Abstract
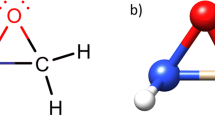
Halogen bonding refers to the non-covalent interactions of halogen atoms X in some molecules, RX, with negative sites on others. It can be explained by the presence of a region of positive electrostatic potential, the σ-hole, on the outermost portion of the halogen’s surface, centered on the R–X axis. We have carried out a natural bond order B3LYP analysis of the molecules CF3X, with X = F, Cl, Br and I. It shows that the Cl, Br and I atoms in these molecules closely approximate the \(s^{2} p^{2}_{x} p^{2}_{y} p^{1}_{z} \) configuration, where the z-axis is along the R–X bond. The three unshared pairs of electrons produce a belt of negative electrostatic potential around the central part of X, leaving the outermost region positive, the σ-hole. This is not found in the case of fluorine, for which the combination of its high electronegativity plus significant sp-hybridization causes an influx of electronic charge that neutralizes the σ-hole. These factors become progressively less important in proceeding to Cl, Br and I, and their effects are also counteracted by the presence of electron-withdrawing substituents in the remainder of the molecule. Thus a σ-hole is observed for the Cl in CF3Cl, but not in CH3Cl.

Schematic representation of the atomic charge generation. The molecular electrostatic potential (MEP) is calculated using the AM1* Hamiltonian. The semiempirical MEP is then scaled to DFT or ab initio level and atomic charges are generated from it by the restrained electrostatic potential (RESP) fit method.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dumas J-M, Peurichard H, Gomel M (1978) J Chem Res Synop 54–55
Dumas J-M, Geron C, Peurichard H, Gomel M (1976) Bull Soc Chim France 720–728
Dumas J-M, Kern M, Janier-Dubry JL (1976) Bull Soc Chim France 1785–1790
Murray-Rust P, Motherwell WDS (1979) J Am Chem Soc 101:4374–4376
Murray-Rust P, Stallings WC, Monti CT, Preston RK, Glusker JP (1983) J Am Chem Soc 105:3206–3214
Ramasubbu N, Parthasarathy R, Murray-Rust P (1986) J Am Chem Soc 108:4308–4314
Bent HA (1968) Chem Rev 68:587–648
Hassel O (1970) Science 170:497–502
Bernard-Houplain M-C, Sandorfy C (1973) Can J Chem 51:1075–1082
Bernard-Houplain M-C, Sandorfy C (1973) Can J Chem 51:3640–3646
Di Paolo T, Sandorfy (1974) Chem Phys Lett 26:466–469
Di Paolo T, Sandorfy C (1974) Can J Chem 52:3612–3622
Auffinger P, Hays FA, Westhof E, Shing Ho P (2004) Proc Nat Acad Sci 101:16789–16794
Metrangolo P, Neukirch H, Pilati T, Resnati G (2005) Acc Chem Res 38:386–395
Brinck T, Murray JS, Politzer P (1992) Int J Quantum Chem, Quantum Biol Symp 19:57–64
Murray JS, Paulsen K, Politzer P (1994) Proc Indian Acad Sci (Chem Sci) 106:267–275
Politzer P, Lane P, Concha MC, Ma Y, Murray JS (2006) J Mol Model DOI 10.1007/s00894-006-0154-7 (this issue)
Stewart RF (1972) J Chem Phys 57:1664–1668
Naray-Szabo G, Ferenczy GG (1995) Chem Rev 95:829–847
Bader RFW, Carroll MT, Cheeseman JR, Chang C (1987) J Am Chem Soc 109:7968–7979
Weinstein H, Politzer P, Srebrenik S (1975) Theor Chim Acta 38:159–163
Politzer P, Murray JS (2002) Theor Chem Accts 108:134–142
Flükiger PF (1992) Development of the molecular graphics package MOLEKEL and its application to selected problems in organic and organometallic chemistry. Thèse No. 2561. Département de chimie physique, Université de Genève, Genève
Portmann S, Lüthi HP (2000) CHIMIA 54:766–770; http://www.cscs.ch/molekel/index.html
Lommerse JPM, Stone AJ, Taylor R, Allen FH (1996) J Am Chem Soc 118:3108–3116
Valerio G, Raos G, Meille SV, Metrangolo P, Resnati G (2000) J Phys Chem A 104:1617–1620
Romaniello P, Lelj F (2002) J Phys Chem A 106:9114–9119
Reed AE, Curtiss LA, Weinhold F (1988) Chem Rev 88:899–926
Becke AD (1993) J Chem Phys 98:5648–5652
Lee C, Yang W, Parr RG (1988) Phys Rev B 37:785–789
Ditchfield R, Hehre WJ, Pople JA (1971) J Chem Phys 54:724–728
Hehre WJ, Ditchfield R, Pople JA (1972) J Chem Phys 56:2257–2261
Hariharan PC, Pople JA (1974) Mol Phys 27:209–214
Gordon MS (1980) Chem Phys Lett 76:163–168
Hariharan PC, Pople JA (1973) Theo Chim Acta 28:213–222
Blaudeau J-P, McGrath MP, Curtiss LA, Radom L (1997) J Chem Phys 107:5016–5021
Francl MM, Pietro WJ, Hehre WJ, Binkley JS, DeFrees DJ, Pople JA, Gordon MS (1982) J Chem Phys 77:3654–3665
Binning RC Jr, Curtiss LA (1990) J Comp Chem 11:1206–1216
Rassolov VA, Pople JA, Ratner MA, Windus TL (1998) J Chem Phys 109:1223–1229
Rassolov A, Ratner MA, Pople JA, Redfern PC, Curtiss LA (2001) J Comp Chem 22:976–984
Clark T, Chandrasekhar J, Spitznagel GW, Schleyer PvR (1983) J Comp Chem 4:294–301
Godbout N, Salahub DR, Andzelm J, Wimmer E (1992) Can J Chem 70:560–571
Sosa C, Andzelm J, Elkin BC, Wimmer E, Dobbs KD, Dixon DA (1992) J Phys Chem 96:6630–6636
Kutzelnigg W (1984) Angew Chem 96:262–286
Kutzelnigg W (1984) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 23:272–295
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clark, T., Hennemann, M., Murray, J.S. et al. Halogen bonding: the σ-hole. J Mol Model 13, 291–296 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-006-0130-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-006-0130-2