Abstract
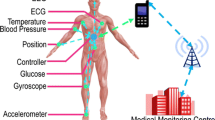
As the elderly population has rapidly increased in recent years, people aged 60 and older now constitute 20–30 % of the population in developed countries. Due to reduced overall mental and physical functionality, people have developed various chronic degenerative diseases related to the circulatory and musculoskeletal systems. An aging society leads to longer life spans as well as the need to develop special residential facilities for disease treatment and support of the elderly population. In this ubiquitous age, people can obtain information regardless of place or time and therefore receive telemedicine health services anywhere and anytime. This situation requires embedded system technology for portable telemedicine devices, computer network technology for remote examination, information security technology to manage individual medical data, database technology to process and store a large quantity of medical information, expert system technology to help doctors make sound judgments, software design and test technology to create easy-to-use software, image processing technology to make accurate diagnoses based on image information, multi-searching technology to analyze complex data from various medical institutions, staff, and service providers, and context-aware technology based on wireless sensors that can be used to understand the status of users requesting a specific telemedicine health service. Therefore, in this paper, we proposed the telemedicine health service using an LTE-A-based relay antenna. The antenna proposed in this paper is a planar monopole antenna in which a feed line and a radiation patch are connected in front of a substrate and a plane ground exists opposite to a dielectric in telemedicine. Since a planar monopole antenna requires a length of lambda/4 to generate resonance, it has a demerit in size. The proposed antenna was assigned a current value close to 0 at the central part of the square loop emitter in order to supplement this demerit, and the physical length of the antenna was minimized by folding it inside the square loop center to a frequency of 900 MHz, which is the frequency of domestic SK’s LTE band. In addition, coupling combination was applied at the center of the tip of the T-shape patch and the square loop line folded inside to generate a resonance of 2.4 GHz, which is the high-frequency band of the domestic LTE band. To maximize relay efficiency, relay power allocation and relay routing method were carried out. Selective transmission method was applied to improve reception of the LTE system.









Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Catholic Institute of u-Healthcare in Korea, http://www.cmcuhealth.or.kr. AIMMED, http://www.aimmed.co.kr.
References
Lim JE, Choi OH, Na HS, Baik DK (2009) A context-aware fitness guide system for exercise optimization in U-health. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 13(3):370–379
Kim J, Choi HS, Wang H, Agoulmine N (2010) POSTECH’s U-Health smart home for elderly monitoring and support. In: Proceeding of IEEE international symposium world of wireless mobile and multimedia networks, vol 1, pp 1–6
Kim JK, Lee D, Chung KY (2012) Ontology driven interactive healthcare with wearable sensors. Multimed Tools Appl. doi:10.1007/s11042-012-1195-9
Drosatos G, Efraimidis PS (2011) Privacy-preserving statistical analysis on ubiquitous health data. In: Proceeding of 8th international conference on trust, privacy and security in digital business, vol 1, pp 24–36
Martinez I, Escayola J, Espronceda MM, Serrano L (2008) Standard-based middleware platform for medical sensor networks and u-health. In: Proceedings of the 17th international conference on computer communications and networks, vol 1, pp 1–6
Drosatos G, Efraimaidis PS (2011) Privacy-enhanced management of ubiquitous health monitoring data. In: Proceedings of the 4th international conference on pervasive technologies related to assistive environments. doi:10.1145/2141622.2141667
Shin W, Cha YD, Yoon GW (2010) ECG/PPG integer signal processing for a ubiquitous health monitoring system. J Med Syst 34(5):891–898
Blobel B, Holena M (1995) Comparing middleware concepts for advanced healthcare system architectures. Int J Med Inform 46(2):69–85
Han DS, Lee MK, Park SJ (2010) THE-MUSS: mobile u-health service system. Biomedicine 97(2):178–188
Michael R (2007) Applying emergent ubiquitous technologies in health: the need to respond to new challenges of opportunity, expectation, and responsibility. Int J Med Inform 76(Suppl 3):349–352
Elgazzar K, Aboelfotoh M, Martin P, Hassanein HS (2012) Ubiquitous health monitoring using mobile web services. Procedia Comput Sci 10:332–339
Lo CC, Chen CH, Cheng DY, Kung HY (2011) Ubiquitous healthcare service system with context-awareness capability: design and implementation. Expert Syst Appl 38(4):4416–4436
Dong H, Hussain FK, Chang E (2011) A framework for discovering and classifying ubiquitous services in digital health ecosystems. J Comput Syst Sci 77(4):687–704
Lin CC, Lee RG, Hsiao CC (2008) A pervasive health monitoring service system based on ubiquitous network technology. Int J Med Inform 77(7):461–469
Sohn MS, Hahn DW, Lee JW (2006) The strategy development of u-health service. In: Proceedings of PICMET technology management for the global future, vol 5, pp 1931–1934
Yamazaki A, Koyama A, Arai J, Barolli L (2009) Design and implementation of a ubiquitous health monitoring system. Int J Web Grid Serv 5(4):339–355
Kim GH, Kim YG, Chung KY (2013) Towards virtualized and automated software performance test architecture. Multimed Tools Appl. doi:10.1007/s11042-013-1536-3
Ha KY, Lee JW (2008) U-health and Regulatory Implications in Korea. In: Portland international conference on management of engineering and technology, PICMET, vol 1, pp 351–355
Durresi A, Durresi M, Merkoci A, Barolli L (2008) Networked biomedical system for ubiquitous health monitoring. Mob Inf Syst 4(3):211–218
Sohn MS, Lee JW (2007) u-health in Korea: opportunities and challenges. In: Proceedings of Portland international center for management of engineering and technology, vol 1, pp 2791–2794
Lee YD, Chung WY (2009) Wireless sensor network based wearable smart shirt for ubiquitous health and activity monitoring. Sens Actuators B Chem 140(2):390–395
Jeong KS, Jung EY, Park DK (2009) Trend of wireless u-Health. In: Proceedings of the 9th international conference on communications and information technologies, vol 1, pp 829–833
Maass W, Varshney U (2012) Design and evaluation of Ubiquitous Information Systems and use in healthcare. Decis Support Syst 54(1):597–609
Touati F, Tabish R, Mnaouer AB (2013) Towards u-health: an indoor 6LoWPAN based platform for real-time healthcare monitoring. In: Proceedings of the 6th joint IFIP wireless and mobile networking conference, vol 1, pp 1–4
Song CW, Chung KY, Jung JJ, Rim K, Lee JH (2011) Localized approximation method using inertial compensation in WSNs. Inf Int Interdiscip J 14(11):3591–3600
Choi OH, Lim JE, Na HS, Baik DK (2006) Modeling for missing tissue compensator fabrication using RFID tag in u-health. In: Proceedings of the 7th international conference on biological and medical data analysis, vol 1, pp 463–471
Subramaniam C, Nayak A, Thunuguntla S (2010) Actor based domain specific privacy model for u-Healthcare system. In: Proceedings of 6th international conference digital content multimedia technology and its applications, vol 1, pp 381–385
Jung YG, Han MS, Chung KY, Lee SJ (2011) A study of a valid frequency range using correlation analysis of throat signal. Inf Int Interdiscip J 14(11):3791–3799
Kim J, Kang M, Hwang B (2011) A method for detecting arrhythmia using a RR interval from ECG data in U-Health system. In: Proceedings of the 5th international conference on ubiquitous information management and communication. doi:10.1145/1968613.1968632
Ho L, Moh M, Walker Z, Hamada T, Su C (2005) A prototype on RFID and sensor networks for elder healthcare: progress report. In: Proceedings of the 2005 ACM SIGCOMM workshop on experimental approaches to wireless network design and analysis. doi:10.1145/1080148.1080164
Durresi A, Merkoci A, Durresi M, Barolli L (2007) integrated biomedical system for ubiquitous health monitoring. In Proceedings the 1st international conference on network-based information systems, vol 1, pp 397–405
Wang CS, Tzeng YR (2008) A Wireless Networking Technologies Overview Over Ubiquitous Service Applications. In: Proceedings of the 4th international conference on networked computing and advanced information management, vol 1, pp 156–161
Shin DK, Jung H, Lee KD, Lee JH, Park R (2013) Performance improvement of intelligent u-Port system using metallic object applications. Multimed Tools Appl. doi:10.1007/s11042-013-1599-1
Arnrich B, Osmani V, Riva G, Bardram J (2010) UbiHealth 2010: the 5th international workshop on ubiquitous health and wellness. In: Proceedings of the 12th ACM international conference adjunct papers on ubiquitous computing, vol 1, pp 497–500
Jung SC, Chang S (2007) Ad-Hoc communications based on mobile nodes for health care in u-city. In: Proceedings of international conference on convergence information technology, vol 1, pp 487–490
Muhammad S, Raazi KR, Lee SY, Lee YK (2009) TIMAR: an efficient key management scheme for ubiquitous health care environments. In: Proceedings of the 5th international icst mobile multimedia communications conference. doi:10.4108/ICST.MOBIMEDIA2009.7598
Yu WD, Patel J, Mehta V, Joshi A (2012) An approach to design a SOA services governance architecture for an u-healthcare system with mobility. Int J E-Health Med Commun 3(2):36–65
Kim YH, Lim IK, Lee JK (2011) Mobile based HIGHT encryption for secure biometric information transfer of USN remote patient monitoring system. In: Proceedings of the 2011 international conference on computational science and its applications, vol 5, pp 83–95
Kim SJ, Dave B (2010) Silver towns and smart technologies. In: Proceedings of the 22nd conference of the computer-human interaction special interest group of Australia on computer-human interaction, vol 1, issue 1, pp 168–1781
Yu YS, Choi SH, Park HK, Lee C, Jeong YS, Kim SH (2010) A power-, delay- and emergency-efficient Protocol of ubiquitous sensor network systems for silver town applications. J Supercomput 54(1):122–137
Kim SJ, Dave B (2011) Smart silver towns: prospects and challenges. In: Proceedings of the 9th international conference on toward useful services for elderly and people with disabilities: smart homes and health telematics, vol 1, issue 1, pp 129–136
Le XH, Lee S, Lee YK, Lee H, Khalid M (2010) Activity-oriented access control to ubiquitous hospital information and services. Inf Sci 180(16):2979–2990
Yoon JS, Yoon TE, George JF (2011) Anticipating information needs for senior portal contents. J Comput Hum Behav 27(2):1012–1020
Dimitrios K (2005) Communication technologies (ICTs) by small-enterprise clusters in Vietnam. Inf Technol Int Dev 2(4):21–39
Sorwar G, Blair D (2007) A subscription based generic medical event management system for telemedicine applications. In: Proceedings of the 3rd IASTED international conference on telehealth, vol 1, issue 1, pp 160–166
Akematsu Y, Tsuji M (2009) Economic effect of e-health: focusing on the reduction of days spent for treatment. In: Proceedings 11th international conference on e-health networking, applications and services, vol 1, pp 14–20
Metso A, Pulli P, Hickey S, Zheng X (2009) Ubiquitous services for senior citizens-living process detection and middleware. In: Proceedings of the 2009 Eight IEEE/ACIS international conference on computer and information science, vol 1, pp 846–851
Cortes U, Urdiales C, Roberta A (2007) Intelligent healthcare managing: an assistive technology approach. In: Proceedings of the 9th international work conference on artificial neural networks, vol 1, pp 1045–1051
Agosto DE, Abbas J (2010) High school seniors’ social network and other ICT use preferences and concerns. In: Proceedings of the 73rd ASIS&T annual meeting on navigating streams in an information ecosystem, vol 47, no 65, pp 23–31
Mato RM, Salvo MA, Lee J (2008) Balanced clustering using mobile agents for the ubiquitous healthcare systems. In: Proceedings of the 2008 third international conference on convergence and hybrid information technology, vol 2, pp 686–691
Phang CW, Li Y, Sutanto J, Atreyi K (2005) Senior citizens’ adoption of e-government: in quest of the antecedents of perceived usefulness. In: Proceedings of the 38th annual Hawaii international conference on system sciences, vol 5, pp 130–131
Kim B, Kim YJ, Lee IS, You I (2007) Design and implementation of a ubiquitous ECG monitoring system using SIP and the Zigbee network. In: Proceedings of the future generation communication and networking, vol 1, pp 599–604
Mordini E, Wright D, Wadhwa K, Hert P, Mantovani E, Thestrup J, Steendam G, Amico A, Vater I (2011) Senior citizens and the ethics of e-inclusion. Ethics Inf Technol 11(3):203–220
Su WT, Kuo YH, Huang PC (2008) A QoS-driven approach for service-oriented device anycasting in ubiquitous environments. Comput Netw 52(18):3342–3357
Moser S, Bruppacher SE, Simoni FD (2011) Public representation of ubiquitous ICT applications in the outpatient health sector. Int J Technol Human Interact 7(4):62–80
Gartenberg D, Thornton R, Masood M, Pfannenstiel D, Taylor D, Parasuraman R (2013) Collecting health-related data on the smart phone: mental models, cost of collection, and perceived benefit of feedback. Pers Ubiquit Comput 17(3):561–570
Munnelly J, Clarke S (2007) ALPH: a domain-specific language for crosscutting pervasive healthcare concerns. In: Proceedings of the 2nd workshop on domain specific aspect languages. doi:10.1145/1255400.1255404
Chan L, Zhang J, Narauanan M, Celler B, Lovell N (2008) A health monitoring and evaluation system for assessing care needs of residents in aged-care facilities. In: Proceedings of the 6th IASTED international conference on biomedical engineering, vol 1, pp 414–418
Kwon PJ, Kim H, Kim U (2009) A Study on the web-based intelligent self-diagnosis medical system. Adv Eng Softw 40(6):402–406
Tafa Z (2010) Sensor networks in pervasive healthcare computing. Int J Adv Pervasive Ubiquitous Comput 2(3):1–20
Sneha S, Varshney U (2009) Enabling ubiquitous patient monitoring: model, decision protocols, opportunities and challenges. Decis Support Syst 46(3):606–619
Lee HJ, Lee SH, Ha KS, Jang HC, Chung WY, Kim JY, Chang YS, Yoo DH (2009) Ubiquitous healthcare service using Zigbee and mobile phone for elderly patients. Int J Med Inform 78(3):193–198
Kim YJ, Jung KK, Moon G, Shin DS, Kang HY (2009) Hallym Jikimi 3rd system: web-based monitoring for u-health care service. In: Proceedings of 4th international conference on persuasive technology. doi:10.1145/1541948.1541962
Shin DK, Jung H, Chung KY, Park R (2013) Performance analysis of advanced bus information system using LTE antenna. Multimed Tools Appl. doi:10.1007/s11042-013-1539-0
Park R, Jung H, Jung KY, Kim KJ (2013) Performance analysis of LTE downlink system using relay-based selective transmission. Pers Ubiquit Comput. doi:10.1007/00779-013-0674-y
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (No. 2013M3C8A2A02078523).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, R.C., Jung, H., Shin, DK. et al. Telemedicine health service using LTE-Advanced relay antenna. Pers Ubiquit Comput 18, 1325–1335 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00779-013-0744-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00779-013-0744-1