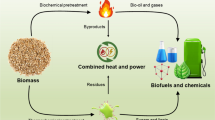
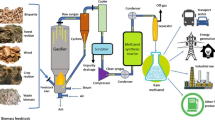
Abstract
Energy demands, pollution and global warming induced by globalization are rising, thus calling for alternative sources of energies. In particular, biofuels are increasingly used for transportation, electric power and heat energy generation. Biofuels can mitigate greenhouse gas emissions by up to 50%. Biofuels are produced from organic matter and waste such as dry lignocellulose, algae, yeast, restaurant greases, food grain, non-food grain and animal fats. Biofuel from crop residues can be promoted by government subsidies to reduce the fuel price and meet the requirement of industries, transportation and agricultural sectors.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACP:
-
Acyl carrier protein
- BTL:
-
Biomass to liquid
- BTUs:
-
British thermal units
- Cas:
-
CRISPR associated
- CCS:
-
Carbon capture and storage
- CHP:
-
Carbon heat and power
- CO2 :
-
Carbon dioxide
- CSLF:
-
Cellulose solvent-based lignocellulose fractionation
- CRISPR:
-
Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats
- DME:
-
Dimethyl ether
- DOE:
-
Department of Energy
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- EtOH:
-
Bioethanol
- eq/M.J:
-
Equivalent per megajoule
- 2-EH:
-
2-Ethylhexanol
- FAs:
-
Fatty acids
- FT:
-
Fischer–Tropsch
- g/g:
-
Gram by gram
- Gt:
-
Gigatonnes
- GHGs:
-
Greenhouse gases
- H2 :
-
Biohydrogen
- H2O:
-
Water
- H2S:
-
Hydrogen sulfide
- IBPGM:
-
Integrated biomass pyrolysis, gasification and methanol synthesis
- KOH:
-
Potassium hydroxide
- LHV:
-
Lower heating value
- MEC:
-
Microbial electrolysis cell
- MeOH:
-
Methanol
- MEF:
-
Microbial electrolysis cell
- MFC:
-
Microbial fuel cell
- Mo/Pt/WOx :
-
Molybdenum/platinum/tungsten oxide
- MT:
-
Million tonnes
- Mteo:
-
Million tonnes of oil equivalent
- NaOH:
-
Sodium hydroxide
- NER:
-
Net energy ratio
- NOX :
-
Nitrogen oxides
- NMB:
-
National mission on biodiesel
- OPEFB:
-
Oil palm empty fruit bunch
- PAHs:
-
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
- PBRs:
-
Photo-bioreactors
- PEM:
-
Polymer electrolyte membrane
- PS:
-
Photo-system
- PoGA15A:
-
Starch-digesting glucoamylase
- S. cerevisiae :
-
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- SNG:
-
Synthetic natural gas
- SPSC01:
-
Self-flocculating yeast strain
- SO2 :
-
Sulfur dioxide
- SO3 :
-
Sulfur trioxide
- SSF:
-
Separate hydrolysis and fermentation
- TAG:
-
Triacylglycerol
- w/v:
-
Weight by volume
- US:
-
United States
- USA:
-
United States of America
- XUSE:
-
Xylose-utilizing engineered S. cerevisiae strain
- v/v:
-
Volume by volume
References
Abukhadra MR, Dardir FM, Shaban M Ezzat, Ahmed A, Soliman MF (2018) Spongy Ni/Fe carbonate-fluorapatite catalyst for efficient conversion of cooking oil waste into biodiesel. Environ Chem Lett 16:665–670. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-017-0695-2
Adegoke TV, Osho A, Palmer OG, Olodun OA, Adeyelu AT (2018) Production of biodiesel from green alga Oedogonium capillare. J Chem Environ Biol Eng 2(2):70–73. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.jcebe.20180202.15
Aghbashlo M, Tabatabaei M, Soltanian S, Ghanavati H (2019) Biopower and biofertilizer production from organic municipal solid waste: an energy environmental analysis. Renew Energy 143:64–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.04.109
Alam F, Mobin S, Chowdhury H (2015) Third generation biofuel from algae. Procedia Eng 105:763–768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2015.05.068
Al-Fadhli FM, Baaqeel H, El-Halwagi MM (2019) Modular design of carbon–hydrogen–oxygen symbiosis networks over a time horizon with limited natural resources. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 141:107535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2019.107535
Anandarajah G, Dowall WM, Ekins P (2013) Decarbonizing road transport with hydrogen and electricity: long term global technology learning scenarios. Int J Hydrog Energy 38(8):3419–3432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.12.110
Ansari FA, Ravindran B, Gupta SK, Rawat MNI, Bux F (2019) Techno-economic estimation of wastewater phycoremediation and environmental benefits using Scenedesmus obliquus microalgae. J Environ Manag 240:293–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.03.123
Anto S, Mukherjee SS, Muthappa R, Mathimani T, Deviram G, Kumar SS, Verma TN, Pugazhendhi A (2019) Algae as green energy reserve: technological outlook on biofuel production. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125079
Aresta M, Dibenedetto A, Colonna M, Carone T, Fragale C (2005) Production of biodiesel from macroalgae by supercritical CO2 extraction and thermochemical liquefaction. Environ Chem Lett 3:136–139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-005-0020-3
Arifin Y, Tanudjaja E, Dimyati A, Pinontoan R (2014) A second generation biofuel from cellulosic agricultural by-product fermentation using Clostridium species for electricity generation. Energy Procedia 47:310–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2014.01.230
Baldino C, Pavlenko N, Searle S, Christensen A (2018) The potential for low-carbon renewable methane as a transport fuel in France, Italy, and Spain. Working paper, International Council on Clean Transportation, pp 1–16. https://theicct.org/publications/potential-renewable-methane-france-italy-spain. Accessed June 2019
Baliga R, Powers SE (2010) Sustainable algae biodiesel production in cold climates. In a special issue of bioprocess development for biofuels and bioproducts. Int J Chem Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/102179
Banja M, Jégard M, Motola V, Sikkema R (2019) Support for biogas in the EU electricity sector—a comparative analysis. Biomass Bioenergy 128:105313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2019.105313
Barreiro DL, Prins W, Ronsse F, Brilman W (2013) Hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL) of microalgae for biofuel production: state of the art review and prospects. Biomass Bioenergy 53:113–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.12.029
Basso LC, Amorin HV, Oliveira AJ, Lopes ML (2008) Yeast selection for fuel ethanol production in Brazil. FEMS Yeast Res 8:1155–1163. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1567-1364.2008.00428.x
Beagle E, Belmont E (2019) Comparative life cycle assessment of biomass utilization for electricity generation in the European Union and the United States. Energy Policy 128:267–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2019.01.006
Bertrand V, Dequiedt B, Cadre EL (2014) Biomass for electricity in the EU-27: potential demand, CO2 abatements and breakeven prices for co-firing. Energy Policy 73:631–644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2014.06.007
Bourgeois E, Dequiedt S, Lelièvre M, van Oort F, Lamy O, Ranjard L, Maron AP (2015) Miscanthus bioenergy crop stimulates nutrient-cycler bacteria and fungi in wastewater-contaminated agricultural soil. Environ Chem Lett 13:503–511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-015-0532-4
Breetza HL, Salon D (2018) Do electric vehicles need subsidies? Ownership costs for conventional, hybrid, and electric vehicles in 14 U.S. cities. Energy Policy 120:238–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2018.05.038
Brigljević B, Liu JJ, Lim H (2019) Comprehensive feasibility assessment of a poly-generation process integrating fast pyrolysis of S. japonica and the Rankine cycle. Appl Energy 254:113704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.113704
Buijs NA, Siewers V, Nielsen J (2013) Advanced biofuel production by the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Opin Chem Biol 17(3):480–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2013.03.036
Buitrón G, Carrillo-Reyes J, Morales M, Faraloni C, Torzillo G (2017) Biohydrogen production from microalgae. In: Gonzalez-Fernandez C, Muñoz R (eds) Chapter 9, From feedstock cultivation to end-products, microalgae-based biofuels and bioproducts. Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy, Sawston, pp 209–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-08-101023-5.00009-1
Bull JW, Jobstvogt N, Böhnke-Henrichs A, Mascarenhas A, Sitas N, Baulcomb C, Lambini CK, Rawlins M, Baral H, Zähringer J, Carter-Silk E, Balzan MV, Kenter JO, Häyhä T, Petz K, Koss R (2016) Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats: a SWOT analysis of the ecosystem services framework. Ecosyst Serv 17:99–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2015.11.012
Cerazy-Waliszewska J, Jeżowski S, Łysakowski P, Waliszewska B, Zborowska M, Sobańska K, Ślusarkiewicz-Jarzina A, Białas W, Pniewski T (2019) Potential of bioethanol production from biomass of various Miscanthus genotypes cultivated in three-year plantations in west-central Poland. Ind Crops Prod 141:111790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.111790
Chauhan SK, Gangopadhyay S, Singh N (2009) Environmental aspects of biofuels in road transportation. N. Environ Chem Lett 7:289–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-008-0185-7
Chemodanov A, Robin A, Golberg A (2017) Design of marine macroalgae photobioreactor integrated into the building to support agriculture for biorefinery and bioeconomy. Bioresour Technol 241:1084–1093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.06.061
Cheng J, Sun J, Huang Y, Feng J, Zhou J, Cen K (2013) Dynamic microstructures and fractal characterization of cell wall disruption for microwave irradiation-assisted lipid extraction from wet microalgae. Bioresour Technol 150:67–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.09.126
Cherubini F, Strømman AH (2011) Life cycle assessment of bioenergy systems: state of the art and future challenges. Bioresour Technol 102:437–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.08.010
Cherubini F, Strømman AH, Hertwich E (2011) Effects of boreal forest management practices on the climate impact of CO2 emissions from bioenergy. Ecol Model 223(1):59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2011.06.021
Chisti Y (2007) Biodiesel from microalgae. Biotechnol Adv 25:294–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2007.02.001
Cho K, Hoffmann MR (2017) Molecular hydrogen production from wastewater electrolysis cell with multi-junction BiOx/TiO2 anode and stainless steel cathode: Current and energy efficiency. Appl Catal B Environ 202:671–682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.09.067
Cho S, Kim J (2019) Multi-site and multi-period optimization model for strategic planning of a renewable hydrogen energy network from biomass waste and energy crops. Energy 185:527–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.07.053
Choi YY, Patel AK, Hong ME, Chang WS, Sim SJ (2019) Microalgae bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS): an emerging sustainable bioprocess for reduced CO2 emission and biofuel production. Bioresour Technol Rep 7:100270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2019.100270
Chollacoop N, Saisirirat P, Sukkasi S, Tongroon M, Fukuda T, Fukuda A, Nivitchanyong S (2013) Potential of greenhouse gas emission reduction in Thai road transport by ethanol bus technology. Appl Energy 102:112–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.07.039
Das GG (2017) Food–feed–biofuel trilemma: biotechnological innovation policy for sustainable development. J Policy Model. 39(3):410–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpolmod.2017.03.004
Denton J (2019) Icebergs of fat, oil, and grease are growing in the sewers beneath our feet. Here’s why. https://psmag.com/environment/teenage-mutant-ninja-fatbergs. Accessed June 2019
Dijk M, Erdei B, Galbe M, Nygård Y, Olsson L (2019) Strain-dependent variance in short-term adaptation effects of two xylose-fermenting strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Bioresour Technol 292:121922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121922
Dimitriou I, Goldingay H, Bridgwater AV (2018) Techno-economic and uncertainty analysis of biomass to liquid (BTL) systems for transport fuel production. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 88:160–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.02.023
Doloman A, Pererva Y, Cortez MH, Sims RC, Miller CD (2019) Augmentation of granular anaerobic sludge with algalytic bacteria enhances methane production from microalgal biomass. Fermentation 5(4):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation5040088
dos Santos RG, Ventura P, Bordado JC, Mateus MM (2017) Direct and efficient liquefaction of potato peel into bio-oil. Environ Chem Lett 15:453–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-017-0620-8
Dumortier J (2016) Impact of agronomic uncertainty in biomass production and endogenous commodity prices on cellulosic biofuel feedstock composition. GCB Bioenergy 8:35–50. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcbb.12238
Elegbede I, Matemilola S, Kies F, Fadeyi O, Saba A, Rios PDL, Adekunbi F, Lawal-Are A, Fashina-Bombata H (2017) Risk analysis and development of algae biofuel from aquatic and terrestrial systems. Energy Procedia 128:324–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2017.08.320
Elkady M, Zaatout A, Balbaa O (2015) Production of biodiesel from waste vegetable oil via KM micromixer. J Chem 630168:9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/630168
Esposito DV (2017) Membraneless electrolyzers for low-cost hydrogen production in a renewable energy future. Joule 1:651–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2017.07.003
Fernandez-Moya R, Da Silva NA (2017) Engineering Saccharomyces cerevisiae for high-level synthesis of fatty acids and derived products. FEMS Yeast Res. 17(7):fox71. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsyr/fox071
Fontes S (2010) World Energy Council. Biofuels: policies, standards and technologies World Energy Council. World Energy Council. https://www.worldenergy.org/assets/downloads/PUB_Biofuels_Policies_Standards_and_Technologies_2010_WEC.pdf. Accessed June 2019
Fulvio FD, Forsell N, Korosuo A, Obersteiner M, Hellweg S (2019) Spatially explicit LCA analysis of biodiversity losses due to different bioenergy policies in the European Union. Science Total Environ 651:1505–1516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.419
García-Olivares A, Solé J, Osychenko O (2018) Transportation in a 100% renewable energy system. Energy Convers Manag 158:266–285. https://doi.org/10.1016//j.enconman.2017.12.053
Gargalo CL, Cheali P, Posada JA, Carvalho A, Gernaey KV, Sin G (2016) Assessing the environmental sustainability of early stage design for bioprocesses under uncertainties: an analysis of glycerol bioconversion. J Clean Prod 139:1245–1260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.08.156
Ge X, Burner DM, Xu J, Phillips GC, Sivakumar G (2011) Bioethanol production from dedicated energy crops and residues in Arkansas, USA. Biotechnol J 6(1):66–73. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201000240
Gendy TS, El-Temtamy SA (2013) Commercialization potential aspects of microalgae for biofuel production: an overview. Egypt J Pet 22:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpe.2012.07.001
Goerndt ME, Wilson BT, Aguilar FX (2019) Comparison of small area estimation methods applied to biopower feedstock supply in the Northern U.S. region. Biomass Bioenergy 121:64–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2018.12.008
Gomes V, Saade M, Lim B, Silva M (2018) Exploring lifecycle energy and greenhouse gas emissions of a case study with ambitious energy compensation goals in a cooling-dominated climate. Energy Build 173:302–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2018.04.063
Gonçalves AL, Pires JCM, Simões M (2013) Green fuel production: processes applied to microalgae. Environ Chem Lett 11:315–324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-013-0425-3
Gonzalez-Salazar MA, Venturini M, Poganietz WR, Finkenrath M, Kirsten T, Acevedo H, Spina PR (2016) Development of a technology roadmap for bioenergy exploitation including biofuels, waste-to-energy and power generation & CHP. Appl Energy 180:338–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.07.120
Harnesk D (2019) Biomass-based energy on the move—the geographical expansion of the European Union’s liquid biofuel regulation. Geoforum 98:25–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoforum.2018.09.019
Haro P, Johnsson F, Thunman H (2016) Improved syngas processing for enhanced Bio-SNG production: a techno-economic assessment. Energy 101:380–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2016.02.037
Hemaiswarya S, Raja R, Carvalho IS, Ravikumar R, Zambare V, Barh D (2012) An Indian scenario on renewable and sustainable energy sources with emphasis on algae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96(5):1125–1135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4487-0
Henriques TM, Pereira SR, Serafim LS, Xavier AMRB (2018) Two-stage aeration fermentation strategy to improve bioethanol production by Scheffersomyces stipitis. Fermentation 4:97. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation4040097
Hibino T, Kobayashi K, Ito M, Nagao M, Fukui M, Teranishi S (2018) Direct electrolysis of waste newspaper for sustainable hydrogen production: an oxygen-functionalized porous carbon anode. Appl Catal B Environ 231:191–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.03.021
Ho SH, Huang SW, Chen CY, Hasunuma T, Kondo A, Chan JS (2013) Characterization and optimization of carbohydrate production from an indigenous microalga Chlorella vulgaris FSP-E. Bioresour Technol 135:157–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.10.100
Hoang PTN, Ko JK, Gong G, Um Y, Lee SM (2018) Genomic and phenotypic characterization of a refactored xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for lignocellulosic biofuel production. Biotechnol Biofuels 11:268. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-018-1269-7
How SB, Ngan SL, Hong BH, Lam LH, Ng WPQ, Yusup S, Ghani WAWAK, Kansha Y, Chan YH, Cheah KW, Shahbazh M, Singhd HKG, Yusuf NR, Shuhailide AFA, Rambli J (2019) An outlook of Malaysian biomass industry commercialization: Perspectives and challenges. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 113:109277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.109277
Hu BB, Li MY, Wang YT, Zhu MJ (2018) Enhanced biohydrogen production from dilute acid pretreated sugarcane bagasse by detoxification and fermentation strategy. Int J Hydrog Energy 43(42):19366–19374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.08.164
Hu Y, Zhu Z, Nielsen J, Siewers V (2019) Engineering Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells for production of fatty acid-derived biofuels and chemicals. Open Biol 9:190049. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsob.190049
Huang Y, Yi Q, Wei G, Kang J, Li W, Feng J, Xie K (2018) Energy use, greenhouse gases emission and cost effectiveness of an integrated high- and low-temperature Fisher–Tropsch synthesis plant from a lifecycle viewpoint. Appl Energy 228:1009–1019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.07.007
Hundt KB, Reddy V (2011) Algal biodiesel production from power plant exhaust and its potential to replace petrodiesel and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Int J Low Carbon Technol 6(4):294–298. https://doi.org/10.1093/ijlct/ctr017
Hwang JH, Kabra AN, Ji MK, Choi J, El-Dalatony MM, Jeon BH (2016) Enhancement of continuous fermentative bioethanol production using combined treatment of mixed microalgal biomass. Algal Res 17:14–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2016.03.029
Im-orb K, Arpornwichanop A (2020) Process and sustainability analyses of the integrated biomass pyrolysis, gasification, and methanol synthesis process for methanol production. Energy 193:116788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.116788
Ishak S, Kamari A (2019) Biodiesel from black soldier fly larvae grown on restaurant kitchen waste. Environ Chem Lett 17:1143–1150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-00844-y
Ito M, Hori T, Teranishi S, Nagao M, Hibino T (2018) Intermediate-temperature electrolysis of energy grass Miscanthus sinensis for sustainable hydrogen production. Sci Rep 8:16186. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-34544-y
Jia J, Seitz LC, Benck JD, Huo Y, Chen Y, Ng JWD, Bilir T, Harris JS, Jaramillo TF (2016) Solar water splitting by photovoltaic-electrolysis with a solar-to-hydrogen efficiency over 30%. Nat Commun 7:13237. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13237
Jin E, Sutherland JW (2018) An integrated sustainability model for a bioenergy system: forest residues for electricity generation. Biomass Bioenergy 119:10–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2018.09.005
Jo S, Park S, Kim HJ, Lee JT (2019) Combustion improvement and emission reduction through control of ethanol ratio and intake air temperature in reactivity controlled compression ignition combustion engine. Appl Energy 250:1418–1431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.05.012
John RP, Anisha GS, Nampoothiri KM, Pandey A (2011) Micro and macroalgal biomass: a renewable source for bioethanol. Bioresour Technol 102(1):186–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.06.139
Jong S, Hoefnagels R, Wetterlund E, Pettersson K, Faaij A, Junginger M (2017) Cost optimization of biofuel production—the impact of scale, integration, transport and supply chain configurations. Appl Energy 195:1055–1070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.03.109
Jorquera O, Kiperstok A, Sales EA, Embirucu M, Ghirardi ML (2010) Comparative energy life-cycle analyses of microalgal biomass production in open ponds and photobioreactors. Bioresour Technol 101(4):1406–1413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.09.038
Jrad A, Hmadeh M, Tarboush BJA, Awada G, Ahmad M (2020) Structural engineering of Zr-based metal–organic framework catalysts for optimized biofuel additives production. Chem Eng J 382:122793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122793
Kara K, Ouanji F, Mahi ME, Lotfi EM, Kacimi M, Mahfoud Z (2019) Biodiesel synthesis from vegetable oil using eggshell waste as a heterogeneous catalyst. J Biofuel. https://doi.org/10.1080/17597269.2019.1580972
Karl (2011) Hawaiian utility uses 100% biofuel in 90 MW oil-fired turbine—make biofuel. www.makebiofuel.co.uk/hawaiian-utility-uses-100-biofuel-in-90mw-oil-fired-turbine/. Accessed June 2019
Kaza N (2020) Urban form and transportation energy consumption. Energy Policy 136:111049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2019.111049
Kazemifard S, Nayebzadeh H, Saghatoleslami N, Safakish E (2019) Application of magnetic alumina-ferric oxide nanocatalyst supported by KOH for in situ transesterification of microalgae cultivated in wastewater medium. Biomass Bioenergy 129:105338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2019.105338
Kim S, Sung T, Kim KC (2018) Performance and greenhouse gas reduction analysis of biogas-fueled solid-oxide fuel cells for a sewage sludge and food waste treatment facility. Energy 11:600. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11030600
Kojima E, Zhang K (1999) Growth and hydrocarbon production of microalga Botryococcus braunii in bubble column photobioreactors. J Biosci Bioeng 87(6):811–815. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1389-1723(99)80158-3
Kommers N (2013) Algae biofuel can cut CO2 emissions by up to 68 percent compared to petroleum fuels finds new peer reviewed study. MINNEAPOLIS (September19). https://algaebiomass.org/algae-biofuel-can-cut-co2-emissions-by-more-than-50-compared-to-petroleum-fuels-finds-new-peer-reviewed-study/. Accessed June 2019
Kothari R, Pandey A, Ahmad S, Kumar A, Pathak VV, Tyagi VV (2017) Microalgal cultivation for value-added products: a critical enviro-economical assessment. 3 Biotech 7(4):243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-0812-8
Kovač A, Marciuš D, Budin L (2019) Solar hydrogen production via alkaline water electrolysis. Int J Hydrog Energy 44(20):9841–9848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.11.007
Kumar R, Kumar P (2017) Future microbial applications for bioenergy production: a perspective. Front Microbiol 8:450. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00450
Kumar L, Maithel S, Raju KV, Ram Mohan MP (2006) Liquid biofuels for transportation: India country study on potential and implications for sustainable agriculture and energy. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/259225852. Accessed June 2019
Kumar AN, Chatterjee S, Hemalatha M, Avanthi A, Min B, Kim SH, Mohan SV (2019a) Deoiled algal biomass derived renewable sugars for bioethanol and biopolymer production in biorefinery framework. Bioresour Technol 296:122315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122315
Kumar MD, Kaliappan S, Gopikumar S, Zhen G, Banu JR (2019b) Synergetic pretreatment of algal biomass through H2O2 induced microwave in acidic condition for biohydrogen production. Fuel 253:833–839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.05.066
Kumari N, Singh RK (2019) Biofuel and co-products from algae solvent extraction. J Environ Manag 247:196–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.06.042
Kuo TC, Lin S-H, Tseng M-L, Chiu ASF, Hsue C-W (2019) Biofuels for vehicles in Taiwan: using system dynamics modeling to evaluate government subsidy policies. Resour Conserv Recycl 145:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.02.005
Larsson M, Grönkvist S, Alvfors P (2016) Upgraded biogas for transport in Sweden—effects of policy instruments on production, infrastructure deployment and vehicle sales. J Clean Prod 112:3774–3784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.08.056
Lee YG, Jin YS, Cha YL, Seo JH (2017) Bioethanol production from cellulosic hydrolysates by engineered industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Bioresour Technol 228:355–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.12.042
Lenhart S, Nelson-Marsh N, Wilson EJ, Solan D (2016) Electricity governance and the Western energy imbalance market in the United States: the necessity of interorganizational collaboration. Energy Res Soc Sci 19:94–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.erss.2016.05.015
Li S, Chen G (2018) Factors affecting the effectiveness of bioelectrochemical system applications: data synthesis and meta-analysis. Batteries 4(3):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries4030034
Li M, Xu J, Xie H, Wang Y (2018) Transport biofuels technological paradigm based conversion approaches towards a bio-electric energy framework. Energy Convers Manag 172:554–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2018.07.049
Liu Z, Johnson TG, Altman I (2016) The moderating role of biomass availability in biopower co-firing—a sensitivity analysis. J Clean Prod 135:523–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.06.101
Liu H, Wang X, Wu Y, Zhang X, Jin C, Zheng Z (2019) Effect of diesel/PODE/ethanol blends on combustion and emissions of a heavy duty diesel engine. Fuel 257:116064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116064
Lu C, Zhang H, Zhang Q, Chu C, Tahir N, Ge X, Jing Y, Hu J, Li Y, Zhang Y, Zhang T (2019) An automated control system for pilot-scale biohydrogen production: design, operation and validation. Int J Hydrog Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.04.28
Macedo IC, Seabra JEA, Silva JEAR (2008) Green house gases emissions in the production and use of ethanol from sugarcane in Brazil: the 2005/2006 averages and a prediction for 2020. Biomass Bioenergy 32:582–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2007.12.006
Machado IMP, Atsumi S (2012) Cyanobacterial biofuel production. J Biotechnol 162(1):50–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2012.03.005
Mahbub N, Gemechu E, Zhang H, Kumar A (2019) The life cycle greenhouse gas emission benefits from alternative uses of biofuel coproducts. Sustain Energy Technol Assess 34:173–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2019.05.001
Mahmoud R, Ibrahim M, Ali G (2016) Closed photobioreactor for microalgae biomass production under indoor growth conditions. J Algal Biomass Util 7(1):86–92
Mamadzhanov A, McCluskey JJ, Li T (2019) Willingness to pay for a second-generation bioethanol: a case study of Korea. Energy Policy 127:464–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2018.12.001
Manolis EN, Zagas TD, Karetsos GK, Poravou CA (2019) Ecological restrictions in forest biomass extraction for a sustainable renewable energy production. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 110:290–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.04.078
Martín M (2017) Artificial versus natural reuse of CO2 for DME production: are we any closer? Engineering 3(2):166–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2017.02.002
Masmoudi O, Delorme X, Gianessi P (2019) Job-shop scheduling problem with energy consideration. Int J Prod Econ 216:12–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2019.03.021
Mathimania T, Pugazhendhi A (2019) Utilization of algae for biofuel, bio-products and bio-remediation. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 17:326–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2018.12.007
Matsushika A, Sawayama S (2011) Comparative study on a series of recombinant flocculent Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains with different expression levels of xylose reductase and xylulokinase. Enzym Microb Technol 48(6–7):466–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2011.02.002
Mayur M, Gerard M, Schott P, Bessler WG (2018) Lifetime prediction of a polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell under automotive load cycling using a physically-based catalyst degradation model. Energy 11:2054. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11082054
Méndez A, Gascó G, Ruiz B, Fuente E (2019) Hydrochars from industrial macroalgae “Gelidium Sesquipedale” biomass wastes. Bioresour Technol 275:386–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.12.074
Mirza SS, Qazi JI, Liang Y, Chen S (2019) Growth characteristics and photofermentative biohydrogen production potential of purple non sulfur bacteria from sugar cane bagasse. Fuel 255:115805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.115805
Mondou M, Skogstad G, Bognar J (2018) What are the prospects for deploying advanced biofuels in Canada? Biomass Bioenergy 116:171–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2018.06.014
Montpart N, Ribot-Llobet E, Garlapati VK, Rago L, Baeza JA, Guisasola A (2014) Methanol opportunities for electricity and hydrogen production in bioelectrochemical systems. Int J Hydrog Energy 39(2):770–777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.10.151
Moriarty P, Yan X, Wang SJ (2019) Liquid biofuels: not a long-term transport solution. Energy Procedia 158:3265–3270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2019.01.986
Mulholland E, Rogan F, Gallachóir BPÓ (2017) From technology pathways to policy roadmaps to enabling measures—a multi-model approach. Energy 138:1030–1041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.07.116
Mutter A (2019) Mobilizing sociotechnical imaginaries of fossil-free futures—electricity and biogas in public transport in Linköping, Sweden. Energy Res Soc Sci 49:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.erss.2018.10.025
Narala RR, Garg S, Sharma KK, Thomas-Hall SR, Deme M, Li Y, Schenk PM (2016) Comparison of microalgae cultivation in photobioreactor, open raceway pond, and a two-stage hybrid system. Front Energy Res 4:29. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenrg.2016.00029
Nedbalová L, Střížek A, Sigler K, Řezanka T (2016) Effect of salinity on the fatty acid and triacylglycerol composition of five haptophyte algae from the genera Coccolithophora, Isochrysis and Prymnesium determined by LC-MS/APCI. Phytochemistry 130:64–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2016.06.001
Nguyen T, Abdin Z, Holm T, Mérida W (2019) Grid-connected hydrogen production via large-scale water electrolysis. Energy Convers Manag 200:112108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2019.112108
Oliveira O, Gianesella S, Silva V, Mata T, Caetano N (2017) Lipid and carbohydrate profile of a microalga isolated from wastewater. Energy Procedia 136:468–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2017.10.305
Parra-Ramírez D, Martinez A, Cardona CA (2018) Technical and economic potential evaluation of the strain Escherichia coli MS04 in the ethanol production from glucose and xylose. Biochem Eng J 140:123–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2018.09.015
Paz-Mireles CL, Razo-Flores E, Trejo G, Cercado B (2019) Inhibitory effect of ethanol on the experimental electrical charge and hydrogen production in microbial electrolysis cells (MECs). J Electroanal Chem 835:106–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.01.028
Pereira LG, Chagas MF, Dias MOS, Cavalett O, Bonomi A (2015) Life cycle assessment of butanol production in sugarcane biorefineries in Brazil. J Clean Prod 96:557–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.01.059
Pérez-Camacho MN, Curry R, Cromie T (2019) Life cycle environmental impacts of biogas production and utilisation substituting for grid electricity, natural gas grid and transport fuels. Waste Manag 95:90–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2019.05.045
Pfaffingera CE, Severin TS, Apel AC, Göbel J, Sauter J, Weuster-Bo D (2019) Light-dependent growth kinetics enable scale-up of well-mixed phototrophic bioprocesses in different types of photobioreactors. J Biotechnol 297:41–48
Pick MJ (2019) The renewable energy strategies of oil majors—from oil to energy? Energy Strat Rev 26:100370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2019.100370
Poudel J, Karki S, Sanjel N, Shah M, Oh SC (2017) Comparison of biodiesel obtained from virgin cooking oil and waste cooking oil using supercritical and catalytic transesterification. Energy 10:546. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10040546
Preethi, Mohamed Usman TM, Banu JR, Gunasekaran M, Kumar G (2019) Biohydrogen production from industrial wastewater: an overview. Bioresour Technol Rep 7:100287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2019.100287
Quéméner EDL, Bridier A, Tian JH, Madigou C, Bureau C, Qi Y, Bouchez T (2019) Biorefinery for heterogeneous organic waste using microbial electrochemical technology. Bioresour Technol 292:121943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121943
Rabin E (2003) Biodiesel: a cleaner, greener fuel for the 21st century. https://www.greenbiz.com/news/2003/01/26/biodiesel-cleaner-greener-fuel-21st-century. Accessed June 2019
Raheem A, Prinsen P, Vuppaladadiyam AK, Zhao M, Luque R (2018) A review on sustainable microalgae-based biofuel and bioenergy production: recent developments. J Clean Prod 181:42–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.125
Ram M, Aghahosseini A, Breyer C (2019) Job creation during the global energy transition towards 100% renewable power system by 2050. Technol Forecast Soc Change 151:119682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2019.06.008
Ramirez JA, Rainey TJ (2019) Comparative techno-economic analysis of biofuel production through gasification, thermal liquefaction and pyrolysis of sugarcane bagasse. J Clean Prod 229:513–527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.017
Rassoulinejad-Mousavi SM, Mao Y, Zhang Y (2018) Reducing greenhouse gas emissions in Sandia methane-air flame by using a biofuel. Renew Energy 128:313–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.05.079
Raud M, Kikas T, Sippula O, Shurpali NJ (2019) Potentials and challenges in lignocellulosic biofuel production technology. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 111:44–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.05.020
Rawat I, Kumar RR, Mutanda T, Bux F (2011) Dual role of microalgae: phycoremediation of domestic wastewater and biomass production for sustainable biofuels production. Appl Energy 88(10):3411–3424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2010.11.025
Röder M, Thiffault E, Martínez-Alonso C, Senez-Gagnon F, Paradis L, Thornley P (2019) Understanding the timing and variation of greenhouse gas emissions of forest bioenergy systems. Biomass Bioenergy 121:99–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2018.12.019
Romaní A, Pereira F, Johansson B, Domingues L (2015) Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ethanol strains PE-2 and CAT-1 for efficient lignocellulosic fermentation. Bioresour Technol 179:150–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.12.020
Roux JM, Lamotte H, Achard JL (2017) An overview of microalgae lipid extraction in a biorefinery framework. Energy Procedia 112:680–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2017.03.1137
Runguphan W, Keasling JD (2013) Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for production of fatty acid-derived biofuels and chemicals. Metab Eng 21:103–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2013.07.003
Sa MT, Vb AKH, Dc S, Kothari S (2011) Utility of microbes for production of future biofuel. Int J Curr Sci Res 1(3):139–145
Sadaf S, Iqbal J, Ullah I, Bhatti HN, Nourene S, Rehman H, Nisar J, Iqbal M (2018) Biodiesel production from waste cooking oil: an efficient technique to convert waste into biodiesel. Sustain Cities Soc 41:220–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2018.05.037
Salleh MM, Ibrahim MF, Roslan AM, Abd-Aziz S (2019) Fermentation with delayed yeast extract feeding and in situ recovery. Sci Rep 9:7443. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-43718-1
Santana A, Maçaira J, Larrayoz MA (2012) Continuous production of biodiesel from vegetable oil using supercritical ethanol/carbon dioxide mixtures. Fuel Process Technol 96:214–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2011.12.021
Sayed ET, Saito Y, Tsujiguchi T, Nakagawa N (2012) Catalytic activity of yeast extract in biofuel cell. J Biosci Bioeng 114(5):521–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2012.05.021
Schemme S, Breuer JL, Köller M, Meschede S, Walman F, Samsun RC, Peters R, Stolten D (2019) H2-based synthetic fuels: a techno-economic comparison of alcohol, ether and hydrocarbon production. Int J Hydrog Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.05.028
Shafiei E, Davidsdottir B, Leaver J, Stefansson H, Asgeirsson EI (2015) Comparative analysis of hydrogen, biofuels and electricity transitional pathways to sustainable transport in a renewable-based energy system. Energy 83(1):614–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2015.02.071
Shafiei E, Leaver J, Davidsdottir B (2017) Cost-effectiveness analysis of inducing green vehicles to achieve deep reductions in greenhouse gas emissions in New Zealand. J Clean Prod 150:339–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.032
Sharma A, Arya SK (2017) Hydrogen from algal biomass: a review of the production process. Biotechnol Rep (Amst) 5:63–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2017.06.001
Sharma J, Kumar SS, Bishnoi NR, Pugazhendhi A (2018a) Enhancement of lipid production from algal biomass through various growth parameters. J Mol Liq 269:712–720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.08.103
Sharma PK, Saharia M, Srivstava R, Kumar S, Sahoo L (2018b) Tailoring microalgae for efficient biofuel production. Front Mar Sci 5:382. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2018.00382
Sheng J, Feng X (2015) Metabolic engineering of yeast to produce fatty acid-derived biofuels: bottlenecks and solutions. Front Microbiol 6:554. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.00554
Shi Z, Zhao B, Tang S, Yang X (2018) Hydrotreating lipids for aviation biofuels derived from extraction of wet and dry algae. J Clean Prod 204:906–915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.351
Shittu E, Kamdem BG, Weigelt C (2019) Heterogeneities in energy technological learning: evidence from the U.S. electricity industry. Energy Policy 132:1034–1049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2019.06.052
Shobana S, Saratale GD, Pugazhendhi A, Arvindnarayan S, Periyasamy S, Kumar G, Kim S-H (2017) Fermentative hydrogen production from mixed and pure microalgae biomass: key challenges and possible opportunities. Int J Hydrog Energy 42(42):26440–26453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.07.050
Silva De Souza A, Oliveira Junior AM, De Farias Silva CE, Abud De Souza AK (2016) Inhibitors influence on ethanol fermentation by Pichia stipitis. Chem Eng Trans 49:367–372. https://doi.org/10.3303/CET1649062
Singh TS, Verma TN (2019) An assessment study of using Turel Kongreng (river mussels) as a source of heterogeneous catalyst for biofuel production. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 20:101185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2019.101185
Siqueira SF, Francisco ÉC, Queiroz MI, de Menezes CR, Zepka LQ, Jacob-Lopes E (2016) Third generation biodiesel production from microalgae Phormidium autumnale. Braz J Chem Eng 33(03):427–433. https://doi.org/10.1590/0104-6632.20160333s20150134
Slade R, Bauen A (2013) Micro-algae cultivation for biofuels: Cost, energy balance, environmental impacts and future prospects. Biomass Bioengy 53:29–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.12.019
Solé J, García-Olivares A, Turiel A, Ballabrera-Poy J (2018) Renewable transitions and the net energy from oil liquids: a scenarios study. Renew Energy Part A 116:258–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.09.035
Sotirov M, Storch S (2018) Resilience through policy integration in Europe? Domestic forest policy changes as response to absorb pressure to integrate biodiversity conservation, bioenergy use and climate protection in France, Germany, the Netherlands and Sweden. Land Use Policy 79:977–989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.04.034
Sun M, Sheng GP, Zhang L, Xia CR, Mu ZX, Liu XW, Wang HL, Yu HQ, Qi R, Yu T, Yang M (2008) An MEC-MFC-coupled system for biohydrogen production from acetate. Environ Sci Technol 42(21):8095–8100. https://doi.org/10.1021/es801513c
Sun H, Luo S, Jin R, He Z (2017) Ensemble engineering and statistical modeling for parameter calibration towards optimal design of microbial fuel cells. J Power Sources 356:288–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.02.051
Swain RB, Karimu A (2020) Renewable electricity and sustainable development goals in the EU. World Dev 125:104693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.019.104693
Tan JS, Phapugrangkul P, Lee CK, Lai Z-W, Bakar MHA, Murugan P (2019) Banana frond juice as novel fermentation substrate for bioethanol production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 21:101293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2019.101293
Tani T, Taguchi H, Akamatsu T (2017) Analysis of metabolisms and transports of xylitol using xylose- and xylitol-assimilating Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biosci Bioeng 123(5):613–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2016.12.012
Tylor J, Halfmann JC, Zahler JD, Zhou R, Gibbons WR (2016) Increasing the tolerance of filamentous cyanobacteria to next-generation biofuels via directed evolution. Algal Res 18:250–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2016.06.023
Unrean P, Fui BCL, Rianawati E, Acda M (2018) Comparative techno-economic assessment and environmental impacts of rice husk-to-fuel conversion technologies. Energy 151:581–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.03.112
Väisänen S, Havukainen J, Uusitalo V, Havukainen M, Soukka R, Luoranen M (2016) Carbon footprint of biobutanol by ABE fermentation from corn and sugarcane. Renew Energy 89:401–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2015.12.016
Verdezoto PLC, Vidoza JA, Gallo WLR (2019) Analysis and projection of energy consumption in Ecuador: energy efficiency policies in the transportation sector. Energy Policy 134:110948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2019.110948
Vidales AG, Omanovic S, Tartakovsky B (2019) Combined energy storage and methane bioelectrosynthesis from carbon dioxide in a microbial electrosynthesis system. Bioresour Technol Rep 8:100302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2019.100302
Walls LE, Velasquez-Orta SB, Romero-Frasca E, Learya P, Noguez IY, Ledesma MTO (2019) Non-sterile heterotrophic cultivation of native wastewater yeast and microalgae for integrated municipal wastewater treatment and bioethanol production. Biochem Eng J 151:107319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2019.107319
Wang J, Zhangm Q, Wei Y, Yang G, Wei F (2019) Integrated furnace for combustion/gasification of biomass fuel for tobacco curing. Waste Biomass Valoris 10:2037. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0205-1
Water T (2017) Company report, media news-releases. Monster Whitechapel fatberg given new lease of biodiesel life. https://corporate.thameswater.co.uk/Media/News-releases/Monster-Whitechapel-fatberg-given-new-lease-of-biodiesel-life. Accessed June 2019
Woertz IC, Benemann JR, Du N, Unnasch S, Mendola D, Mitchell BG, Lundquist TJ (2014) Life cycle greenhouse gases emissions from microalgal biodiesel—a CA-GREET model. Environ Sci Technol 48:6060–6068. https://doi.org/10.1021/es403768q
Woodbury PB, Kemanian AR, Jacobson M, Langholtz M (2018) Improving water quality in the Chesapeake Bay using payments for ecosystem services for perennial biomass for bioenergy and biofuel production. Biomass Bioenergy 114:132–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2017.01.024
Work VH, Radakovits R, Jinkerson RE, Meuser JE, Elliott LG, Vinyard DJ, Laurens LML, Dismukes GC, Posewit MC (2010) Increased lipid accumulation in the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii sta7-10 starchless isoamylase mutant and increased carbohydrate synthesis in complemented strains. Eukaryot Cell 9:1251–1261. https://doi.org/10.1128/EC.00075-10
Xiao L, Liu F, Xu H, Feng D, Liu J, Han G (2019) Biochar promotes methane production at high acetate concentrations in anaerobic soils. Environ Chem Lett 17:1347–1352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-019-00863-3
Xu QS, Yan YS, Feng JX (2016) Efficient hydrolysis of raw starch and ethanol fermentation: a novel raw starch-digesting glucoamylase from Penicillium oxalicum. Biotechnol Biofuels 9:216. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-016-0636-5
Yang Z, Guo R, Xu X, Wang L, Dai M (2016) Enhanced methane production via repeated batch bioaugmentation pattern of enriched microbial consortia. Bioresour Technol 216:471–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.05.062
Yang L, Chen J, Qin S, Zeng M, Jiang Y, Hu L, Xiao P, Hao W, Hu Z, Lei A, Wang J (2018) Growth and lipid accumulation by different nutrients in the microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biotechnol Biofuels 11:40. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-018-1041-z
Yang M, Qi H, Liu F, Ren Y, Pan X, Zhang L, Liu X, Wang H, Pang J, Zheng M, Wang A, Zhang T (2019) One-pot production of cellulosic ethanol via tandem catalysis over a multifunctional Mo/Pt/WOx catalyst. Joule 3(8):1937–1948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2019.05.020
Yao R, Shimizu K (2013) Recent progress in metabolic engineering for the production of biofuels and biochemicals from renewable sources with particular emphasis on catabolite regulation and its modulation. Process Biochem 48(9):1409–1417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2013.02.032
Yao S, Lyu S, An Y, Lu J, Gjermansen C, Schramm A (2019) Microalgae-bacteria symbiosis in microalgal growth and biofuel production: a review. J Appl Microbiol 126(2):359–368. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14095
Yew GY, Lee SY, Show PL, Tao Y, Law CL, Trung T, Nguyen C, Chang JS (2019) Recent advances in algae biodiesel production: from upstream cultivation to downstream processing. Bioresour Technol Rep 7:100227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2019.100227
Yrjol J, Paavilainen J (2004) Modelling and analyses of heat exchangers in a biomass boiler plant. Int J Energy Res 28:473–494. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.976
Yu Z, Song M, Pei H, Han F, Jiang L, Hou Q (2017) The growth characteristics and biodiesel production of ten algae strains cultivated in anaerobically digested effluent from kitchen waste. Algal Res 24:265–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2017.04.010
Yu M, Robati M, Oldfield P, Wiedmann T, Crawford R, Nezhad AA, Carmichael D (2020) The impact of value engineering on embodied greenhouse gas emissions in the built environment: a hybrid life cycle assessment. Build Environ 168(15):106452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2019.106452
Yue D, You F, Snyder SW (2014) Biomass-to-bioenergy and biofuel supply chain optimization: overview, key issues and challenges. Comput Chem Eng 66:36–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2013.11.016
Yun C-J, Hwang K-O, Han S-S, Ri H-G (2019) The effect of salinity stress on the biofuel production potential of freshwater microalgae Chlorella vulgaris YH703. Biomass Bioenergy 127:105277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2019.105277
Zeman P, Hönig V, Kotek M, Táborský J, Obergruber M, Mařík J, Hartová V, Pechout M (2019) Hydrotreated vegetable oil as a fuel from waste materials. Catalysts 9(4):337. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal9040337
Zhan J, Rong J, Wang Q (2017) Mixotrophic cultivation, a preferable microalgae cultivation mode for biomass/bioenergy production, and bioremediation, advances and prospect. Int J Hydrog Energy 42(12):8505–8517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.12.021
Zhang H, Chen W (2015) The role of biofuels in China’s transport sector in carbon mitigation scenarios. Energy Procedia 75:2700–2705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2015.07.682
Zhang Y, Liu D, Chen Z (2017) Production of C2–C4 diols from renewable bioresources: new metabolic pathways and metabolic engineering strategies. Biotechnol Biofuels 10:299. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-017-0992-9
Zheng Q, Shumway CR (2008) Washington biofuel feedstock supply under price uncertainty. In: Conference paper/presentation. Western Agricultural Economics Association. 2008 annual meeting, Big Sky, Montana. http://purl.umn.edu/42304.pp.21. https://doi.org/10.22004/ag.econ.42304
Zollmann M, Traugott H, Chemodanov A, Liberzon A, Golberg A (2018) Exergy efficiency of solar energy conversion to biomass of green macroalgae Ulva (Chlorophyta) in the photobioreactor. Energy Convers Manag 167:125–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2018.04.090
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srivastava, R.K., Shetti, N.P., Reddy, K.R. et al. Biofuels, biodiesel and biohydrogen production using bioprocesses. A review. Environ Chem Lett 18, 1049–1072 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-00999-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-00999-7