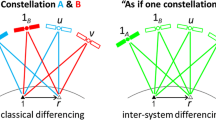
Abstract
Double-differenced (DD) ambiguities between overlapping frequencies from different GNSS constellations can be fixed to integers if the associated differential inter-system biases (DISBs) are well known. In this case, only one common pivot satellite is sufficient for inter-system ambiguity resolution. This will be beneficial to ambiguity resolution (AR) and real-time kinematic (RTK) positioning especially when only a few satellites are observed. However, for GPS and current operational BDS-2, there are no overlapping frequencies. Due to the influence of different frequencies, the inter-system DD ambiguities still cannot be fixed to integers even if the DISBs are precisely known. In this contribution, we present an inter-system differencing model for combined GPS and BDS single-frequency RTK positioning through real-time estimation of DISBs. The stability of GPS L1 and BDS B1 DISBs is analyzed with different receiver types. Along with parameterization and using the short-term stability of DISBs, the DD ambiguities between GPS and BDS pivot satellites and the between-receiver single-difference ambiguity of the GPS pivot satellite can be estimable jointly with the differential phase DISB term from epoch to epoch. Then the inter-system differencing model can benefit from the near time-constant DISB parameters and thus has better multi-epoch positioning performance than the classical intra-system differencing model. The combined GPS and BDS single-frequency RTK positioning performance is evaluated with various simulated satellite visibilities. It will be shown that compared with the classical intra-system differencing model, the proposed model can effectively improve the positioning accuracy and reliability, especially for severely obstructed situations with only a few satellites observed.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deng C, Tang W, Liu J, Shi C (2014) Reliable single-epoch ambiguity resolution for short baselines using combined GPS/BeiDou system. GPS Solut 18(3):375–386
Euler HJ, Goad CC (1991) On optimal filtering of GPS dual frequency observations without using orbit information. Bull Geod 65(2):130–143
Gao W, Gao C, Pan S (2017) A method of GPS/BDS/GLONASS combined RTK positioning for middle-long baseline with partial ambiguity resolution. Surv Rev 49(354):212–220
He H, Li J, Yang Y, Xu J, Guo H, Wang A (2014) Performance assessment of single- and dual-frequency BeiDou/GPS single-epoch kinematic positioning. GPS Solut 18(3):393–403
Jiang N, Xu Y, Xu T, Xu G, Sun Z, Schuh H (2017) GPS/BDS short-term ISB modelling and prediction. GPS Solut 21(1):163–175
Julien O, Alves P, Cannon ME, Zhang W (2003) A tightly coupled GPS/GALILEO combination for improved ambiguity resolution. In: Proceedings of the ION GNSS 2003 European navigation conference, Graz, Austria
Li X, Ge M, Dai X, Ren X, Mathias F, Jens W (2015) Accuracy and reliability of multi-GNSS real-time precise positioning: GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, and Galileo. J Geod 89(6):607–635
Li B, Lou L, Shen Y (2016) GNSS elevation-dependent stochastic modelling and its impacts on the statistic testing. J Surv Eng 142(2):04015012
Li G, Wu J, Zhao C, Tian Y (2017) Double differencing within GNSS constellations. GPS Solut 21(3):1161–1177
Montenbruck O, Hauschild A, Steigenberger P (2014) Differential code bias estimation using multi-GNSS observations and global ionosphere maps. Navigation 61(3):191–201
Nadarajah N, Khodabandeh A, Teunissen PJG (2015) Assessing the IRNSS L5-signal in combination with GPS, Galileo, and QZSS L5/E5a-signals for positioning and navigation. GPS Solut 20(2):289–297
Odijk D, Teunissen PJG (2008) ADOP in closed form for a hierarchy of multi-frequency single-baseline GNSS models. J Geod 82:473–492
Odijk D, Teunissen PJG (2013a) Characterization of between-receiver GPS-Galileo inter-system biases and their effect on mixed ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut 17(4):521–533
Odijk D, Teunissen PJG (2013b) Estimation of differential intersystem biases between the overlapping frequencies of GPS, Galileo, BeiDou and QZSS. In: Proceedings of 4th international colloquium scientific and fundamental aspects of the Galileo programme, December 4–6, Prague, Czech Republic
Odijk D, Nadarajah N, Zaminpardaz S, Teunissen PJG (2016) GPS, Galileo, QZSS and IRNSS differential ISBs: estimation and application. GPS Solut 21(2):439–450
Odolinski R, Teunissen PJG (2016) Single-frequency, dual-GNSS versus dual-frequency, single-GNSS: a low-cost and high-grade receivers GPS-BDS RTK analysis. J Geod 90(11):1255–1278
Odolinski R, Teunissen PJG, Odijk D (2014) Combined GPS + BDS + Galileo + QZSS for long baseline RTK positioning. In: Proceedings of ION GNSS 2014, Institute of Navigation, Tampa, FL, USA, September 8–12, pp 2326–2340
Odolinski R, Teunissen PJG, Odijk D (2015) Combined BDS, Galileo, QZSS and GPS single-frequency RTK. GPS Solut 19(1):151–163
Pan S, Meng X, Gao W, Wang S, Dodson A (2014) A new approach for optimizing GNSS positioning performance in harsh observation environments. J. Navigation 67(06):1029–1048
Paziewski J, Wielgosz P (2015) Accounting for Galileo-GPS intersystem biases in precise satellite positioning. J Geod 89(1):81–93
Paziewski J, Wielgosz P (2017) Investigation of some selected strategies for multi-GNSS instantaneous RTK positioning. Adv Space Res 59(1):12–23
Takasu T, Yasuda A (2010) Kalman-filter-based integer ambiguity resolution strategy for long-baseline RTK with ionosphere and troposphere estimation. In: Proceedings of ION GNSS 2010, Institute of Navigation, Portland, OR, USA, September 21–24, pp 161–171
Teunissen PJG (1995) The least squares ambiguity decorrelation adjustment: a method for fast GPS integer estimation. J Geod 70:65–82
Teunissen PJG, Verhagen S (2009) The GNSS ambiguity ratio-test revisited: a better way of using it. Surv Rev 41(312):138–151
Teunissen PJG, Odolinski R, Odijk D (2014) Instantaneous BeiDou + GPS RTK positioning with high cut-off elevation angles. J Geod 88(4):335–350
Tian Y, Ge M, Neitzel F, Zhu J (2017) Particle filter-based estimation of inter-system phase bias for real-time integer ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut 21(3):949–961
Torre AD, Caporali A (2015) An analysis of intersystem biases for multi-GNSS positioning. GPS Solut 19(2):297–307
Acknowledgements
This work is partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41574026), the National Key Technologies R&D Program (Grant No. 2016YFB0502101), the Primary Research and Development Plan of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. BE2016176) and the Scientific Research Foundation of Graduated School of Southeast University (Grant No.YBJJ1635). The authors gratefully acknowledge GNSS Research Centre of Curtin University for providing the multi-GNSS observation data. Thanks also go to the China Scholarship Council (CSC) for the funding of the first author’s living expenses during his study at the University of Nottingham in the UK. Miss Roxanne Parnham at the Sino-UK Geospatial Engineering Centre of the University of Nottingham is acknowledged for the proofreading.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, W., Meng, X., Gao, C. et al. Combined GPS and BDS for single-frequency continuous RTK positioning through real-time estimation of differential inter-system biases. GPS Solut 22, 20 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-017-0687-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-017-0687-5