Abstract
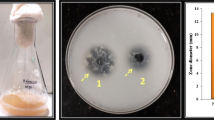
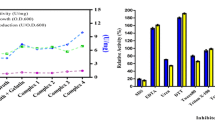
A total of 33 halophilic protease producers were isolated from different salt samples collected from Emisal salt company at Lake Qarun, Fayoum, Egypt. Of these strains, an extremely halophilic strain that grew optimally at 30 % (w/v) NaCl was characterized and identified as Halobacterium sp. strain HP25 based on 16S rRNA gene sequencing and phenotypic characterization. A halo-alkali-thermophilic protease was purified in three successive steps from the culture supernatant. The purified halophilic protease consisted of a single polypeptide chain with a molecular mass of 21 kDa and was enriched 167-fold to a specific activity of 6350 U mg−1. The purified enzyme was active over a broad pH range from 6.0 to 11.0, with maximum activity at pH 8.0, exhibited a broad temperature range from 30 to 80 °C with optimum activity at 60 °C, and was active at salt concentrations ranging from 5 to 25 % (w/v), with optimum activity at 17 % NaCl (w/v). The K M and V max values of the purified halophilic protease with casein as a substrate were 523 µg mL−1 and 2500 µg min−1 mL−1, respectively. In addition, this enzyme was stable in the tested organic solvents and laundry detergents such methanol, propanol, butanol, hexane, Persil and Ariel. The unusual properties of this enzyme allow it to be used for various applications, such as the ripening of salted fish. Furthermore, its stability and activity in the presence of organic solvents and detergents also allow the use of this enzyme for further novel applications and as an additive in detergent formulations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alqueres SC, Almeida RV, Clementino MM, Vieira RP, Almeida WI, Cardoso AM, Martins OB (2007) Exploring the biotechnological applications in the archaeal domain. Braz J Microbiol 38:398–405
Barett AJ (1994) Proteolytic enzymes: serine and cysteine peptidases. Methods Enzymol 244:1–15
Bhatnagar T, Boutaiba S, Hacene H, Cayol J, Fardeau M, Olivier B, Baratti J (2005) Lipolytic activity from halobacteria: screening and hydrolase production. FEMS Microbiol Lett 42:133–140
Beynon R, Bond JB (2001) Proteolytic enzymes, a practical approach. IRL Press, New York, p 113
Bradford MM (1976) A dye binding assay for protein. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Colwell RR, Clayton RA, Ortiz-Conde BA, Jacobs D, Russek-Cohen E (1995) The microbial species concept and biodiversity. In: Allsopp D, Colwell R, Hawksworth L (eds) Microbial diversity and ecosystem function. Wallingford, UK, pp 3–15
Delgado-García M, Valdivia-Urdiales B, Aguilar-González CN, Contreras-Esquivel JC, Rodríguez-Herrera R (2012) Halophilic hydrolases as a new tool for the biotechnological industries. J Sci Food Agric 92:2575–2580
Fastrez J, Fersht AR (1973) Demonstration of the acyl-enzyme mechanism for the hydrolysis of peptides and anilides by chymotrypsin. Biochemistry 12:2025–2034
Folin O, Ciocalteu V (1929) On tyrosine and tryptophan determination in proteins. J Biol Chem 73:627–649
Gibbons NE (1974) The family Halobacteriaceae. In: Buchanan RE, Gibbons NE (eds) Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology, 8th edn. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 269–272
Gimenez MI, Studdert CA, Sanchez JJ, Decastro RE (2000) Extracellular protease of Natriala magadii; purification and biochemical characterization. Extremophiles 4:181–188
Gomes J, Steiner M (2004) The biocatalytic potential of extremophiles and extremozymes. Food Technol Biotechnol 42:223–235
Grant J, Hargrave B, MacPherson P (2002) Sediment properties and benthic–pelagic coupling in the North Water. Deep-Sea Res 49:5259–5275
Gupta R, Beg QK, Khan S, Chauhan B (2002) An overview on fermentation, downstream processing and properties of microbial alkaline proteases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:381–395
Hartley BS (1960) Proteolytic enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem 29:45–72
Hezayen FF, Tindall BJ, Steinbüchel A, Rehm B (2002) Characterization of a novel halophilic archaeon, Halobiforma haloterrestris gen. nov., sp. nov., and transfer of Natronobacterium nitratireducens to Halobiforma nitratireducens comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:2272–2280
Izotova SL, Strongin AY, Chekulaeva LN, Sterkin NE, Ostoslavskaya VI, Lyublinskaya LA, Timokhina EA, Stepanova VM (1983) Purification and properties of serine protease from Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol 155:826–830
Johnsen K, Andersen S, Jacobsen CS (1996) Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of phenanthrene-degrading fluorescent Pseudomonas biovars. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:3818–3825
Juhasz O, Skarka B (1990) Purification and characterization of an extracellular proteinase from Brevibacterium linens. Can J Microbiol 36:510–512
Kamekura M, Seno YA (1990) Halophilic extracellular protease from a halophilic archaebacterium strain 172 p1. Biochem Cell Biol 68:352–359
Kanlayakrit W, Bovornreungroj P, Oka T, Goto M (2004) Production and characterization of protease from an extremely halophilic Halobacterium sp. PB407. Kasetsart J (Nat Sci) 38:15–20
Kim CJ, Oh MJ, Choi SH (1992) Characteristics of the alkaline proteinase from the moderate halophile, Halomonas sp. ES 10. J Korean Agric Chem Soc 35:37–41
Kumar S, Karan R, Kapoor S, Singh S, Khare S (2012) Screening and isolation of halophilic bacteria producing industrially important enzymes. Braz J Microbiol 43:1595–1603
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lorentz KA (1976) Simple polyacrylamide gradient gel preparation for estimating molecular weights. Anal Biochem 76:214–220
Margesin R, Schiner F (2001) Potential of halotolerant and halophilic microorganisms for biotechnology. Extremophiles 5:73–83
Mesbah NM, Wiegel J (2014) Purification and biochemical characterization of halophilic alkalithermophilic protease AbCP from Alkalibacillus sp. NM-Fa4. J Mol Catal B Enzym 105:74–81
Moreno M, Pérez D, Garcia MT, Mellado E (2013) Halophilic bacteria as a source of novel hydrolytic enzymes. Life 3:38–51
Mormile MR, Biesen MA, Gutierrez MC, Ventosa A, Pavlovich JB, Onstott TC, Fredrickson JK (2003) Isolation of Halobacterium salinarum retrieved directly from halite brine inclusions. Environ Microbiol 5:1094–1102
Murray E, Brenner J, Colwell R, De Vos P, Goodfellow M, Grimont D, Pfennig N, Stackebrandt E, Zavarzin A, International Committee on Systematic Bacteriology (1990) Report of the ad hoc committee on approaches to taxonomy within the Proteobacteria. Int J Syst Bacteriol 40:213–215
Oren A (2002) The order Halobacteriales. In: Dworkin M (ed) The prokaryotes: an evolving electronic resource for the microbiological community. Springer-Verlag, New York. URL:http://www.prokaryotes.com. [WWW document]
Oren A (2010) Industrial and environmental applications of halophilic microorganisms. Environ Technol 31:825–834
Oren A (2012) Taxonomy of the family Halobacteriaceae: a paradigm for changing concepts in prokaryote systematics. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:263–271
Oren A, Gurevich P, Gemmell RT, Teske A (1995) Halobaculum gomorrense gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel extremely halophilic archaeon from Dead Sea. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45:747–754
Page RDM (1996) Tree view: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput Appl Biosci 12:357–358
Rao B, Tanksale A, Ghatge M, Deshpande V (1998) Molecular and biotechnological aspects of microbial proteases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:597–635
Reddy CA, Beveridge TJ, Breznak JA, Marzluf GA, Schmidt TM, Snyder LR (2007) Methods for general and molecular microbiology, 3rd edn. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC
Rodriguez-Valera F, Lillo JG (1992) Halobacteria as producers of polyhydroxyalkanoates. FEMS Microbiol Rev 103:181–186
Rohban R, Amoozegar MA, Ventosa A (2009) Screening and isolation of halophilic bacteria producing extracellular hydrolysis from Howz Soltan Lake, Iran. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36:333–340
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbour-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor, New York, pp 10.51–10.67
Sehgal SN, Gibbons NE (1960) Effect of metal ions on the growth of Halobacterium cutirubrum. Can J Microbiol 6:165–169
Selim S, Hagagy N, Abdel Aziz M, El-Meleigy E, Pessione E (2014) Thermostable alkaline halophilic-protease production by Natronolimnobius innermongolicus WN18. Nat Prod Res 28:1476–1479
Sinha R, Khare SK (2012) Isolation and characterization of halophilic Virgibacillus sp. EMB13: purification and characterization of its protease for detergent application. Indian J Biotechnol 11:416–426
Studdert CA, Herrera MK, Gil MP, Sanchez JJ, De Castro RE (2001) Purification, biochemical characterization of the haloalkaliphilic archeon Natronococcus occultus extracellular serine protease. J Gen Microbiol 41:375–383
Sumantha A, Larroche C, Pandey A (2006) Microbiology and industrial biotechnology of food-grade proteases: a perspective. Food Technol Biotechnol 44:211–220
Takii Y, Kuriyama N, Suzuki Y (1990) Alkaline serine protease produced from citric acid by Bacillus alkalophilus subsp. halodurans KP 1239. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 34:57–62
Thompson J, Gibson TJ, Plewinak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The Clustal X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4867-488
Ventosa A, Nieto JJ (1995) Biotechnological applications and potentialities of halophilic microorganisms. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 11:85–94
Ventosa A, Oren A (1996) Halobacterium salinarum nom. corrig., a name to replace Halobacterium salinarium (Elazari-Volcani) and to include Halobacterium halobium and Halobacterium cutirubrum. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:347
Vidyasagar M, Prakash S, Mahajan V, Yogesh S, Shouche KS (2009) Purification and characterization of an extreme halothermophilic protease from bacterium Chromohalobacter sp. TVSP101. Braz J Microbiol 40:12–19
Voet O, Voet JG (2004) Biochemistry, 3rd edn. Wiley, USA, pp 521–527
Woese C (1993) The archaea: their history and significance. In: Kates M, Kushner D, Matheson A (eds) The biochemistry of archaea (Archaebacteria). Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp vii–xxix
Yachai M, Tanasupawat S, Itoh T, Benjakul S, Visessanguan W, Valyasevi R (2008) Halobacterium piscisalsi sp. nov., from fermented fish (pla-ra) in Thailand. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2136–2140
Yang Y, Cui HL, Zhou PJ, Lie SJ (2006) Halobacterium jilantaiense sp. nov., a halophilic archaeon isolated from a saline lake in Inner Mongolia, China. Int J Syst Bacteriol 56:2353–2355
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Martin Krehenbrink for helpful revision of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by F. Robb.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elbanna, K., Ibrahim, I.M. & Revol-Junelles, AM. Purification and characterization of halo-alkali-thermophilic protease from Halobacterium sp. strain HP25 isolated from raw salt, Lake Qarun, Fayoum, Egypt. Extremophiles 19, 763–774 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-015-0752-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-015-0752-3