Abstract
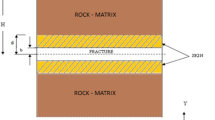
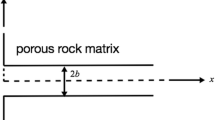
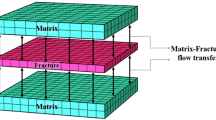
Matrix diffusion and sorption are among the key processes impacting the efficiency of natural attenuation in the subsurface. While these processes have been studied extensively in fractured media, limited information exists on the sorption nonlinearity. To address this shortfall, a numerical model has been developed that couples matrix diffusion and nonlinear sorption at the scale of a single fracture using the dual-porosity concept. The study is limited to a constant continuous-solute-source boundary condition. The influence of sorption intensities on dispersivity and macro-dispersion coefficient is investigated using a method of spatial moments. Results suggest that mixing of solutes is significantly lowered by nonlinear sorptive behavior, with respect to the mixing caused by matrix diffusion for linearly sorbing solutes. Also, the magnitude of time dependent dispersivity during the pre-asymptotic regime is lower for nonlinearly sorbing solutes with respect to the linearly sorbing solutes. Reduced mixing is also observed for nonlinearly sorbing solutes under combined mechanisms of matrix diffusion and decay.
Résumé
Les phénomènes de diffusion et de sorption comptent parmi les processus clés qui influent sur l’atténuation naturelle en subsurface. Si ces processus ont été massivement étudiés en milieu fracturé, il existe en revanche peu d’informations sur la non-linéarité de la sorption. Afin de combler cette lacune, un modèle numérique a été développé ; il couple la diffusion dans la matrice et la sorption non-linéaire à l’échelle d’une fracture unitaire en utilisant le concept de double porosité. La seule condition aux limites fixée pour toute l’étude est une source de soluté constante et continue. L’influence de l’intensité de la sorption sur la dispersivité et sur le coefficient de macro-dispersion est étudié via une méthode utilisant les moments spatiaux. Les résultats suggèrent que les mélanges de solutés sont significativement réduits par les phénomènes de sorption non-linéaires, comparativement aux mélanges causés par la diffusion pour des solutés à sorption linéaire. C’est pourquoi la dispersivité, dépendante du temps, est plus faible pour les solutés à sorption non-linéaire que pour les solutés à sorption linéaire, lors du régime pré-asymptotique. Des mélanges réduits ont également été observés pour des solutés à sorption non-linéaire, sous les mécanismes combinés de diffusion dans la matrice et de dégradation.
Resumen
La difusión intersticial y la adsorción se encuentran entre los procesos clave que impactan la eficiencia de la atenuación natural en el subsuelo. Mientras que estos procesos se han estudiado extensamente en medios fracturados existe información limitada acerca de la no linealidad de la adsorción. Para abordar esta situación se ha desarrollado un modelo numérico que acopla la difusión intersticial y la adsorción no lineal a la escala de una sola fractura usando el concepto de porosidad doble. El estudio se restringe a condiciones limitantes de fuente de soluto constante y continuo. Se investiga la influencia de las intensidades de adsorción sobre el coeficiente de dispersión-macro y dispersividad usando un método de momentos espaciales. Los resultados sugieren que la mezcla de solutos disminuye significativamente mediante comportamiento de adsorción no lineal, en relación con la mezcla causada por difusión intersticial para solutos con adsorción lineal. Se observa que la magnitud de la dispersividad dependiente del tiempo durante el régimen pre-asintótico es más baja para solutos con adsorción no lineales en relación a los solutos con adsorción lineal. También se observa mezcla reducida para solutos con adsorción no lineal bajo mecanismos combinados de difusión intersticial y desintegración.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abulaban A, Nieber JL (2000) Modeling the effects of nonlinear equilibrium sorption on the transport of solute plumes in saturated heterogeneous porous media. Adv Water Resour 23(8):893–905
Abulaban A, Nieber JL, Misra D (1998) Modeling plume behavior for nonlinearly sorbing solutes in saturated homogeneous porous media. Adv Water Resour 21:487–498
Acharya RC (2004) Upscaling of nonlinear reactive transport: from pore to core. PhD Thesis, Wageningen University, The Netherlands, 153 pp
Adams EE, Gelhar LW (1992) Field study of dispersion in a heterogeneous aquifer: 2. spatial moments analysis. Water Resour Res 28(12):3293–3307
Allen-King RM, Groenevelt H, Mackay DM, Warren CJ (1996) Nonlinear chlorinated-solvent sorption in four aquitards. J Contam Hydrol 22:203–221
Aris R (1956) On the dispersion of a solute in a fluid flowing through a tube. Proc Roy Soc London A 235:67–77
Ball WP, Roberts PV (1991a) Long term sorption of halogenated organic chemicals by aquifer materials: 1. equilibrium. Environ Sci Technol 25(7):1223–1236
Ball WP, Roberts PV (1991b) Long term sorption of halogenated organic chemicals by aquifer materials: 2. intraparticle diffusion. Environ Sci Technol 25(7):1237–1249
Banton O, Bangoy LM (1997) Hydrogeologie, multiscience ennvironnmentale des eaux souterraines [Hydrologeology, environmental multiscience of groundwater]. Presses de l’Universite du Quebec/AUPELF, Sainte-Foy, Quebec, 460 pp
Bear J (1993) Modeling flow and contaminant transport in fractured rocks. In: Bear J, Tsang C-F, de Marsily G (eds) Flow and contaminant transport in fractured rock. Academic, San Diego, CA, pp 1–37
Bosma WJP, van der Zee SEATM (1995) Dispersion of a continuously injected, nonlinearly adsorbing solute in chemically or physically heterogeneous porous formations. J Contam Hydrol 18(3):181–198
Boving TB, Grathwohl P (2001) Tracer diffusion coefficients in sedimentary rocks: correlation to porosity and hydraulic conductivity. J Contam Hydrol 53:85–100
Birgersson L, Widén H, Ågren T, Neretnieks I (1992) Tracer migration experiments in the Stripa mine 1980–1991. SKB STRIPA Technical Report TR 92–25, Swedish Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Company, Stockholm
Byegard J, Skarnemark G, Skålberg M (1991) Radioactive tracer study performed in a dipole geometry in a highly conductive fracture zone. Mater Res Soc Symp Proc 212:677–684
Chiou CT, Kile DE (1998) Deviations from sorption linearity on soils of polar and nonpolar organic compounds at low relative concentrations. Environ Sci Technol 32(3):338–343
Chiou CT, Kile DE, Rutherford DW, Sheng G, Boyd SA (2000) Sorption of selected organic compounds from water to a peat soil and its humic-acid and humin fractions: potential sources of the sorption nonlinearity. Environ Sci Technol 34(7):1254–1258
Crawford J, Moreno L, Neretnieks I (2003) Determination of the flow-wetted surface in fractured media. J Contam Hydrol 61:361–369
Curtis GP, Roberts PV, Reinhard M (1986) A natural gradient experiment on solute transport in a sand aquifer: 4. sorption of organic solutes and its influence on mobility. Water Resour Res 22(13):2059–2067
Cvetkovic V, Selroos JO, Cheng H (1999) Transport of reactive solute in single fractures. J Fluid Mech 318:335–356
D’Alessandro M, Mousty F, Bidoglio G, Guimerà J, Benet I, Sánchez-Vila X, García Gutiérrez M, Yllera De Llano A (1997) Field tracer experiment in a low permeability fractured medium: results from El Berrocal site. J Contam Hydrol 26(1–4):189–201
Ezzedine S, Rubin Y (1997) Analysis of the Cape Cod tracer data. Water Resour Res 33(1):1–11
Fischer HB, List EJ, Koh RCY, Imberger J, Brooks NH (1979) Mixing in inland and coastal waters. Academic, San Diego, CA
Freeze JF, Cherry JA (1979) Groundwater. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ
Freyberg DL (1986) A natural gradient experiment on solute transport in a sand aquifer: 2. spatial moments and the advection and dispersion of nonreactive tracers. Water Resour Res 22(13):2031–2036
Garabedian SP, LeBlanc DR, Gelhar LW, Celia MA (1991) Large-scale natural gradient tracer test in sand and gravel, Cape Cod, Massachusetts: 2. analysis of spatial moments for a nonreactive tracer. Water Resour Res 27(5):911–924
Gelhar LW (1993) Stochastic subsurface hydrology. Prentice-Hall, Englewood cliffs, NJ
Goltz MN, Roberts PV (1987) Using the method of moments to analyze three-dimensional diffusion-limited solute transport from temporal and spatial perspectives. Water Resour Res 23(8):1575–1585
Grisak GE, Pickens JF (1980) Solute transport through fractured media: 1. the effect of matrix diffusion. Water Resour Res 16(4):719–730
Guven O, Molz FJ, Melville JG (1984) An analysis of dispersion in a stratified aquifer. Water Resour Res 20(10):1337–1354
Hadermann J, Heer W (1996) The Grimsel (Switzerland) migration experiment: integrating field experiments, laboratory investigations and modelling. J Contam Hydrol 21:87–100
Haggerty R, Fleming SW, Meigs LC, McKenna SA (2001) Tracer tests in a fractured dolomite: 2. analysis of mass transfer in single-well injection-withdrawal tests. Water Resour Res 37(5)1129–1142
Hamaker JW, Thompson JM (1972) Adsorption. In: Goring CM, Hamaker JW (eds) Organic chemicals in the soil environment. Dekker, New York
Heath MT (2002) Scientific computing: an introductory survey, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Heer W, Hadermann J (1994) Grimsel test site: modelling radionuclide migration field experiments. Nagra Technical Report 94–18, National Cooperative for the Disposal of Radioactive Waste, Wettingen, Switzerland
Himmelsbach T, Hotzl H, Maloszewski P (1998) Solute transport processes in a highly permeable fault zone of Lindau fractured rock test site (Germany). Ground Water 36(5):792–800
Horn FJM, Kipp RL Jr (1971) Induced transport in pulsating flow. AIChE J 17:621
Huang W, Young TM, Schlautman MA, Yu H, Weber WJ Jr (1997) A distributed reactivity model for sorption by soils and sediments: 9. general isotherm nonlinearity and applicability of the dual reactive domain model. Environ Sci Technol 31(6):1703–1710
Huyakorn PS, Pinder GF, (1983) Computational methods in subsurface flow. Academic, San Diego, CA, 473 pp
Huyakorn PS, Lester BH, Mercer JW (1983) An efficient finite element technique for modeling transport in fractured porous media: 1, single species transport. Water Resour Res 19(3):841–854
Karapanagioti HK, Sabatini DA (2000) Impacts of heterogeneous organic matter on phenanthrene sorption: different aquifer depths. Environ Sci Technol 34(12):2453–2460
Karapanagioti HK, Kleineidam S, Sabatini DA, Grathwohl P, Ligouis B (2000) Impact of heterogeneous organic matter on phenanthrene sorption: equilibrium and kinetic studies with aquifer material. Environ Sci Technol 34(3):406–414
Kennedy CA, Lennox WC (1995) Control volume model of solute transport in a single fracture. Water Resour Res 31(2):313–322
Kleineidam S, Rugner H, Ligouis B, Grathwohl P (1999) Organic matter facies and equilibrium sorption of phenanthrene. Environ Sci Technol 33(10):1637–1644
Landstrom O, Klockars CE, Persson O, Andersson K, Torstenfelt B, Allard B, Larsson SA, Tullborg E-L (1982) A comparison of in-situ radionuclide migration studies in the Studsvik area and laboratory measurements. In: Lutze W (ed) Scientific basis for nuclear waste management–V. Elsevier, New York
Maloszewski P, Zuber A (1985) On the theory of tracer experiments in fissured rocks with a porous matrix. J Hydrol 79:333–358
Maloszewski P, Zuber A (1990) Mathematical modeling of tracer behavior in short-term tracer experiments in fissured rocks. Water Resour Res 26:1517–1528
Maloszewski P, Zuber A (1991) Influence of matrix diffusion and exchange reactions on radiocarbon ages in fissured carbonate aquifers. Water Resour Res 27(8):1937–1945
Maloszewski P, Zuber A (1992) On the calibration and validation of mathematical models for the interpretation of tracer experiments in groundwater. Adv Water Resour 15:47–62
McCarty PL, Reinhard M, Rittman BE (1981) Trace organics in ground water. Environ Sci Technol 15:40–51
McGinley PM, Katz LE, Weber WJ Jr (1996) Competitive sorption and displacement of hydrophobic organic contaminants in saturated subsurface soil systems. Water Resour Res 32:3571–3577
Montas HJ, Mohtar RH, Hassan AE, AlKhal FA (2000) Heuristic space-time design of monitoring wells for contaminant plume characterization in stochastic flow fields. J Contam Hydrol 43:271–301
Moreno L, Neretnieks I (1993) Fluid flow and solute transport in a network of channels. J Contam Hydrol 14:163–192
Neretnieks I (1993) Solute transport in fractured rock: applications to radionuclide waste repositories. In: Bear J, Tsang CF, de Marsily G (eds) Flow and contaminant transport in fractured rock. Academic, San Diego, CA, pp 39–127
Neretnieks I (1980) Diffusion in the rock matrix: an important factor in radionuclide retardation? J Geophys Res 85(B8):4379–4397
Neretnieks I (1981) Age dating of groundwater in fissured rock: influence of water volume in micropores. Water Resour Res 17(2):421–422
Pinder GF (1984) Groundwater contaminant transport modeling. Environ Sci Technol 18:108A–114A
Rasmuson A, Neretnieks I (1981) Migration of radionuclides in fissured rock: the influence of micropore diffusion and longitudinal dispersion. J Geophys Res 86(B5):3749–3758
Rehfeldt K, Tompson A, Hassan A, Reimus P, Halford K (2004) The role of dispersion in radionuclide transport: data and modeling requirements. Report prepared for U.S. Department of Energy under Contract No. DE-AC52-03NA99205, DOE, Washington, DC
Rivett MO, Allen-King RM (2003) A controlled field experiment on groundwater contamination by a multicomponent DNAPL: dissolved-plume retardation. J Contam Hydrol 66:117–146
Sato H (1999) Matrix diffusion of simple cations, anions, neutral species in fractured crystalline rocks. Nucl Technol 127(2):199–211
Sekhar M, Suresh Kumar G, Misra D (2006) Numerical modeling and analysis of solute velocity and macro-dispersion for linearly and non-linearly sorbing solutes in a single fracture with matrix diffusion. J Hydrol Eng 11(4):319–328
Shan C, Pruess K (2005) Sorbing tracers: a potential tool for determining effective heat transfer area in hot fractured rock systems. SGP-TR-176 Proceedings, Thirtieth Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, California, 31 January–2 February 2005
Simon W, Reichter P (1997) Properties of exact and approximate traveling wave solutions for transport with nonlinear and nonequilibrium sorption. Water Resour Res 33(5):1139–1147
Srivastava R, Brusseau ML (1996) Nonideal transport of reactive solutes in heterogeneous porous media: 1. numerical model development and moment analysis. J Contam Hydrol 24(2):117–143
Sudicky EA, Frind EO (1982) Contaminant transport in fractured porous media: analytical solutions for a system of parallel fractures. Water Resour Res 18(6):1634–1642
Suresh Kumar G (2004) Modeling and analysis of solute transport in a single fracture with matrix diffusion. PhD Thesis, Indian Institute of Science, IISc(Bangalore), 121 pp
Tang DH, Frind EO, Sudicky EA (1981) Contaminant transport in fractured porous media: analytical solution for a single fracture. Water Resour Res 17(3):467–480
Taylor GE (1953) Dispersion of soluble matter in solvent flowing slowly through a tube. Proc R Soc A London 219:186–203
Tsang YW, Tsang CF (2001) A particle-tracking method for advective transport in fractures with diffusion into finite matrix blocks. Water Resour Res 37(3):831–835
Vereecken H, Doring U, Hardelauf H, Jaekel U, Hashagen U, Neuendorf O, Schwarze H, Seidemann R (2000) Analysis of solute transport in a heterogeneous aquifer: the Krauthausen field experiment. J Contam Hydrol 45:329–358
Wallach R, Parlange J-Y (1998) Modeling transport in a single crack by the dual-porosity concept with a boundary layer at the interface. J Contam Hydrol 34:121–138
Weber WJJ, McGinley PM, Katz LE (1991) Sorption phenomena in subsurface systems: concepts, models and effects on contaminant fate and transport. Water Res 25(5):499–528
Wels C, Smith L, Vandergraaf T (1996) Influence of specific surface area on transport of sorbing solutes in fractures: an experimental analysis. Water Resour Res 32(7):1943–1954
Xia G, Ball WP (1999) Adsorption-partitioning uptake of nine low polarity organic chemicals on a natural sorbent. Environ Sci Technol 33(2):262–269
Xia G, Ball WP (2000) Polanyi-based model for the competitive sorption of low-polarity organic contaminants on a natural sorbent. Environ Sci Technol 34(7):1246–1253
Xing B, Pignatello JJ (1997) Dual-mode sorption of low-polarity compounds in glassy poly(vinyl chloride) and soil organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 31(3):792–799
Young DF, Ball WP (1999) Two-region linear/nonlinear sorption modeling: batch and column experiments. Environ Toxicol Chem 18(8):1686–1693
Acknowledgements
Thanks are extended to the associate editor and the anonymous reviewers whose editorial and substantive comments improved the paper. Thanks also go to the Managing Editor (Prof C. Simmons) and Technical Editorial Advisor (Mrs. Sue Duncan) for their editorial comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suresh Kumar, G. Effect of sorption intensities on dispersivity and macro-dispersion coefficient in a single fracture with matrix diffusion. Hydrogeol J 16, 235–249 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-007-0234-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-007-0234-5