Abstract
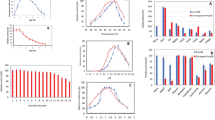
A halophilic archaeon, Haloarcula sp. strain S-1, produced extracellular organic solvent-tolerant α-amylase. Molecular mass of the enzyme was estimated to be 70 kDa by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. This amylase exhibited maximal activity at 50°C in buffer containing 4.3 M NaCl, pH 7.0. Moreover, the enzyme was active and stable in various organic solvents (benzene, toluene, and chloroform, etc.). Activity was not detected at low ionic strengths, but it was detected in the presence of chloroform at low salt concentrations. On the other hand, no activity was detected in the presence of ethyl alcohol and acetone.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of proteins utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Danson MJ, Hough DW (1997) The structural basis of halophilicity. Comp Biochem Physiol 3:307–312
Doukyu N, Kuwahara H, Aono R (2003) Isolation of Paenibacillus illinoisensis that produces cyclodextrin glucanotransferase resistant to organic solvents. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 67:334–340
Dym O, Mevarech M, Sussman JL (1995) Structural features that stabilize halophilic malate dehydrogenase from archaebacterium. Science 267:1344–1346
Haseltine C, Rolfsmeier M, Blum P (1996) The glucose effect and regulation of the α-amylase synthesis in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus. J Bacteriol 4:945–950
Inoue A, Horikoshi K (1991) Estimation of solvent-tolerance of bacteria by solvent parameter log P. J Ferment Bioeng 71:194–196
Janecek S, Leveque E, Belarbi A, Haye B (1999) Close evolutionary relatedness of α-amylase from archaea and plants. J Mol Evol 48:421–426
Juez G, Rodriguez-Valera F, Ventosa A, Kushner DJ (1986) Haloarcula hispanica spec. nov. and Haloferax gibbonsii spec. nov., two new species of extremely halophilic archaebacteria. Syst Appl Microbiol 8:75–79
Kadziola A, Søgaard M, Svensson B (1998) Molecular structure of a barley α-amylase-inhibitor complex: implications for starch binding and catalysis. J Mol Biol 278:205–217
Kamekura M, Dyall-Smith ML (1995) Taxonomy of the family Halobacteriaceae and the description of two genera Halorubrobacterium and Natrialba. J Gen Appl Microbiol 41:333–350
Kamekura M, Seno Y (1990) A halophilic extracellular protease from a halophilic archaebacterium strain 172 P1. Biochem Cell Biol 68:352–359
Kanai H, Kobayashi T, Aono R, Kudo T (1995) Natronococcus amylolyticus sp. nov., a haloalkaliphilic archaeon. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45:762–766
Kobayashi K, Kanai H, Hayashi T, Akiba T, Akaboshi R, Horikoshi K (1992) Haloalkaliphilic maltotriose-forming α-amylase from the archaebacterium Natronococcus sp. strain Ah-36. J Bacteriol 174:3439–3444
Kobayashi K, Kanai H, Aono R, Horikoshi K, Kudo T (1994) Cloning, expression, and nucleotide sequence of the α-amylase gene from the haloalkaliphilic archaeon Natronococcus sp. strain Ah-36. J Bacteriol 176:5131–5134
Machius M, Wiegand G, Huber R (1995) Crystal structure of calcium depleted Bacillus lincheniformis α-amylase at 2.2 Å resolution. J Mol Biol 246:545–559
Mardern D, Ebel C, Zaccai G (2000) Halophilic adaptation of enzymes. Extremophiles 4:91–98
Marhuenda-Egea FC, Bonete MJ (2002) Extreme halophilic enzymes in organic solvents. Curr Opin Biotechnol 13:385–389
Ogino H, Miyamoto K, Yasuda M, Ishimi K, Ishikawa H (1999a) Growth of organic solvent-tolerant Pseudomonas aeruginosa LST-03 in the presence of various organic solvents and production of lipolytic enzyme in the presence of cyclohexane. Biochem Eng J 4:1–6
Ogino H, Yamada M, Watanabe F, Ichinose H, Yasuda M, Ishikawa H (1999b) Peptide synthesis catalyzed by organic solvent-stable protease from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PST-01 in monophasic aqueous-organic solvent systems. J Biosci Bioeng 88:513–518
Perez-Pomares F, Bautista V, Ferrer J, Pire C, Marhuenda-Egea FC, Bonete MJ (2003) α-Amylase activity from the halophilic archaeon Haloferax mediterranei. Extremophiles 7:299–306
Rodriguez-Valera F, Juez G, Kushner DJ (1983) Halobacterium mediterranei spec. nov., a new carbohydrate-utilizing extreme halophile. Syst Appl Microbiol 4:369–387
Usami R, Fukushima T, Mizuki T, Inoue A, Yoshida Y, Horikoshi K (2003) Organic solvent tolerance of halophilic archaea. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 67:1809–1812
Vihinen M, Mäntsälä P (1989) Microbial amylolytic enzymes. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 24:329–418
Zviagintseva IS, Beliaev SS, Borzenkov IA, Kostrikina NA, Milekhina EI, Ivanov MV (1995) Halophilic archaebacteria from the Kalamkass oilfield. Mikrobiologiia 64:83–87
Acknowledgements
Part of this study has been supported by a grant for the 21st Century’s Center of Excellence Programs organized by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan, since 2003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by K. Horikoshi
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukushima, T., Mizuki, T., Echigo, A. et al. Organic solvent tolerance of halophilic α-amylase from a Haloarchaeon, Haloarcula sp. strain S-1. Extremophiles 9, 85–89 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-004-0423-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-004-0423-2