Abstract
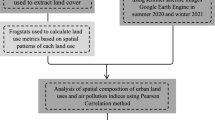
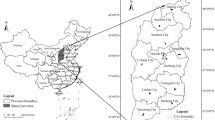
Air pollution has always been a concern with increasing urbanization and poor land use planning adding to the problem. This study sets out to investigate the relationship between land use composition of an area and its ambient concentration of 10-μm-or-less particulate matter (PM10). For this study, Iskandar Malaysia has been chosen as the study area. To compensate for the limited number of air quality monitoring stations in the study area, Terra MODIS aerosol optical depth Level 2 products are used to assess PM10 concentration spatially. Land use data were developed from LANDSAT images used together with the land use database from the local authority. Finally, the relationship between land use composition and concentrations of PM10 in the study area are explained using contour ternary plots. The plots show how different compositions of three major urban land uses (residential, commercial, industrial) in an area results in different concentration levels of PM10. Concentrations of PM10 are evidently more affected by commercial land use, followed by industrial land use. Hence, responsible authorities in Iskandar Malaysia could control or reduce air pollution in an area by planning a better land use composition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abas MR, Oros DR, Simoneit BRT (2004) Biomass burning as the main source of organic aerosol particulate matter in Malaysia during haze episodes. Chemosphere 55:1089–1095
Afroz R, Hassan MN, Ibrahim NA (2003) Review air pollution and health impacts in Malaysia. Environ Res 92(2):71–77
Aja OC, Al-Kayiem HH (2013) Review of municipal solid waste management options in Malaysia, with an emphasis on sustainable waste-to-energy options. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 16:693–710
Department of Environment, DOE Malaysia (2015) Malaysia environmental quality report 2014. Department of Environment, Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment, Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur
Ee-Ling O, Mustaffa NIH, Amil N, Khan MF, Latif MT (2015) Source contribution of PM 2.5 at different locations on the Malaysian Peninsula. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 94:537–542
Fuller DO, Murphy K (2006) The ENSO-fire dynamic in insular Southeast Asia. Clim Change 74(4):435–455
Haq G, Schwela D (2008) Urban air pollution in Asia, foundation course on air quality management in Asia. Stockholm Environment Institute, Stockholm
Harrison RM (2004) Key pollutants—airborne particles. Sci Total Environ 334–335(2004):3–8. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.04.059
Hyer EJ, Chew BN (2010) Aerosol transport model evaluation of an extreme smoke episode in Southeast Asia. Atmos Environ 44(11):1422–1427
Ling OHL, Ting KH, Shaharuddin A, Kadaruddin A, Yaakob MJ (2010) Urban growth and air quality in Kuala Lumpur City, Malaysia. Environ Asia 3:123–128
Majumdar D, Majhi BK, Dutta A, Mandal R, Jash T (2015) Study on possible economic and environmental impacts of electric vehicle infrastructure in public road transport in Kolkata. Clean Technol Environ Policy 17:1093–1101. doi:10.1007/s10098-014-0868-7
Nguyen DC (2010) Influence of transboundary pollution of biomass burning on ionic compounds in urban particulates. Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, National University of Singapore, Singapore
Ouyang Y, Zhang JE, Cui L (2014) Estimating impacts of land use on groundwater quality using trilinear analysis. Environ Monit Assess 186:5353–5362. doi:10.1007/s10661-014-3784-8
Ramanathan V, Carmichael G (2008) What is black carbon, Center for Climate and Energy Solution. Nat Geosci 1:221–227
Resitoglu IA, Altinisik K, Keskin A (2015) The pollutant emissions from diesel-engine vehicles and exhaust aftertreatment systems. Clean Technol Environ Policy 17:15–27. doi:10.1007/s10098-014-0793-9
Rizzo A, Glasson J (2012) Iskandar Malaysia. Cities 29(6):417–427
Sellitto MA, Borchardt M, Pereira GM, Bubicz ME (2015) Tool for environmental performance assessment of city bus transit operations: case studies. Clean Technol Environ Policy 17:1053–1064. doi:10.1007/s10098-014-0892-7
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the funding support for this work provided by Ministry of Education, Malaysia and Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM) under Others Grant of Vot number R.J1300000.7301.4B145 and Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) under the Scheme of SATREPS Program (Science and Technology Research Partnership for Sustainable Development) for the Project Development of Low Carbon Scenario for Asian Region.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zahari, M.A.Z., Majid, M.R., Ho, C.S. et al. Relationship between land use composition and PM10 concentrations in Iskandar Malaysia. Clean Techn Environ Policy 18, 2429–2439 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-016-1263-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-016-1263-3