Abstract
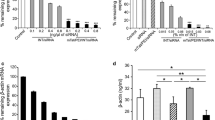
The aim of the present study was to develop a novel transfection method for short interfering RNA (siRNA). A nanotube with surfactant activity, A6K, consisting of six alanine residues and a hydrophilic head, lysine, was compared to the conventional cationic transfectant reagents siFECTOR and Lipofectamine 2000. Cytotoxicity for the human glioblastoma cell lines U87MG, A172, and T98G was examined with the MTS assay. Transfection efficiency was analyzed with FITC-labeled siRNA targeting matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 mRNA by fluorescent activity on microscopy. The ultrastructure of A6K was evaluated by electron microscopy. The level of cytotoxicity associated with A6K in the U87MG cells was significantly lower than with siFECTOR and Lipofectamine 2000. Transfection efficiency for siRNA was increased in a dose- and time-dependent fashion. The relative expression of MMP-2 mRNA to β-actin was reduced in a dose-dependent manner by real-time RT-PCR analysis. The ultrastructure of the A6K was transformed to micelle formation when mixed with the siRNA. The lipid-like self-assembling peptide, A6K, has genes in the micelle associated with the hydrophilic tail. This transfection method is a novel and stable technique with lower cytotoxicity than the current standard methods.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gutierrez AA, Lemoine NR, Sikora K (1992) Gene therapy for cancer. Lancet 339:715–721
Gabriel RA, Yang GY (2007) Gene therapy in cerebrovascular diseases. Curr Gene Ther 7:421–433
Kuo WT, Huang HY, Huang YY (2009) Intracellular trafficking, metabolism and toxicity of current gene carriers. Curr Drug Metab 10:885–894
Zeng J, Wang X, Wang S (2007) Self-assembled ternary complexes of plasmid DNA, low molecular weight polyethyleneimine and targeting peptide for nonviral gene delivery into neurons. Biomaterials 28:1443–1451
Khoe U, Yang Y, Zhang S (2008) Synergistic effect and hierarchical nanostructure formation in mixing two designer lipid-like peptide surfactants Ac-A6D-OH and Ac-A6K-NH2. Macromol Biosci 8:1060–1067
Bucak S, Cenker C, Nasir I, Olsson U, Zackrisson M (2009) Peptide nanotube nematic phase. Langmuir 25:4262–4426
Nagai A, Nagai Y, Qu H, Zhang S (2007) Dynamic behaviors of lipid-like self-assembling peptide A6D and A6K nanotubes. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 7:2246–2252
Acknowledgments
Daizo Yoshida, MD, PhD, and Jiro Takei (3D-Matrix, Japan Ltd.) have applied for a patent for transfection agent as an inventor/co-inventor to the European Patent Office (2280 HV RIJSWIJK, Netherlands) (application no. 09809913.8/patent no. JP2009064614).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida, D., Kim, K., Takumi, I. et al. A transfection method for short interfering RNA with the lipid-like self-assembling nanotube, A6K. Med Mol Morphol 46, 86–91 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-013-0011-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-013-0011-6