Abstract
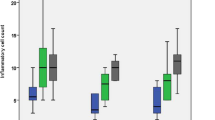
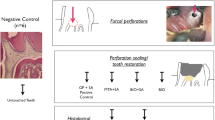
The aim of this study was to compare the histologic response elicited by repairing furcal perforations with mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) and a new endodontic material in the name of “calcium enriched mixture (CEM) cement” in dogs’ teeth. Thirty-four premolars were randomly divided into four groups: MTA (n = 15), CEM (n = 15), positive, and negative controls (n = 4). Root canal therapy were carried out; perforations were made, and the furcation areas were then repaired with MTA or CEM cement. The animals were sacrificed after 3 months. The teeth and their adjacent structures were processed and stained with hematoxylin and eosin stain for histological evaluation. Chi-square test was used to evaluate hard tissue formation, and Mann–Whitney U test was used for the histological evaluation of inflammation. Specimens in positive controls showed severe inflammatory infiltration, prominent granulation tissue, and epithelial proliferation; negative controls demonstrated normal periodontal ligament without inflammatory reactions. Hard tissue formation was observed in all the specimens of the two experimental groups. In inflammatory evaluation, mild inflammation was detected in the experimental groups, and no statistically significant differences were observed between them. MTA and CEM cement showed similar favorable biological response in furcation perforation repair, especially in inducing the formation of cementum-like hard tissue.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sinai I (1977) Endodontic perforations: their prognosis and treatment. J Am Dent Assoc 95:90–95
Bryan EB, Woollard G, Mitchell WC (1999) Nonsurgical repair of furcal perforations: a literature review. Gen Dent 47:274–278
Salman MA, Quinn F, Dermody J, Hussey D, Colaffey N (1999) Histological evaluation of repair using a bioresorbable membrane beneath a resin-modified glass ionomer after mechanical furcation perforation in dogs teeth. J Endod 25:181–186
Holland R, Otoboni Filho JA, de Souza V, Nery MJ, Bernabe PFE, Dezan E Jr (2001) Mineral trioxide aggregate repair of lateral root perforations. J Endod 27:281–284
Lemon RR (1992) Nonsurgical repair of perforation defects. Internal matrix concept. Dent Clin North Am 36:439–457
Holland R, Bisco Ferreira L, de Souza V, Otoboni Filho JA, Murata SS, Dezan E Jr (2007) Reaction of the lateral periodontium of dogs’ teeth to contaminated and noncontaminated perforations filled with mineral trioxide aggregate. J Endod 33:1192–1197
Balla R, LoMonaco CJ, Skribner J, Lin LM (1991) Histological study of furcation perforations treated with tricalcium phosphate, hydroxylapatite, amalgam, and life. J Endod 17:234–238
Yildirim T, Gencoglu N, Firat I, Perk C, Guzel O (2005) Histologic study of furcation perforations treated with MTA or Super-EBA in dog’s teeth. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 100:120–124
Pitt Ford TR, Torabinejad M, McKendry DJ, Hong CU, Kariyawasam SP (1995) Use of mineral trioxide aggregate for repair of furcal perforations. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 79:756–763
Lee SJ, Monsef M, Torabinejad M (1993) Sealing ability of a mineral trioxide aggregate for repair of lateral root perforations. J Endod 19:541–544
Torabinejad M, White DJ (1995) Tooth filling material and method of use. US Office Patent Number 5415547
Torabinejad M, Hong Cu MC, Donald F, Pitt Ford TR (1995) Physical and chemical properties of a new root-end filling material. J Endod 21:349–353
Asgary S, Eghbal MJ, Parirokh M, Brink F (2005) Chemical differences between white and gray mineral trioxide aggregate. J Endod 31:101–103
Asgary S, Parirokh M, Eghbal MJ, Brink F (2004) A comparative study of white mineral trioxide aggregate and white Portland cements using X-ray microanalysis. Aust Endod J 30:89–92
Asgary S, Eghbal MJ, Parirokh M, Ghoddusi J, Kheirieh S, Brink F (2009) Comparison of mineral trioxide aggregate’s composition with Portland cements and a new endodontic cement. J Endod 35:243–250
Torabinejad M, Chivian N (1999) Clinical application of mineral trioxide aggregate. J Endod 25:197–205
Pitt Ford TR, Torabinejad M, Abedi HR, Backland LK, Kariyawasam SP (1996) Using mineral trioxide aggregate as a pulp-capping material. J Am Dent Assoc 127:1491–1494
Noetzel J, Ozer K, Reisshauer BH, Anil A, Rossler A, Neumann K, Kielbassa AM (2006) Tissue responses to an experimental calcium phosphate cement and mineral trioxide aggregate as materials for furcation perforation repair: a histological study in dogs. Clin Oral Invest 10:77–83
Zhu YQ, Xia WW, Xia L (2003) Histological evaluation of repair of furcation perforation in dogs using mineral trioxide aggregate. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue 12:47-50 (Abstract)
Sarkar NK, Caicedo R, Ritwik P, Moiseyeva R, Kawashima I (2005) Physicochemical basis of the biologic properties of mineral trioxide aggregate. J Endod 31:97–100
Asgary S, Eghbal MJ, Parirokh M, Ghoddusi J (2008) Effect of two storage solutions on surface topography of two root-end fillings. Aust Endod J (published online: 25 Nov 2008)
Roberts HW, Toth JM, Berzins DW, Charlton DG (2008) Mineral trioxide aggregate material use in endodontic treatment: a review of the literature. Dent Mater 24:149–164
Torabinejad M, Higa RK, McKendry DJ, Pitt Ford TR (1994) Dye leakage of four root end filling materials: effects of blood contamination. J Endod 20:159–163
Ghoddusi J, Tavakkol Afshari J, Donyavi Z, Brook A, Disfani R, Esmaeelzadeh M (2008) Cytotoxic effect of a new endodontic cement and mineral trioxide aggregate on L929 line culture. Iranian Endodontic J 3:17–23
Al-Hezaimi K, Al-Shalan TA, Naghshbandi J, Oglesby S, Simon JH, Rotstein I (2006) Antibacterial effect of two mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) preparations against Enterococcus faecalis and Streptococcus sanguis in vitro. J Endod 32:1053–1056
Torabinejad M, Pitt Ford TR, McKendry DJ, Abedi HR, Miller DA, Kariyawasam SP (1997) Histologic assessment of mineral trioxide aggregate as a root-end filling in monkeys. J Endod 23:225–228
Hamad HA, Tordik PA, McClanahan SB (2006) Furcation perforation repair comparing gray and white MTA: a dye extraction study. J Endod 32:337–340
Ferris DM, Baumgartner JC (2004) Perforation repair comparing two types of mineral trioxide aggregate. J Endod 30:422–424
Chng HK, Islam I, Yap AU, Tong YW, Koh ET (2005) Properties of a new root-end filling material. J Endod 31:665–668
Asgary S, Parirokh M, Eghbal MJ, Ghoddusi J (2006) SEM evaluation of pulp reaction to different pulp capping materials in dog’s teeth. Iranian Endodontic J 1:117–122
Asgary S, Shahabi S, Jafarzadeh T, Amini S, Kheirieh S (2008) The properties of a new endodontic material. J Endod 34:990–993
Amini Ghazvini S, Abdo Tabrizi M, Kobarfard F, Akbarzadeh Baghban AR, Asgary S (2009) Ion release and pH of a new endodontic cement, MTA and Portland cement. Iranian Endodontic J 4:74–78
Asgary S, Eghbal MJ, Parirokh M, Ghanavati F, Rahimi H (2008) A comparative study of histological response towards different pulp capping materials and a novel experimental cement. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 106:609–614
Asgary S, Eghbal MJ, Parirokh M, Torabzadeh H (2006) Sealing ability of three commercial mineral trioxide aggregates and an experimental root-end filling material. Iranian Endodontic J 1:101–105
Asgary S, Eghbal MJ, Parirokh M (2008) Sealing ability of a novel endodontic cement as a root-end filling material. J Biomed Mater Res A 87:706–709
Asgary S, Ehsani S (2009) Permanent molar pulpotomy with a new endodontic cement: a case series. J Conserv Dent 12:31–36
Asgary S, Akbari Kamrani F (2008) Antibacterial effects of five root canal sealing materials. J Oral Scie 50:469–474
Asgary S, Moosavi SH, Yadegari Z, Shahriari S (2009) Cytotoxic effect of MTA and New Endodontic Cement in human gingival fibroblast cells: a SEM evaluation. N Y State Dent J (in press)
Panzarini SR, Holland R, de Souza V, Poi WR, Sonoda CK, Pedrini D (2007) Mineral trioxide aggregates a root canal filling material in reimplanted teeth. Microscopic analysis in monkeys. Dent Traumatol 23:265–272
Asgary S, Akbari Kamrani F, Taheri S (2007) Evaluation of antimicrobial effect of mineral trioxide aggregate, calcium hydroxide, and CEM cement. Iranian Endodontic J 2:105–109
Weldom J, Pashley D, Loushine R, Weller R, Kimbrough W (2002) Sealing ability of mineral trioxide aggregate and Super-EBA when used as furcation repair materials, a longitudinal study. J Endod 28:467–470
Doudi MF (2001) Microscopic management of endodontic procedural errors: perforation repair. Dent update 28:176–180
Al Daafas A, Al Nazhan S (2007) Histological evaluation of contaminated furcal perforation in dogs’ teeth repaired by MTA with or without internal matrix. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 103:92–99
Torabinejad M, Hong Cu, Lee SF, Monsef M, Pitt Ford TR (1995) Investigation of mineral trioxide aggregate for root- end filling in dogs. J Endod 21:603–608
Acknowledgments
This study was supported, in part, by Iran Center for Dental Research, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samiee, M., Eghbal, M.J., Parirokh, M. et al. Repair of furcal perforation using a new endodontic cement. Clin Oral Invest 14, 653–658 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-009-0351-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-009-0351-8