Abstract
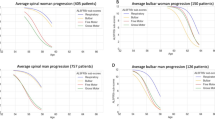
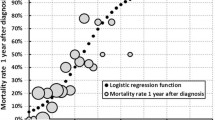
Very few studies examined trend over time of the revised Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Functional Rating Scale (ALSFRS-R) and factors influencing it; previous studies, then, included only patients attending tertiary ALS Centres. We studied ALSFRS-R decline, factors influencing this trend and survival in a population-based setting. From 2009 onwards, a prospective registry records all incident ALS cases among residents in Emilia Romagna (population: 4.4 million). For each patient, demographic and clinical details (including ALSFRS-R) are collected by caring physicians at each follow-up. Analysis was performed on 402 incident cases (1279 ALSFRS-R assessments). The average decline of the ALSFRS-R was 0.60 points/month during the first year after diagnosis and 0.34 points/month in the second year. ALSFRS-R decline was heterogeneous among subgroups. Repeated measures mixed model showed that ALSFRS-R score decline was influenced by age at onset (p < 0.01), phenotype (p = 0.01), body mass index (BMI) (p < 0.01), progression rate at diagnosis (ΔFS) (p < 0.01), El Escorial Criteria—Revised (p < 0.01), and FVC% at diagnosis (p < 0.01). Among these factors, at multivariate analysis, only age, site of onset and ΔFS independently influenced survival. In this first population-based study on ALSFRS-R trend, we confirm that ALSFRS-R decline is not homogeneous among ALS patients and during the disease. Factors influencing ALSFRS-R decline may not match with those affecting survival. These disease modifiers should be taken into consideration for trials design and in clinical practice during discussions with patients on prognosis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hardiman O, van den Berg LH, Kiernan MC (2011) Clinical diagnosis and management of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Rev Neurol 7:639–649. doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2011.153
Cedarbaum JM, Stambler N, Malta E, Fuller C, Hilt D, Thurmond B, Nakanishi A (1999) The ALSFRS-R: a revised ALS functional rating scale that incorporates assessments of respiratory function. BDNF ALS Study Group (Phase III). J Neurol Sci 169:13–21
Kaufmann P, Levy G, Montes J, Buchsbaum R, Barsdorf AI, Battista V, Arbing R, Gordon PH, Mitsumoto H, Levin B (2007) Thompson JL; QALS study group. Excellent inter-rater, intra-rater, and telephone-administered reliability of the ALSFRS-R in a multicenter clinical trial. Amyotroph Lateral Scler 8:42–46
Kasarskis EJ, Dempsey-Hall L, Thompson MM, Luu LC, Mendiondo M, Kryscio R (2005) Rating the severity of ALS by caregivers over the telephone using the ALSFRS-R. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord. 6:50–54
Miano B, Stoddard GJ, Davis S, Bromberg MB (2004) Interevaluator reliability of the ALS functional rating scale. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 5:235–239
The Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Functional Rating Scale (1996) Assessment of activities of daily living in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. The ALS CNTF treatment study (ACTS) phase I-II Study Group. Arch Neurol 53:141–147
Kaufmann P, Levy G, Thompson JL, Delbene ML, Battista V, Gordon PH, Rowland LP, Levin B, Mitsumoto H (2005) The ALSFRS-R predicts survival time in an ALS clinic population. Neurology 64:38–43
Gordon PH, Cheng B, Salachas F, Pradat PF, Bruneteau G, Corcia P, Lacomblez L, Meininger V (2010) Progression in ALS is not linear but is curvilinear. J Neurol 257:1713–1717. doi:10.1007/s00415-010-5609-1
Mandrioli J, Biguzzi S, Guidi C, Venturini E, Sette E, Terlizzi E, Ravasio A, Casmiro M, Salvi F, Liguori R, Rizzi R, Pietrini V, Chierici E, Santangelo M, Granieri E, Mussuto V, Borghi A, Rinaldi R, Fini N, Georgoulopoulou E, De Pasqua S, Vinceti M, Bonvicini F, Errals Group, Ferro S, D’Alessandro R (2014) Epidemiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in Emilia Romagna Region (Italy): a population based study. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener 15:262–268. doi:10.3109/21678421.2013.865752
Chiò A, Calvo A, Moglia C, Mazzini L, Mora G, PARALS study group (2011) Phenotypic heterogeneity of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a population based study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 82:740–746. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2010.235952
Kimura F, Fujimura C, Ishida S, Nakajima H, Furutama D, Uehara H, Shinoda K, Sugino M, Hanafusa T (2006) Progression rate of ALSFRS-R at time of diagnosis predicts survival time in ALS. Neurology 66:265–267
Brooks BR, Miller RG, Swash M, Munsat TL, World Federation of Neurology Research Group on Motor Neuron Diseases (2000) El Escorial revisited: revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 1:293–299
Gomeni R, Fava M, Pooled Resource Open-Access ALS Clinical Trials Consortium (2014) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis disease progression model. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener. 15:119–129. doi:10.3109/21678421.2013.838970
Creemers H, Grupstra H, Nollet F, van den Berg LH, Beelen A (2015) Prognostic factors for the course of functional status of patients with ALS: a systematic review. J Neurol 262:1407–1423. doi:10.1007/s00415-014-7564-8
Gordon PH, Cheng B, Montes J, Doorish C, Albert SM, Mitsumoto H (2007) Outcome measures for early phase clinical trials. Amyotroph Lateral Scler 8:270–273
Watanabe H, Atsuta N, Nakamura R, Hirakawa A, Watanabe H, Ito M, Senda J, Katsuno M, Izumi Y, Morita M, Tomiyama H, Taniguchi A, Aiba I, Abe K, Mizoguchi K, Oda M, Kano O, Okamoto K, Kuwabara S, Hasegawa K, Imai T, Aoki M, Tsuji S, Nakano I, Kaji R, Sobue G (2015) Factors affecting longitudinal functional decline and survival in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener 16:230–236. doi:10.3109/21678421.2014.990036
Franchignoni F, Mora G, Giordano A, Volanti P, Chiò A (2013) Evidence of multidimensionality in the ALSFRS-R Scale: a critical appraisal on its measurement properties using Rasch analysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 84:1340–1345. doi:10.1136/jnnp-2012-304701
Tanaka Y, Yoshikura N, Harada N, Yamada M, Koumura A, Sakurai T, Hayashi Y, Kimura A, Hozumi I, Inuzuka T (2012) Late-onset patients with sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in Japan have a higher progression rate of ALSFRS-R at the time of diagnosis. Intern Med 51:579–584
Magnus T, Beck M, Giess R, Puls I, Naumann M, Toyka KV (2002) Disease progression in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: predictors of survival. Muscle Nerve 25:709–714
Castrillo-Viguera C, Grasso DL, Simpson E, Shefner J, Cudkowicz ME (2010) Clinical significance in the change of decline in ALSFRS-R. Amyotroph Lateral Scler. 11:178–180. doi:10.3109/17482960903093710
Chiò A, Canosa A, Gallo S et al (2011) ALS clinical trials: do enrolled patients accurately represent the ALS population? Neurology 77:1432–1437
Franchignoni F, Mandrioli J, Giordano A, Ferro S, ERRALS Group (2015) A further Rasch study confirms that ALSFRS-R does not conform to fundamental measurement requirements. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener 27:1–7 [Epub ahead of print]
Wicks P, Massagli MP, Wolf C, Heywood J (2009) Measuring function in advanced ALS: validation of ALSFRS-EX extension items. J Eur Neurol 16:353–359
Miller RG, Moore DH, Spitalny GM, Gordon PH (2007) Is the ALSFRS-R rate of decline linear over time? Amyotroph Lateral Scler 8(Suppl 1):140–155
Acknowledgments
Jessica Mandrioli has received research support from Regione EmiIia Romagna (Programma di ricerca Regione-Università 2010–2012, area 2, Ricerca per il Governo Clinico). Emilia Romagna Registry for ALS is supported by a grant from the Emilia Romagna Regional Health Authority. The authors acknowledge all the ERRALS groups.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix: ERRALS group
Appendix: ERRALS group
Project coordinator: J. Mandrioli
Collaborating centres:
Department of Neuroscience, St. Agostino Estense Hospital, Modena, Italy (J. Mandrioli, N. Fini, E. Georgoulopoulou, A. Fasano, P. Nichelli)
Department of Neurology, Bufalini Hospital, Cesena, Italy (S. Biguzzi, E. Venturini, M. G. Passarin)
Department of Neurology, Forlì Hospital, Forlì, Italy (C. Guidi, W. Neri)
Department of Neurology, St. Anna Hospital, Ferrara, Italy (E. Sette, V. Tugnoli, M. R. Tola)
Department of Neurology, G. Da Saliceto Hospital, Piacenza, Italy (E. Terlizzi, D. Guidetti)
Department of Neurology, Infermi Hospital, Rimini, Italy (M. Currò Dossi, M. Pasquinelli, J. Andruccioli, A. Ravasio)
Department of Neurology, Faenza and Ravenna Hospital, Ravenna, Italy (M. Casmiro, F. Rasi)
Department of Neurology and IRCCS Istituto delle Scienze Neurologiche di Bologna, Bellaria Hospital, Bologna, Italy (F. Salvi, I. Bartolomei, R. Michelucci)
Department of Biomedical and Neuromotor Science and IRCCS Istituto delle Scienze Neurologiche di Bologna, University of Bologna, Bologna, Italy (P. Avoni, S. De Pasqua, R. Liguori)
Department of Neurology, IRCCS Arcispedale Santa Maria Nuova, Reggio Emilia, Italy (R. Rizzi, E. Canali, N. Marcello)
Department of Neuroscience, University of Parma, Parma, Italy (A. Grassi, L. Delay, V. Pietrini)
Department of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, Respiratory Disease and Lung Function Unit, University of Parma, Parma, Italy (M. Aiello)
Department of Neurology, Fidenza Hospital, Parma, Italy (E. Chierici, E. Montanari)
Department of Neurology, Carpi Hospital, Modena, Italy (M. Santangelo, S. Amidei, G. Greco)
Department of Neuroscience, University of Ferrara, Ferrara, Italy (I. Casetta, E. Groppo, E. Granieri)
Department of Neurology, Imola Hospital, Bologna, Italy (P. De Massis, V. Mussuto)
Department of Neurology and IRCCS Istituto delle Scienze Neurologiche di Bologna, Maggiore Hospital, Bologna, Italy (A. Borghi, A. Gabellini, T. Sacquegna)
Department of Neuroscience, St. Orsola-Malpighi University Hospital, Bologna, Italy (R. Rinaldi, F. Cirignotta)
Department of Hospital Services, Emilia Romagna Regional Health Authority, Bologna, Italy (S. Ferro)
Neuroepidemiology Unit, IRCCS Istituto delle Scienze Neurologiche di Bologna, Italy (R. D’Alessandro)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mandrioli, J., Biguzzi, S., Guidi, C. et al. Heterogeneity in ALSFRS-R decline and survival: a population-based study in Italy. Neurol Sci 36, 2243–2252 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-015-2343-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-015-2343-6