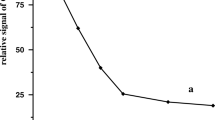
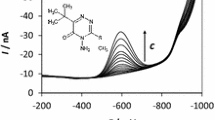
Abstract
Here, we show a fast and sensitive method for the determination of inorganic arsenic in natural waters using differential pulse cathodic stripping voltammetry. All the arsenite determinations were done in 2.0 mol L−1 HCl + 3.15 × 10−4 mol L−1 Cu(II) supporting electrolyte. 1 × 10−3 mol L−1 sodium thiosulphate was used as As(V) reducing agent. The detection limit was 0.5 μg L−1 for both species. The method has been applied to water samples collected in an arsenic-contaminated region of Brazil, in particular, to verify the efficiency of the solar oxidation and removal of arsenic process applied to these waters.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeloju SB, Young TM, Jagner D (1998) Constant current cathodic stripping potentiometric determination of arsenic on a mercury film electrode in the presence of copper ions. Anal Chim Acta 381:207–213
Barra CM, Santelli RE, Abrão JJ, de la Guardia M (2000) Especiação de arsênio – Uma revisão. Quím Nova 23:58–70
CONAMA (2005) Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente. Resolution no. 357, 17/03/2005, D.O.U. 31/03/05, Brasília (Brazil)
Chiu HF, Ho SC, Yang CY (2004) Mortality reduction after installation of tap-water supply system in an arseniasis-endemic area in Southwestern Taiwan. Lung Cancer 46:265–270
de Carvalho LM, Do Nascimento PC, Bohrer D (2004) Speciation analysis of arsenic compounds by voltammetric and polarographic methods: a comparative review of their main advantajes and applications. Quim Nova 27:261–269
Henze G, Joshi AP, Neeb R (1980) Determination of arsenic in the sub-ppb-range by differential pulse cathodic stripping voltammetry. Fresen J Anal Chem 300:267–272
Holak W (1980) Determination of arsenic by cathodic stripping voltammetry with a hanging mercury drop electrode. Anal Chem 52:2189–2192
Horwitz W (1982) Determination of arsenic by cathodic stripping voltammetry with a hanging mercury drop electrode. Anal Chem 54:67–81
Howard AG, Hunt LE (1993) A coupled photo-oxidation-hydride AAS detector for the HPLC of arsenic compounds. Anal Chem 65:2995–2998
Hug S, Wegelin M, Gechter D, Canonica L (2001) Solar oxidation and removal of arsenic at circumneutral pH in iron containing waters. Environ Sci Technol 35:2114–2121
Matschulat J, Borba RP, Deschamps E, Figueiredo BR, Gabrio T, Schwenk M (2000) Human and environmental contamination in the Iron Quadrangle. Appl Geochem 15:181–187
Miller JC, Miller JN (1993) Statistics for analytical chemistry, 3rd edn. Ellis Horwood
Ministério da Saúde (2004) Portaria no. 518, Brasília, 25 March 2004
Stockwell PB, Corns WT (1994) Environmental sensors based on atomic fluorescence, Analyst 119:1641–1646
WHO (World Health Organization) (1993) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 2nd edn, vol 1
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge CNPq for a Ph.D. thesis grant (CNPq No141305/2001−0), and Dr. Carol H. Collins for English revision.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pereira, M.d.S.S., Winter, E., Guimarães, J.R. et al. A simple voltammetric procedure for speciation and evaluation of As removal from water. Environ Chem Lett 5, 137–141 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-007-0094-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-007-0094-1