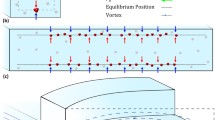
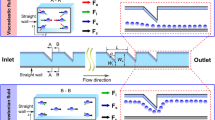
Abstract
Focusing particles (both biological and synthetic) into a tight stream is usually a necessary step prior to counting, detecting, and sorting them. The various particle focusing approaches in microfluidic devices may be conveniently classified as sheath flow focusing and sheathless focusing. Sheath flow focusers use one or more sheath fluids to pinch the particle suspension and thus focus the suspended particles. Sheathless focusers typically rely on a force to manipulate particles laterally to their equilibrium positions. This force can be either externally applied or internally induced by channel topology. Therefore, the sheathless particle focusing methods may be further classified as active or passive by the nature of the forces involved. The aim of this article is to introduce and discuss the recent developments in both sheath flow and sheathless particle focusing approaches in microfluidic devices.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai Y, Joo SW, Jiang Y, Xuan X, Qian S (2009) Transient electrophoretic motion of a charged particle through a converging-diverging microchannel: effect of direct current dielectrophoretic force. Electrophoresis 30:2499–2506
Ai Y, Park S, Zhu J, Xuan X, Beskok A, Qian S (2010a) DC electrokinetic particle transport in an L-shaped microchannel. Langmuir 26:2937–2944
Ai Y, Qian S, Liu S, Joo SW (2010b) Dielectrophoretic choking phenomenon in a converging-diverging microchannel. Biomicrofluidics 4:013201
Anderson JL (1989) Colloid transport by interfacial forces. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 21:61–99
Aoki R, Yamada M, Yasuda M, Seki M (2009) In-channel focusing of flowing microparticles utilizing hydrodynamic filtration. Microfluid Nanofluid 6:571–576
Asmolov ES (1999) The inertial lift on a spherical particle in a plane Poiseuille flow at large channel Reynolds number. J Fluid Mech 381:63–87
Ateya DA, Erickson JS, Howell PB Jr, Hilliard LR, Golden JP, Ligler FS (2008) The good, the bad, and the tiny: a review of microflow cytometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 391:1485–1498
Barbulovic-Nad I, Xuan X, Lee JSH, Li D (2006) DC-dielectrophoretic separation of microparticles using an oil droplet obstacle. Lab Chip 6:274–279
Barrett LM, Skulan AJ, Singh AK, Cummings EB, Fiechtner GJ (2005) Dielectrophoretic manipulation of particles and cells using insulating ridges in faceted prism microchannels. Anal Chem 77:6798–6804
Berger A, Talbot L, Yao LS (1983) Flow in curved pipes. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 15:461–512
Bhagat AAS, Kuntaegowdanahalli SS, Papautsky I (2008a) Enhanced particle filtration in straight microchannels using shear-modulated inertial migration. Phys Fluid 20:101702
Bhagat AAS, Kuntaegowdanahalli SS, Papautsky I (2008b) Continuous particle separation in spiral microchannels using dean flows and differential migration. Lab Chip 8:1906–1914
Bhagat AAS, Kuntaegowdanahalli SS, Papautsky I (2009) Inertial microfluidics for continuous particle filtration and extraction. Microfluid Nanofluid 7:221–230
Bhagat AAS, Kuntaegowdanahalli SS, Papautsky I (2010) Inertial microfluidics for sheath-less high-throughput flow cytometry. Biomed Microdev. doi:10.1007/s10544-009-9374-9
Braschler T, Demierre N, Nascimento E, Silva T, Oliva AG, Renaud P (2008) Continuous separation of cells by balanced dielectrophoretic forces at multiple frequencies. Lab Chip 8:280–286
Chang CC, Huang ZY, Yang RJ (2007) Three-dimensional hydrodynamic focusing in two-layer polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) microchannels. J Micromech Microeng 17:1479–1486
Chau LK, Osborn T, Wu CC, Yager P (1999) Microfabricated silicon flow-cell for optical monitoring of biological fluids. Anal Sci 15:721–724
Cheng IF, Chang HC, Hou D, Chang HC (2007) An integrated dielectrophoretic chip for continuous bioparticle filtering, focusing, sorting, trapping, and detecting. Biomicrofluidics 1:021503 (1–15)
Cho YK, Kim S, Lee K, Park C, Lee JG, Ko C (2009) Bacteria concentration using a membrane type insulator-based dielectrophoresis in a plastic chip. Electrophoresis 30:3153–3159
Choi S, Park JK (2007) Continuous hydrophoretic separation and sizing of microparticles using slanted obstacles in a microchannel. Lab Chip 7:890–897
Choi S, Park JK (2008) Sheathless hydrophoretic particle focusing in a microchannel with exponentially increasing obstacle arrays. Anal Chem 80:3035–3039
Choi S, Song S, Choi C, Park JK (2007) Continuous blood cell separation by hydrophoretic filtration. Lab Chip 7:1532–1538
Choi S, Song S, Choi C, Park JK (2008) Sheathless focusing of microbeads and blood cells based on hydrophoresis. Small 4:634–641
Choi KH, Rehmani MAA, Doh I, Cho Y (2009a) Numerical study of particle focusing through improved lab-on-a-chip device by positive dielectrophoresis. Microsyst Technol 15:1059–1065
Choi S, Song S, Choi C, Park JK (2009b) Hydrophoretic sorting of micrometer and submicrometer particles using anisotropic microfluidic obstacles. Anal Chem 81:50–55
Choi S, Song S, Choi C, Park JK (2009c) Microfluidic self-sorting of mammalian cells to achieve cell cycle synchrony by hydrophoresis. Anal Chem 81:1964–1968
Chou CF, Zenhausern F (2003) Electrodeless dielectrophoresis for micro total analysis systems. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag 22:62–67
Chou CF, Tegenfeldt JO, Bakajin O, Chan SS, Cox EC, Darnton N, Duke T, Austin RH (2002) Electrodeless dielectrophoresis of single- and double-stranded DNA. Biophys J 83:2170–2179
Chu H, Doh I, Cho Y (2009) A three-dimensional (3D) particle focusing channel using the positive dielectrophoresis (pDEP) guided by a dielectric structure between two planar electrodes. Lab Chip 9:686–691
Chung TD, Kim HC (2007) Recent advances in miniaturized microfluidic flow cytometry for clinical use. Electrophoresis 28:4511–4520
Church C, Zhu J, Wang G, Tzeng TJ, Xuan X (2009) Electrokinetic focusing and filtration of cells in a serpentine microchannel. Biomicrofluidics 3:044109
Clarke RW, White SS, Zhou D, Ying L, Klenerman D (2005) Trapping of proteins under physiological conditions in a nanopipette. Angew Chem 44:3747–3750
Cummings EB, Singh AK (2000) Dielectrophoretic trapping without embedded electrodes. In: Proceedings of SPIE conference micromachining microfabrication, vol 4177, pp 164–173
Cummings EB, Singh AK (2003) Dielectrophoresis in microchips containing arrays of insulating posts: theoretical and experimental results. Anal Chem 75:4724–4731
Davison SM, Sharp KV (2008) Transient simulations of the electrophoretic motion of a cylindrical particle through a 90° corner. Microfluid Nanofluid 4:409–418
Demierre N, Braschler T, Muller R (2008) Focusing and continuous separation of cells in a microfluidic device using lateral dielectrophoresis. Sens Actuators B 132:388–396
Di Carlo D (2009) Inertial microfluidics. Lab Chip 9:3038–3046
Di Carlo D, Irimia D, Tompkins RG, Toner M (2007) Continuous inertial focusing, ordering, and separation of particles in microchannels. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:18892–18897
Di Carlo D, Edd JF, Irimia D, Tompkins RG, Toner M (2008) Equilibrium separation and filtration of particles using differential inertial focusing. Anal Chem 80:2204–2211
Di Carlo D, Edd JF, Humphry KJ, Stone HA, Toner M (2009) Particle segregation and dynamics in confined flows. Phys Rev Lett 102:094503
Edd JF, Di Carlo D, Humphry KJ, Koester S, Irimia D, Weitz DA, Toner M (2008) Controlled encapsulation of single-cells into monodisperse picolitre drops. Lab Chip 8:1262–1264
Faivre M, Abkarian M, Bickraj K, Stone HA (2006) Geometrical focusing of cells in a microfluidic device: an approach to separate blood plasma. Biorheology 43:147–159
Fu AY, Spence C, Scherer A, Arnold FH, Quake SRA (1999) Microfabricated fluorescence-activated cell sorter. Nat Biotechnol 17:1109–1111
Fu LM, Yang RJ, Lin C, Pan Y, Lee GB (2004) Electrokinetically driven micro flow cytometers with integrated fiber optics for on-line cell/particle detection. Anal Chim Acta 507:163–169
Fu LM, Tsai CH, Lin CH (2008) A high-discernment microflow cytometer with microweir structure. Electrophoresis 29:1874–1880
Gallo-Villanueva RC, Rodriguez-Lopez CE, Diaz-de-la-Garza RI, Reyes-Betanzo C, Lapizco-Encinas BH (2009) DNA manipulation by means of insulator-based dielectrophoresis employing direct current electric fields. Electrophoresis 30:4195–4205
Gascoyne PRC, Vykoukal JV (2002) Particle separation by dielectrophoresis. Electrophoresis 23:1973–1983
Gascoyne PRC, Vykoukal JV (2004) Dielectrophoresis-based sample handling in general-purpose programmable diagnostic instruments. Proc IEEE 92:22–42
Goddard GR, Martin JC, Graves SW, Kaduchak G (2006) Ultrasonic particle concentration for sheath-less focusing of particles for analysis in a flow cytometer. Cytometry 69A:66–74
Goddard GR, Sanders CK, Martin JC, Kaduchak G, Graves SW (2007) Analytical performance of an ultrasonicparticle focusing flow cytometer. Anal Chem 79:8740–8746
Godin J, Chen C, Cho SH, Qiao W, Tsai F, Lo Y (2008) Microfluidics and photonics for bio-system-on-a-chip: a review of advancements in technology towards a microfluidic flow cytometry chip. J Biophoton 1:355–376
Golden JP, Kim JS, Erickson JS, Hilliard LR, Howell PB, Anderson GP, Nasir M, Ligler FS (2009) Multi-wavelength microflow cytometer using groove-generated sheath flow. Lab Chip 9:1942–1950
Gossett DR, Di Carlo D (2009) Particle focusing mechanisms in curving confined flows. Anal Chem 81:2459–2465
Hairer G, Vellekoop MJ (2009) An integrated flow-cell for full sample stream control. Microfluid Nanofluid 7:647–658
Hairer G, Parr GS, Svasek P, Jachimowicz A, Vellekoop MJ (2008) Investigations of micrometer sample stream profiles in a three-dimensional hydrodynamic focusing device. Sens Actuators B 132:518–524
Hawkins BG, Smith AE, Syed YA, Kirby BJ (2007) Continuous-flow particle separation by 3D insulative dielectrophoresis using coherently shaped, DC-biased, AC electric fields. Anal Chem 79:7291–7300
Holmes D, Morgan H, Green NG (2006) High throughput particle analysis: combining dielectrophoretic particle focusing with confocal optical detection. Biosens Bioelectron 21:1621–1630
Hou HH, Tsai CH, Fu LM, Yang RJ (2009) Experimental and numerical investigation into micro-flow cytometer with 3-D hydrodynamic focusing effect and micro-weir structure. Electrophoresis 30:2507–2515
Howell PB, Golden JP, Hilliard LR, Erickson JS, Mott DR, Ligler FS (2008) Two simple and rugged designs for creating microfluidic sheath flow. Lab Chip 8:1097–1103
Hsu CH, Di Carlo D, Chen CC, Irimia D, Toner M (2008) Microvortex for focusing, guiding and sorting of particles. Lab Chip 8:2128–2134
Hughes MP (2002) Strategies for dielectrophoretic separation in laboratory-on-a-chip systems. Electrophoresis 23:2569–2582
Huh D, Gu W, Kamotani Y, Grotgerg JB, Takayama S (2005) Microfluidics for flow cytometric analysis of cells and particles. Physiol Meas 26:R73–R98
Hur SC, Tse HTK, Di Carlo D (2009) Sheathless inertial cell ordering for extreme throughput flow cytometry. Lab Chip. doi:10.1039/b919495a
Jeffrey RC, Pearson JRA (1965) Particle motion in laminar vertical tube flow. J Fluid Mech 22:721–735
Jen CP, Chen TW (2008) Selective trapping of live and dead mammalian cells using insulator-based dielectrophoresis within open-top microstructures. Biomed Microdev 11:597–607
Kang K, Kang Y, Xuan X, Li D (2006) Continuous separation of microparticles by size with DC-dielectrophoresis. Electrophoresis 27:694–702
Kang Y, Li D, Kalams SA, Eid JE (2008) DC-dielectrophoretic separation of biological cells by size. Biomed Microdev 10:243–249
Kang Y, Cetin B, Wu Z, Li D (2009) Continuous particle separation with localized AC-dielectrophoresis using embedded electrodes and an insulating hurdle. Electrochim Acta 54:1715–1720
Kersaudy-Kerhoas M, Dhariwal R, Desmulliez MPY (2008) Recent advances in microparticle continuous separation. IET Nanobiotechnol 2:1–13
Kim YW, Yoo JY (2008) The lateral migration of neutrally-buoyant spheres transported through square microchannels. J Micromech Microeng 18:065015(1–13)
Kim YW, Yoo JY (2009a) Axisymmetric flow focusing of particles in a single microchannel. Lab Chip 9:1043–1045
Kim YW, Yoo JY (2009b) Three-dimensional focusing of red blood cells in microchannels for bio-sensing applications. Biosens Bioelectron 24:3677–3682
Kim JS, Anderson GP, Erickson JS, Golden JP, Nasir M, Ligler FS (2009) Multiplexed detection of bacteria and toxins using a microflow cytometer. Anal Chem 81:5426–5432
Kohlheyer D, Unnikrishnan S, Besselink GAJ, Schlautmann S, Schasfoort RBM (2008) A microfluidic device for array patterning by perpendicular electrokinetic focusing. Microfluid Nanofluid 4:557–564
Kulrattanarak T, van der Sman RGM, Schroen CGPH, Boom RM (2008) Classification and evaluation of microfluidic devices for continuous suspension fractionation. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 142:53–65
Kummrow A, Theisen J, Frankowski M, Tuchscheerer A, Yildirim H, Brattke K, Schmidt M, Neukammer J (2009) Microfluidic structures for flow cytometric analysis of hydrodynamically focussed blood cells fabricated by ultraprecision micromachining. Lab Chip 9:972–981
Kuntaegowdanahalli S, Bhagat AAS, Kumar G, Papautsky I (2009) Inertial microfluidics for continuous particle separation in spiral microchannels. Lab Chip 9:2973–2980
Lapizco-Encinas BH, Rito-Palmomares M (2007) Dielectrophoresis for the manipulation of nanoparticles. Electrophoresis 28:4521–4538
Lapizco-Encinas BH, Simmons BA, Cummings EB, Fintschenko Y (2004a) Dielectrophoretic concentration and separation of live and dead bacteria in an array of insulators. Anal Chem 76:1571–1579
Lapizco-Encinas BH, Simmons BA, Cummings EB, Fintschenko Y (2004b) Insulator-based dielectrophoresis for the selective concentration and separation of live bacteria in water. Electrophoresis 25:1695–1704
Lapizco-Encinas BH, Davalos RV, Simmons BA, Cummings EB, Fintschenko Y (2005) An insulator-based (electrodeless) dielectrophoretic concentrator for microbes in water. J Microbiol Method 62:317–326
Lapizco-Encinas BH, Ozuna-Chacon S, Rito-Palomares M (2008) Protein manipulation with insulator-based dielectrophoresis and DC electric fields. J Chromatogr A 1206:45–51
Leal LG (1980) Particle motions in a viscous fluid. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 12:435–476
Lee GB, Lin C, Chang G (2003) Micro flow cytometers with buried SU-8/SOG optical waveguides. Sens Actuators A 103:165–170
Lee GB, Chang CC, Huang SB, Yang RJ (2006) The hydrodynamic focusing effect in rectangular microchannels. J Micromech Microeng 16:1024–1032
Lee MG, Choi S, Park JK (2009) Three-dimensional hydrodynamic focusing with a single sheath flow in a single-layer microfluidic device. Lab Chip 9:3155–3160
Lewpiriyawong N, Yang C, Lam YC (2008) Dielectrophoretic manipulation of particles in a modified microfluidic H-Filter with multi-insulating blocks. Biomicrofluidics 2:034105
Lin CH, Lee GB, Fu LM, Hwey BH (2004) Vertical focusing device utilizing dielectrophoretic force and its application on microflow cytometer. J Microelectromech Syst 13:923–932
Lin R, Ho C, Liu C, Chang H (2006) Dielectrophoresis based-cell patterning for tissue engineering. Biotechnol J 1:949–957
Liu C, Stakenborg T, Peeters S, Lagae L (2009) Cell manipulation with magnetic particles toward microfluidic cytometry. J Appl Phys 105:102014
Mao X, Huang TJ (2008) Focusing fluids and light in micro/nano scale—enabling technologies for single-particle detection. IEEE Nanotechnol Mag 2:22–27
Mao X, Waldeisen JR, Huang TJ (2007) “Microfluidic drifting”—implementing three-dimensional hydrodynamic focusing with a single-layer planar microfluidic device. Lab Chip 7:1260–1262
Mao X, Lin SS, Dong C, Huang TJ (2009) Single-layer planar on-chip flow cytometer using microfluidic drifting based three-dimensional (3D) hydrodynamic focusing. Lab Chip 9:1583–1589
Morgan H, Green NG (2002) AC electrokinetics: colloids and nanoparticles. Research Studies Press, Hertfordshire
Morton KJ, Loutherback K, Inglis DW, Tsui OK, Sturm JC, Chou SY, Austin RH (2008) Hydrodynamic metamaterials: microfabricated arrays to steer, refract, and focus streams of biomaterials. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:7434–7438
Ozuna-Chacon S, Lapizco-Encinas BH, Rito-Palomares M, Martínez-Chapa SO, Reyes-Betanzo C (2008) Performance characterization of an insulator-based dielectrophoretic microdevice. Electrophoresis 29:3115–3122
Pamme N (2007) Continuous flow separations in microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 7:1644–1659
Park J, Song S, Jung H (2009) Continuous focusing of microparticles using inertial lift force and vorticity via multi-orifice microfluidic channels. Lab Chip 9:939–948
Petersson F, Nilsson A, Jonsson H, Laurell T (2005) Carrier medium exchange through ultrasonic particle switching in microfluidic channels. Anal Chem 77:1216–1221
Petersson F, Aberg L, Sword-Nilsson AM, Laurell T (2007) Free flow acoustophoresis: microfluidic-based mode of particle and cell separation. Anal Chem 79:5117–5123
Pohl HA (1978) Dielectrophoresis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Prinz C, Tegenfeldt JO, Austin RH, Cox EC, Sturm JC (2002) Bacterial chromosome extraction and isolation. Lab Chip 2:207–212
Pysher MD, Hayes MA (2007) Electrophoretic and dielectrophoretic field gradient technique for separating bioparticles. Anal Chem 79:4552–4557
Repetti RV, Leonard EF (1964) Segré-Silberberg annulus formation: a possible explanation. Nature 203:1346–1348
Rodriguez-Trujillo R, Mills CA, Samitier J, Gomila G (2007) Low cost micro-Coulter counter with hydrodynamic focusing. Microfluid Nanofluid 3:171–176
Russom A, Gupta AK, Nagrath S, Di Carlo D, Edd JF, Toner M (2009) Differential inertial focusing of particles in curved low-aspect-ratio microchannels. New J Phys 11:075025
Saffman PG (1965) The lift on a small sphere in a slow shear flow. J Fluid Mech 22:385–400
Scott R, Sethu P, Harnett CK (2008) Three-dimensional hydrodynamic focusing in a microfluidic Coulter counter. Rev Sci Instrum 79:046104
Segre G, Silberberg A (1961) Radial particle displacements in Poiseuille flow of suspensions. Nature 189:209–210
Seo J, Lean MH, Kole A (2007a) Membrane-free microfilltration by asymmetric inertial migration. Appl Phys Lett 91:033901
Seo J, Lean MH, Kole A (2007b) Membraneless microseparation by asymmetry in curvilinear laminar flows. J Chromatogr A 1162:126–131
Shi J, Mao X, Ahmed D, Colletti A, Huang TJ (2008) Focusing microparticles in a microfluidic channel with standing surface acoustic waves (SSAW). Lab Chip 8:221–223
Shi J, Ahmed D, Mao D, Lin SS, Huang TJ (2009a) Acoustic tweezers: patterning cells and microparticles using standing surface acoustic waves (SSAW). Lab Chip 9:2890–2895
Shi J, Huang H, Stratton Z, Lawit A, Huang Y, Huang TJ (2009b) Continuous particle separation in a microfluidic channel via standing surface acoustic waves (SSAW). Lab Chip 9:3354–3359
Sims CE, Allbritton NL (2007) Analysis of single mammalian cells on-chip. Lab Chip 7:423–440
Tanaka Y, Sato K, Shimizu T, Yamato M, Okano T, Kitamori T (2007) Biological cells on microchips: new technologies and applications. Biosens Bioelectron 23:449–458
Thwar PK, Linderman JJ, Burns MA (2007) Electrodeless direct current dielectrophoresis using reconfigurable field-shaping oil barriers. Electrophoresis 28:4572–4581
Toner M, Irimia D (2005) Blood-on-a-chip. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 7:77–103
Tsai CG, Hou HH, Fu LM (2008) An optimal three-dimensional focusing technique for micro-flow cytometers. Microfluid Nanofluid 5:827–836
Tsutsui H, Ho CM (2009) Cell separation by non-inertial force fields in microfluidic systems. Mech Res Commun 36:92–103
Voldman J (2006) Electrical forces for microscale cell manipulation. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 8:425–454
Wang L, Lu J, Marchenko SA, Monuki ES, Flanagan LA, Lee AP (2009) Dual frequency dielectrophoresis with interdigitated sidewall electrodes for microfluidic flow-through separation of beads and cells. Electrophoresis 30:1–10
Watkins N, Venkatesan BM, Toner M, Rodriguez W, Bashir R (2009) A robust electrical microcytometer with 3-dimensional hydrofocusing. Lab Chip 9:3177–3184
Xuan X, Li D (2005) Focused electrophoretic motion and selected electrokinetic dispensing of particles and cells in cross-microchannels. Electrophoresis 26:3552–3560
Xuan X, Raghibizadeh S, Li D (2006) Wall effects on electrophoretic motion of spherical polystyrene particles in a rectangular poly(dimethylsiloxane) microchannel. J Colloid Interface Sci 296:743–748
Yamada M, Seki M (2005) Hydrodynamic filtration for on-chip particle concentration and classification utilizing microfluidics. Lab Chip 5:1233–1239
Yamada M, Seki M (2006) Microfluidic particle sorter employing flow splitting and recombining. Anal Chem 78:1357–1362
Yamada M, Kano K, Tsuda Y, Kobayashi J, Yamato M, Seki M, Okano T (2007) Microfluidic devices for size-dependent separation of liver cells. Biomed Microdev 9:637–645
Yamada M, Kobayashi J, Yamato M, Seki M, Okano T (2008) Millisecond treatment of cells using microfluidic devices via two-step carrier-medium exchange. Lab Chip 8:772–778
Yang RJ, Chang CC, Huang SB, Lee GB (2005) A new focusing model and switching approach for electrokinetic flow inside microchannels. J Micromech Microeng 15:2141–2148
Yi CQ, Li CW, Ji SL, Yang MS (2006) Microfluidics technology for manipulation and analysis of biological cells. Anal Chim Acta 560:1–23
Ying LM, White SS, Bruckbauer A, Meadows L, Korchev YE, Klenerman D (2004) Frequency and voltage dependence of the dielectrophoretic trapping of short lengths of DNA and dCTP in a nanopipette. Biophys J 86:1018–1027
Yu C, Vykoukal J, Vykoukal DM, Schwartz JA, Shi L, Gascoyne PRC (2005) A three-dimensional dielectrophoretic particle focusing channel for microcytometry applications. J Microelectromech Syst 14:480–487
Zeng L, Balachandar S, Fischer P (2005) Wall-induced forces on a rigid sphere at finite Reynolds number. J Fluid Mech 536:1–25
Zhao Y, Fujimoto BS, Jeffries GDM, Schiro PG, Chiu DT (2007) Optical gradient flow focusing. Opt Express 15:6167–6176
Zhu J, Xuan X (2009a) Dielectrophoretic focusing of particles in a microchannel constriction using DC-biased AC electric fields. Electrophoresis 30:2668–2675
Zhu J, Xuan X (2009b) Particle electrophoresis and dielectrophoresis in curved microchannels. J Colloid Interface Sci 340:285–290
Zhu J, Tzeng TR, Hu G, Xuan X (2009a) DC dielectrophoretic focusing of particles in a serpentine microchannel. Microfluid Nanofluid 7:751–756
Zhu J, Tzeng JT, Xuan X (2009b) Dielectrophoretic focusing of microparticles in curved microchannels. In: Proceedings of the ASME 2009 international mechanical engineering congress and exposition, IMECE2009-11876, Lake Buena Vista, FL
Zhu J, Tzeng TR, Xuan X (2010) Continuous dielectrophoretic separation of particles in a spiral microchannel. Electrophoresis. doi:10.1002/elps.200900736 (in press)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NSF under grant CBET-0853873 with Marc S. Ingber as the grant monitor. The support from Clemson University through a startup package to Xuan, the Creative Inquiry Program, and the Research Investment Initiative Fund Program is also gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xuan, X., Zhu, J. & Church, C. Particle focusing in microfluidic devices. Microfluid Nanofluid 9, 1–16 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-010-0602-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-010-0602-7