Abstract
This paper deals with molecular modeling of new therapeutic agents for treating the Alzheimer’s disease. The therapeutic line adopted for this study is the cholinergic hypothesis. To modulate positively the cholinergic function through the inhibition of the acetylcholinesterase, a set of candidates was designed from a natural compound extracted from the cashew nutshell liquid, anacardic acid. In silico screening of this chemical library revealed a ligand that is more promising once it is correlated with an active drug through specific topological and electronic descriptors. The protein–ligand docking showed stable binding modes and the binding free energy computed for the active site of the receptor suggests that our ligand presents a potential biological response.

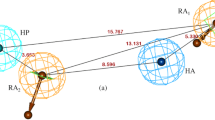
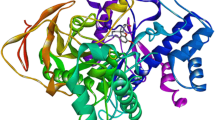
Representation of the three dimensional structure of the AChE, showing the important binding sites of the Gorge and the conformation of the ligand















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alzheimer A (1906) Über einen eigenartigen schweren Erkrankungsproze β der Hirnrinde. Neurologisches Centralblatt 23:1129–1136
Francis PT, Palmer AM, Snape M, Wilcock GK (1999) The cholinergic hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: a review of progress. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 66:137–147
Goedert M, Spillantini MGA (2006) Century of Alzheimer’s disease. Science 314:777–781
Morley JE (2011) Anticholinergic medications and cognition. J Am Med Dir Assoc 12:543–543
Igbal K, Grundke-Igbal I (2000) Alzheimer disease is multifactorial and heterogeneous. Neurobiol Aging 21:901–902
Jellinger KA (2006) Alzheimer 100–highlights in the history of Alzheimer research. J Neural Transm 113:1603–1623
Castro A, Martinez A (2006) Targeting beta-amyloid pathogenesis through acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Curr Pharm Des 12:4377–4387
Karran E, Mercken M, Strooper BD (2011) The amyloid cascade hypothesis for Alzheimer’s disease: an appraisal for the development of therapeutics. Nature Rev Drug Discov 10:698–712
Alonso AC, Grundke-Igbal I, Igbal K (1996) Alzheimer’s disease hyperphosphorylated tau sequesters normal tau into tangles of filaments and disassembles microtubules. Nat Med 2:783–787
Andersen JK (2004) Oxidative stress in neurodegeneration: cause or consequence Nat Med 10:S18–25
Dumont M, Beal MF (2011) Neuroprotective strategies involving ROS in Alzheimer disease. Free Rad Biol Med 51:1014–1026
Cummings JL (2004) Treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: current and future therapeutic approaches. Rev Neurol Dis 1:60–69
Mangialasche F, Solomon A, Winblad B (2010) Alzheimer’s disease: clinical trials and drug development. Lancet Neurol 9:702–716
Shafferman A, Kronman C, Flashner Y, Leitner M, Grosfeld H, Ordentlich A, Gozes Y, Cohen S, Ariel N, Barak D (1992) Mutagenesis of human acetylcholinesterase. Identif Resid Invol Catalyt Activ Polypep Fold 267:17640–17648
Dvira H, Silmanb I, Harela M, Rosenberryc TL, Sussman JL (2010) Acetylcholinesterase: from 3D structure to function. Chemico-Biol Interact 187:10–22
Bennion BJ, Essiz SG, Lau EY, Fattebert J-L, Emigh A, Lightstone FC (2015) A wrench in the works of human acetylcholinesterase: soman induced conformational changes revealed by molecular dynamics simulations. PLoS ONE 10:1–31
Phillips JC, Braun R, Wang W, Gumbart J, Tajkhorshid E, Villa E, Chipot C, Skeel RD, Kale L, Schulten K (2005) Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD. J Comput Chem 26:1781–1802
Martins JBL, Neves AA, Gargano R, Santos ML, Romeiro LAS (2007) Electronic structure calculations toward new potentially AChE inhibitors. Chem Phys Lett 446:304–308
De Paula AAN, Martins JBL, Santos ML, Nascente LC, Romeiro LAS, Areas TFMA, Vieira KST, Gambo NF, Castro NG, Gargano R (2009) New potential AChE inhibitor candidates. Eur J Med Chem 44:3754–3759
Kiametis AS, Martins JBL, Romeiro LAS, Gargano R (2013) Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: modeling potential candidates. Int J Quantum Chem 113:1461–1466
Nascimento ECM, Martins JBL (2011) Electronic structure and PCA analysis of covalent and non-covalent acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. J Mol Model 17:1371–1379
Nascimento ECM, Martins JBL, Gargano R, Santos ML (2008) Theoretical study of classical acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Chem Phys Lett 458:285–289
Samochochi M, Hoffle A, Fehrenbacher A, Jostock R, Ludwig J, Christner C, Radina M, Zerlim M, Ullmer C, Pereira E, Lubbert H, Albuquerque E (2003) Galantamine is an allosterically potentiating ligand of neuronal nicotinic but not of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 305:1024–1036
Cheung J, Rudolph M, Burshteyn F, Cassidy M, Gary E, Love J, Height J, Franklin M (2012) Structures of human acetylcholinesterase in complex with pharmacologically important ligands. J Med Chem 55:10282–10288
Raevsky OA (2004) Physicochemical descriptors in property-based drug design. Mini Rev Med Chem 4:1041–1052
Sakkiah S, Lee KW (2012) Pharmacophore-based virtual screening and density functional theory approach to identifying novel butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors. Acta Pharmacol Sin 33:964–978
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, Montgomery JA Jr, Vreven T, Kudin KN, Burant JC, Millam JM, Iyengar SS, Tomasi J, Barone V, Mennucci B, Cossi M, Scalmani G, Rega N, Petersson GA, Nakatsuji H, Hada M, Ehara M, Toyota K, Fukuda R, Hasegawa J, Ishida M, Nakajima T, Honda Y, Kitao O, Nakai H, Klene M, Li X, Knox JE, Hratchian HP, Cross JB, Adamo C, Jaramillo J, Gomperts R, Stratmann RE, Yazyev O, Austin AJ, Cammi R, Pomelli C, Ochterski JW, Ayala PY, Morokuma K, Voth GA, Salvador P, Dannenberg JJ, Zakrzewski VG, Dapprich S, Daniels AD, Strain MC, Farkas O, Malick DK, Rabuck AD, Raghavachari K, Foresman JB, Ortiz JV, Cui Q, Baboul AG, Clifford S, Cioslowski J, Stefanov BB, Liu G, Liashenko A, Piskorz P, Komaromi I, Martin RL, Fox D J, Keith T, Al-Laham MA, Peng CY, Nanayakkara A, Challacombe M, Gill PMW, Johnson B, Chen W, Wong MW, Gonzalez C, Pople JA (2009). Gaussian09, Inc., Wallingford, CT, USA, Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford, CT
HyperChem Computational Chemistry (1996). Hypercube Inc., New York
Trott O, Olson AJ (2010) AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization and multithreading. J Comput Chem 31:455–461
Smart OS, Neduvelil JG, Wang X, Wallace BA, Sansom MSP (1996) HOLE: A program for the analysis of the pore dimensions of ion channel structural models. J Mol Graph 14:354–360
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Brazilian Research Councils CAPES, CNPq, FINATEC, FAPDF, and the computational support of LBTC-UnB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper belongs to Topical Collection VI Symposium on Electronic Structure and Molecular Dynamics – VI SeedMol
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiametis, A.S., Silva, M.A., Romeiro, L.A.S. et al. Potential acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: molecular docking, molecular dynamics, and in silico prediction. J Mol Model 23, 67 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-017-3228-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-017-3228-9