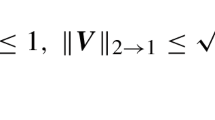Abstract
We produce approximation bounds on a semidefinite programming relaxation for sparse principal component analysis. The sparse maximum eigenvalue problem cannot be efficiently approximated up to a constant approximation ratio, so our bounds depend on the optimum value of the semidefinite relaxation: the higher this value, the better the approximation. In particular, these bounds allow us to control approximation ratios for tractable statistics in hypothesis testing problems where data points are sampled from Gaussian models with a single sparse leading component.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amini, A.A., Wainwright, M.: High-dimensional analysis of semidefinite relaxations for sparse principal components. Ann. Stat. 37(5B), 2877–2921 (2009)
Ben-Tal, A., Nemirovski, A.: On tractable approximations of uncertain linear matrix inequalities affected by interval uncertainty. SIAM J. Optim. 12(3), 811–833 (2002)
Ben-Tal, A., Nemirovski, A.: Non-Euclidean restricted memory level method for large-scale convex optimization. Math. Program. 102(3), 407–456 (2005)
Benaych-Georges, F., Guionnet, A., Maida, M.: Fluctuations of the extreme eigenvalues of finite rank deformations of random matrices. Electron. J. Probab. 16(60), 1621–1662 (2011), ISSN 1083–6489, doi:10.1214/EJP.v16-929
Berthet, Q., Rigollet, P.: Optimal Detection of Sparse Principal Components in High Dimension. Arxiv preprint arXiv:1202.5070 (2012)
Candes, E., Tao, T.: The Dantzig selector: statistical estimation when p is much larger than n. Ann. Stat. 35(6), 2313–2351 (2007)
Clarkson, K.L.: Coresets, sparse greedy approximation, and the Frank–Wolfe algorithm. ACM Trans. Algorithms (TALG) 6(4), 63 (2010)
d’Aspremont, A., El Ghaoui, L., Jordan, M.I., Lanckriet, G.R.G.: A direct formulation for sparse PCA using semidefinite programming. SIAM Rev. 49(3), 434–448 (2007)
d’Aspremont, A., Bach, F., El Ghaoui, L.: Optimal solutions for sparse principal component analysis. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 9, 1269–1294 (2008)
El Ghaoui, L.: On the Quality of a Semidefinite Programming Bound for Sparse Principal Component Analysis. ArXiV math. OC/0601448 (2006)
Goemans, M.X., Williamson, D.P.: Improved approximation algorithms for maximum cut and satisfiability problems using semidefinite programming. J. ACM 42, 1115–1145 (1995)
Jaggi, M.: Convex Optimization Without Projection Steps. Arxiv preprint arXiv:1108.1170 (2011)
Journée, M., Bach, F., Absil, P.A., Sepulchre, R.: Low-Rank Optimization for Semidefinite Convex Problems. Arxiv preprint arXiv:0807.4423 (2008)
Journée, M., Nesterov, Y., Richtárik, P., Sepulchre, R.: Generalized Power Method for Sparse Principal Component Analysis. arXiv:0811.4724 (2008)
Mezard, M., Montanari, A.: Information, Physics, and Computation. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2009)
Mezard, M., Parisi, G., Virasoro, M.A.: Spin Glass Theory and Beyond, vol. 9. World Scientific, Singapore (1987)
Nesterov, Y.: Smooth minimization of non-smooth functions. Math. Program. 103(1), 127–152 (2005)
Papailiopoulos, D.S., Dimakis, A.G., Korokythakis, S.: Sparse PCA Through Low-Rank Approximations. arXiv preprint arXiv:1303.0551 (2013)
Spielman, D., Teng, S.H.: Smoothed analysis of algorithms: Why the simplex algorithm usually takes polynomial time. In: Proceedings of the Thirty-Third Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, pp. 296–305. ACM (2001)
Talagrand, M.: Mean Field Models for Spin Glasses: Basic Examples, vol. 1. Springer, Berlin (2010)
Zwick, U.: Outward rotations: a tool for rounding solutions of semidefinite programming relaxations, with applications to max cut and other problems. In: Proceedings of the Thirty-First Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, pp. 679–687. ACM (1999)
Acknowledgments
AA would like to acknowledge partial support from NSF Grants SES-0835550 (CDI), CMMI-0844795 (CAREER), CMMI-0968842, a starting grant from the European Research Council (project SIPA), a Peek junior faculty fellowship, a Howard B. Wentz Jr. award and a gift from Google. FB would like to acknowledge support from a starting grant from the European Research Council (project SIERRA) and the INRIA associated-team StatWeb. The authors would like to thank Philippe Rigollet and Quentin Berthet for very constructive discussions and introducing them to the detection problem in Sect. 3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
d’Aspremont, A., Bach, F. & Ghaoui, L.E. Approximation bounds for sparse principal component analysis. Math. Program. 148, 89–110 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10107-014-0751-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10107-014-0751-7