafiuon H, Muske KR, Mcninch LC (2010) Review of nonlinear tracking and setpoint control approaches for autonomous underactuated marine vehicles. In: Proceedings of the 2010 American control conference, Baltimore, MD, USA, Jul, pp 5203–5211
Skjetne R, Smogeli Ø, Fossen TI (2004) Modeling, identification and adaptive maneuvering of Cybership II: A complete design with experiments. In: Proceedings of IFAC conference control applications in marine systems, Ancona, Italy, Jul, pp 203–208
Du J, Yang Y, Wang D, Guo C (2013) A robust adaptive neural networks controller for maritime dynamic positioning system. Neurocomputing 110(1):128–136
Shojaei K (2015) Neural adaptive robust control of underactuated marine surface vehicles with input saturation. Appl Ocean Res 53:267–278
Ashrafiuon H, Nersesov S, Clayton G (2017) Trajectory tracking control of planar underactuated vehicles. IEEE Trans Autom Control 62(4):1959–1965
Fischer N, Hughes D, Walters P, Schwartz EM, Dixon WE (2014) Nonlinear RISE-based control of an autonomous underwater vehicle. IEEE Trans Robot 30(4):845–852
He S, Dai SL, Luo F (2019) Asymptotic trajectory tracking control with guaranteed transient behavior for MSV with uncertain dynamics and external disturbances. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 66(5):3712–3720
Ghommam J, Mnif F, Benali A, Derbel N (2006) Asymptotic backstepping stabilization of an underactuated surface vessel. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 14(6):1150–1157
Yu R, Zhu Q, Xia G, Liu Z (2012) Sliding mode tracking control of an underactuated surface vessel. IET Control Theory Appl 6(3):461–466
Ashrafiuon H, Muske KR, McNinch LC, Soltan RA (2008) Sliding-mode tracking control of surface vessels. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 55(11):4004–4012
Qin J, Du J (2019) Adaptive fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode control for underactuated surface vessel trajectory tracking. In: International proceedings of the 19th conference on control, automation and systems, Jeju, Korea, Oct, pp 1365–1370
Shojaei K, Arefi MM (2014) On the neuro-adaptive feedback linearising control of underactuated autonomous underwater vehicles in three-dimensional space. IET Control Theory Appl 9(8):1264–1273
Fossen TI, Breivik M, Skjetne R (2003) Line-of-sight path following of underactuated marine craft. In: Proceedings of 6th IFAC conference on manoeuvring and control of marine craft, Girona, Spain, Sep, pp 211–216
Li J, Du J, Chang WJ (2019) Robust time-varying formation control for underactuated autonomous underwater vehicles with disturbances under input saturation. Ocean Eng 179:180–188
Park BS, Kwon JW, Kim H (2017) Automatica-neural network-based output feedback control for reference tracking of underactuated surface vessels. Automatica 77:353–359
Xie W, Ma B (2015) Robust global uniform asymptotic stabilization of underactuated surface vessels with unknown model parameters. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control 25:1037–1050
Zhang L, Huang B, Liao Y, Wang B (2019) Finite-time trajectory tracking control for uncertain underactuated marine surface vessels. IEEE Access 7:102321–102330
Peng Z, Wang J, Han QL (2019) Path-following control of autonomous underwater vehicles subject to velocity and input constraints via neurodynamic optimization. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 66(11):8724–8732
Zhu G, Du J (2020) Global robust adaptive trajectory tracking control for surface ships under input saturation. IEEE J Ocean Eng 45(2):442–450
Jia Z, Hu Z, Zhang W (2019) Adaptive output-feedback control with prescribed performance for trajectory tracking of underactuated surface vessels. ISA Trans 95:18–26
Gao T, Huang J, Zhou Y, Song YD (2017) Robust adaptive tracking control of an underactuated ship with guaranteed transient performance. Int J Syst Sci 48(2):272–279
Do KD, Jiang ZP, Pan J (2004) Robust adaptive path following of underactuated ships. Automatica 40:929–944
Zheng Z, Huang Y, Xie L, Zhu B (2018) Adaptive trajectory tracking control of a fully actuated surface vessel with asymmetrically constrained input and output. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 26(5):1851–1859
Do KD (2010) Practical control of underactuated ships. Ocean Eng 37(13):1111–1119
Du J, Hu X, Krstić M, Sun Y (2016) Robust dynamic positioning of ships with disturbances under input saturation. Automatica 73:207–214
Chen M, Ge SS, How BVE, Choo YS (2013) Robust adaptive position mooring control for marine vessels. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 21(2):395–409
Dai S, He S, Wang M, Yuan C (2019) Adaptive neural control of underactuated surface vessels with prescribed performance guarantees. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 30(12):3686–3698
Chen L, Cui R, Yang C, Yan W (2020) Adaptive neural network control of underactuated surface vessels with guaranteed transient performance: theory and experimental results. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 67(5):4024–4035
Liang K, Lin X, Chen Y, Li J, Ding F (2020) Adaptive sliding mode output feedback control for dynamic positioning ships with input saturation. Ocean Eng 206:107245
Wang Y, Jiang X, She W, Ding F (2019) Tracking control with input saturation and full-state constraints for surface vessels. IEEE Access 7:144741–144755
Zhu G, Du J, Kao Y (2020) Robust adaptive neural trajectory tracking control of surface vessels under input and output constraints. J Franklin Inst 357(13):8591–8610
Hu Y, Park GK, Wu H, Zhang Q (2017) Robust adaptive fuzzy design for ship linear-tracking control with input saturation. Int J eNavig Marit Econ 6:9–16
Zhang G, Zhang C, Yang T, Zhang W (2020) Disturbance observer-based composite neural learning path following control of underactuated ships subject to input saturation. Ocean Eng 216:108033
Shen Z, Bi Y, Wang Y, Guo C (2020) MLP neural network-based recursive sliding mode dynamic surface control for trajectory tracking of fully actuated surface vessel subject to unknown dynamics and input saturation. Neurocomputing 377:103–112
Qin H, Li C, Sun Y (2020) Adaptive neural network-based fault-tolerant trajectory-tracking control of unmanned surface vessels with input saturation and error constraints. IET Intell Transp Syst 14(5):356–363
Yao Q (2020) Adaptive finite-time sliding mode control design for finite-time fault-tolerant trajectory tracking of marine vehicles with input saturation. J Franklin Inst 357(18):13593–13619
Elhaki O, Shojaei K (2020) A robust neural network approximation-based prescribed performance output-feedback controller for autonomous underwater vehicles with actuators saturation. Eng Appl Artif Intel 88:103382
Shojaei K (2017) Output-feedback formation control of wheeled mobile robots with actuators saturation compensation. Nonlinear Dyn 89:2867–2878
Hu X, Wei X, Han J, Zhang Q (2020) Adaptive disturbance rejection for course tracking of marine vessels under actuator constraint. ISA Trans 100:82–91
Qin H, Li C, Sun Y, Wang N (2020) Adaptive trajectory tracking algorithm of unmanned surface vessel based on anti-windup compensator with full-state constraints. Ocean Eng 200:106906
Donaire A, Perez T (2012) Dynamic positioning of marine craft using a port-Hamiltonian framework. Automatica 48:851–856
Zhang J, Xiang X, Zhang Q, Li W (2020) Neural network-based adaptive trajectory tracking control of underactuated AUVs with unknown asymmetrical actuator saturation and unknown dynamics. Ocean Eng 218:108193
Xian B, Dawson DM, Queiroz MS, Chen J (2004) A continuous asymptotic tracking control strategy for uncertain nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans Autom Control 49(7):1206–1211
Reyhanoglu M (1997) Exponential stabilization of an underactuated autonomous surface vessel. Automatica 33(12):2249–2254
Ma J, Zheng Z, Li P (2015) Adaptive dynamic surface control of a class of nonlinear systems with unknown direction control gains and input saturation. IEEE Trans Cybern 45(4):728–741
Cho GR, Li JH, Park D, Jung JH (2020) Robust trajectory tracking of autonomous underwater vehicles using back-stepping control and time delay estimation. Ocean Eng 201:107131
Queiroz MS, Hu J, Dawson DM, Burg T, Donepudi SR (1997) Adaptive position/force control of robot manipulators without velocity measurements: theory and experimentation. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B Cybern 27(5):796–809
Horn R, Johnson CR (2012) Matrix analysis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Khalil HK, Grizzle JW (2002) Nonlinear systems, Theor 8.4, 3rd edn. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Editor-in-Chief, the Associate Editor, and anonymous reviewers for their invaluable suggestions and comments. This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of P. R. China (Grant number 51079013); the Dalian Science and Technology Innovation Fund Program (grant number 2020JJ26GX020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, J., Du, J. Robust adaptive asymptotic trajectory tracking control for underactuated surface vessels subject to unknown dynamics and input saturation. J Mar Sci Technol 27, 307–319 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00773-021-00835-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00773-021-00835-9