Abstract
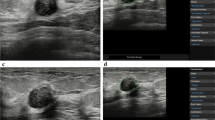
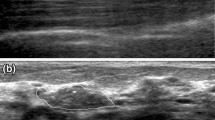
The objective of this study is to retrospectively investigate whether using the newly developed algorithms would improve radiologists’ accuracy for discriminating malignant masses from benign ones on ultrasonographic (US) images. Five radiologists blinded to the histological results and clinical history independently interpreted 226 cases according to the sonographic lexicon of the fourth edition of the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System and assigned a final assessment category to indicate the probability of malignancy. For each case, each radiologist provided three diagnoses: first with the original images, subsequently with the assistant of the resulting images processed by the proposed CAD algorithms which are called as processed images, and another using the processed images only. Observers’ malignancy rating data were analyzed with the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. For reading only with the processed images, areas under the ROC curve (A z) of each reader (0.863, 0.867, 0.859, 0.868, 0.878) were better than that with the original images (0.772, 0.807, 0.796, 0.828, 0.846), difference of the average A z between the twice reading was significant (p < 0.001). Compared with the results single used processed images, A z of utilizing the combined images were increased (0.866, 0.885, 0.872, 0.894, 0.903), but the difference is not statistically significant (p = 0.081). The proposed CAD method has potential to be a good aid to radiologists in distinguishing malignant breast solid masses from benign ones.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T, Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2008. Cancer J Clin 58:71–96, 2008
Smigal C, Jemal A, Ward E, Cokkinides V, Smith R, Howe HL, Thun M: Trends in breast cancer by race and ethnicity: update 2006. CA Cancer J Clin 56:168–183, 2006
Rajkumar SV, Hartmann LC: Screening mammography in women aged 40–49 years. Medicine 78:410–416, 1999
American College of Radiology: Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS), Ultrasound, 4th edition. Reston: American College of Radiology, 2003 Available at: http://www.acr.org/s_acr/sec.asp?CID=882&DID=14550. Accessed September 8, 2004
Hong AS, Rosen EL, Soo MS, Baker JA: BI-RADS for sonography: positive and negative predictive values of sonographic features. Am J Roentgenol 184:1260–1265, 2005
Costantini M, Belli P, Ierardi C, Franceschini G, La Torre G, Bonomo L: Solid breast mass characterisation: use of the sonographic BI-RADS classification. Radiol Med 112:877–894, 2007
Sehgal CM, Cary TW, Kangas SA, Weinstein SP, Schultz SM, Arger PH, Conant EF: Computer-based margin analysis of breast sonography for differentiating malignant and benign masses. J Ultrasound Med 23:1201–1209, 2004
Shen W, Chang R, Moon W, Chou Y, Huang C: Breast ultrasound computer-aided diagnosis using BI-RADS features. Acad Radiol 14:928–939, 2007
Chen CM, Chou YH, Han KC, Hung GS, Tiu CM, Chiou HJ, Chiou SY: Breast lesions on sonograms: computer-aided diagnosis with nearly setting-independent features and artificial neural networks. Radiology 226:504–514, 2003
Huang YL, Chen DR, Jiang YR, Kuo SJ, Wu HK, Moon WK: Computer-aided diagnosis using morphological features for classifying breast lesions on ultrasound. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 32:565–572, 2008
Sahiner B, Chan HP, Roubidoux MA, Hadjiiski LM, Helvie MA, Paramagul C, Bailey J, Nees AV, Blane C: Malignant and benign breast masses on 3D US volumetric images: effect of computer-aided diagnosis on radiologist accuracy. Radiology 242:716–724, 2007
Chen DR, Chang RF, Chen WM, Moon WK: Computer-aided diagnosis for 3-dimensional breast ultrasonography. Arch Surg 138:296–302, 2003
Jackson VP: The role of US in breast imaging. Radiology 177:305–311, 1990
Pal SK, Majumder DKD: Fuzzy Mathematical Approach to Pattern Recognition, New York: Wiley, 1986
Wu CM, Chen YC, Hsieh KS: Texture features for classification of ultrasonic liver images. IEEE Trans Med Imag 11:141–152, 1992
Laws KI: Texture Energy Measures. DARPA Image Understanding Workshop. Los Angeles, CA. 1979, pp 47–51
Guo Y, Cheng H-D, Huang J, Tian JW, Zhao W, Sun L, Su Y: Breast Ultrasound images enhancement using fuzzy logic. Ultrasound Med Biol 32:237–247, 2006
Wagner RF, Smith SW, Sandrik JM, Lopez H: Statistics of speckle in ultrasound B-scans. IEEE Trans Sonics Ultrason 30:156–163, 1983
Guo YH, Cheng HD, Tian JW, Zhang YT: A Novel approach to speckle reduction and its application to ultrasound medical images. Ultrasound Med Biol 35:628–640, 2009
Cheng HD, Li JG: Fuzzy homogeneity and scale space approach to color image segmentation. Pattern Recogn 35:373–393, 2002
Chan TF, Vese LA: Active contours without edges. IEEE Trans Image Process 10:266–277, 2001
Schoonjans F, Zalata A, Depuydt CE, Comhaire FH: MedCalc: a new computer program for medical statistics. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 48:257–262, 1995
Krupinski EA: Computer-aided detection in clinical environment: benefits and challenges for radiologists. Radiology 231:7–9, 2004
Gilbert FJ, Astley SM, McGee MA, Gillan MGC, Boggis CRM, Griffiths PM: Single reading with computer-aided detection and double reading of screening mammograms in the United Kingdom National Breast Screening Program. Radiology 241(1):47–53, 2006
Berg WA, D’Orsi CJ, Jackson VP, Bassett LW, Beam CA, Lewis RS, Crewson PE: Does training in the breast imaging reporting and data system (BI-RADS) improve biopsy recommendations or feature analysis agreement with experienced breast imagers at mammography? Radiology 224:871–880, 2002
Acknowledgement
Financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) is greatly appreciated; grant numbers: 30670546 and 60873142.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Wang, H., Guo, Y. et al. Novel Computer-Aided Diagnosis Algorithms on Ultrasound Image: Effects on Solid Breast Masses Discrimination. J Digit Imaging 23, 581–591 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-009-9245-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-009-9245-1