Abstract
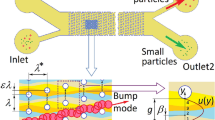
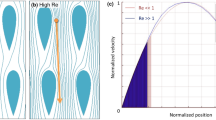
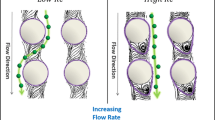
Deterministic lateral displacement arrays have shown great promise for size-based particle analysis and purification in medicine and biology. Here, we demonstrate that the use of an array of triangular rather than circular posts significantly enhances the performance of these devices by reducing clogging, lowering hydrostatic pressure requirements, and increasing the range of displacement characteristics. Experimental data and theoretical models are presented to create a compelling argument that future designs of deterministic lateral displacement arrays should employ triangular posts. The effect of practical considerations, such as vertex rounding, post size, and shape, is also discussed.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beech JP, Tegenfeldt JO (2008) Tunable separation in elastomeric microfluidics devices. Lab Chip 8:657–659
Beech JP, Jönsson P, Tegenfeldt JO (2009) Tipping the balance of deterministic lateral displacement devices using dielectrophoresis. Lab Chip 9:2698–2706
Bhagat AAS, Kuntaegowdanahalli SS, Papautsky I (2008) Continuous particle separation in spiral microchannels using Dean flows and differential migration. Lab Chip 8:1906–1914
Davis JA, Inglis DW, Morton KJ et al (2006) Deterministic hydrodynamics: taking blood apart. PNAS 103(40):14779–14784
Di Carlo D, Irimia D, Tompkins RG, Toner M (2007) Continuous inertial focusing, ordering, and separation of particles in microchannels. PNAS 104(48):18892–18897
Huang LR, Cox EC, Austin RH, Sturm JC (2004) Continuous particle separation through deterministic lateral displacement. Science 304:987–990
Inglis DW, Davis JA, Austin RH, Sturm JC (2006) Critical particle size for fractionation by deterministic lateral displacement. Lab Chip 6:655–658
Lindken R, Rossi M, Große S, Westerweel J (2009) Micro-particle image velocimetry (micropiv): recent developments, applications, and guidelines. Lab Chip 9:2551–2567
Loutherback K, Puchalla J, Austin RH, Sturm JC (2009) Deterministic microfluidic ratchet. Phys Rev Lett 102:045301
Lu H, Gaudet S, Schmidt MA, Jensen KF (2004) A microfabricated device for subcellular organelle sorting. Anal Chem 76:5705–5712
Morton KJ, Sturm JC, Austin RH, Chou SY (2006) Proceedings of the μTAS conference 2006, Tokyo, pp 1014–1016
Pamme N (2007) Continuous flow separations in microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 7:1644–1659
Rida A, Gijs MAM (2004) Manipulation of self-assembled structures of magnetic beads for microfluidic mixing and assaying. Anal Chem 76:6239–6246
Squires TM, Quake SR (2005) Microfluidics: fluid physics at the nanoliter scale. Rev Mod Phys 77:977–1026
White FM (2006) Viscous fluid flow, 3rd edn. McGraw Hill, New York, pp 108, 165–171
Yi CQ, Li CW, Ji SL, Yang MS (2006) Microfluidics technology for manipulation and analysis of biological cells. Anal Chim Acta 560:1–23
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by award number U54CA143803 from the NCI and HG01506 from the NIH. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Cancer Institute or the National Institutes of Health. We thank Noah Jafferis for SEM characterization, Clinton Smith and Steve Chou for device etching, and David Inglis for providing circular post bead data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loutherback, K., Chou, K.S., Newman, J. et al. Improved performance of deterministic lateral displacement arrays with triangular posts. Microfluid Nanofluid 9, 1143–1149 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-010-0635-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-010-0635-y