Abstract
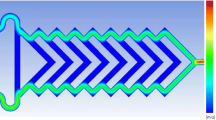
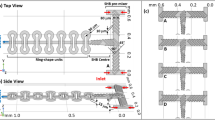
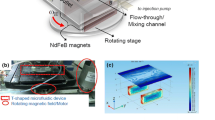
We present a flexible and noninvasive approach for efficient continuous micromixing and microreaction based on direct current-induced thermal buoyancy convection in a single microfluidic unit. Theoretically, microfluids in this microsystem are unevenly heated by powering the asymmetrically arranged microheater. The thermal buoyancy convection is then formed to induce microvortices that cause effective fluidic interface disturbance, thereby promoting the diffusion and convective mass transfer. The temperature distribution and the convection flow in the microchip are first characterized and studied, which can be flexibly adjusted by changing the DC voltage. Then the mixing performance of the presented method is validated by joint numerical and experimental analyses. Specifically, at U = 7 V, the mixing efficiencies are higher than 90% as the flow rate is lower than Qv= 600 nL/s. So high-quality chemical or biochemical reactions needing both suitable heating and efficient mixing can be achieved using this method. Finally, as one example, we use this method to synthesize nano-sized cuprous oxide (Cu2O) particles by effectively mixing the Benedict’s solution and glucose buffer. Remarkably, the particle size can be tuned by changing the voltage and the concentration of Benedict’s solution. Therefore, this micromixer can be attractive for diverse applications needing homogeneous sample mixtures.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrberg CD, Manz A, Chung BG (2016) Polymerase chain reaction in microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 16:3866–3884. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6lc00984k
Akimoto K, Ishizuka S, Yanagita M, Nawa Y, Paul GK, Sakurai T (2006) Thin film deposition of Cu2O and application for solar cells. Sol Energy 80:715–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2005.10.012
Britton J, Raston CL (2017) Multi-step continuous-flow synthesis. Chem Soc Rev 46:1250–1271. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6cs00830e
Cao J, Cheng P, Hong FJ (2007) A numerical study of an electrothermal vortex enhanced micromixer. Microfluid Nanofluid 5:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-007-0201-4
Chang C-C, Yang R-J (2009) Chaotic mixing in electro-osmotic flows driven by spatiotemporal surface charge modulation. Phys Fluids 21:052004. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3139162
Chen JK, Yang RJ (2007) Electroosmotic flow mixing in zigzag microchannels. Electrophoresis 28:975–983. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.200600470
Chen JK, Weng CN, Yang RJ (2009) Assessment of three AC electroosmotic flow protocols for mixing in microfluidic channel. Lab Chip 9:1267–1273. https://doi.org/10.1039/b819547a
Cortes-Quiroz CA, Azarbadegan A, Zangeneh M (2017) Effect of channel aspect ratio of 3-D T-mixer on flow patterns and convective mixing for a wide range of Reynolds number. Sens Actuators B 239:1153–1176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.08.116
Cui W et al (2016) Localized ultrahigh frequency acoustic fields induced micro-vortices for submilliseconds microfluidic mixing. Appl Phys Lett 109:253503. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4972484
Deng Y, Zhou T, Liu Z, Wu Y, Qian S, Korvink JG (2018) Topology optimization of electrode patterns for electroosmotic micromixer. Int J Heat Mass Transf 126:1299–1315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.06.065
Dong Y, Li Y, Wang C, Cui A, Deng Z (2001) Preparation of Cuprous Oxide Particles of Different Crystallinity. J Colloid Interface Sci 243:85–89. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.2001.7857
Feng Q, Sun J, Jiang X (2016) Microfluidics-mediated assembly of functional nanoparticles for cancer-related pharmaceutical applications. Nanoscale 8:12430–12443. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5nr07964k
Feng X et al (2019) Effect of vortex on mass transport and mixing in microcapillary channels. Chem Eng J 362:442–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.055
Flores-Flores E et al (2015) Trapping and manipulation of microparticles using laser-induced convection currents and photophoresis. Biomed Optics Express 6:4079–4087. https://doi.org/10.1364/BOE.6.004079
Ftouni J, Penhoat M, Addad A, Payen E, Rolando C, Girardon JS (2012) Highly controlled synthesis of nanometric gold particles by citrate reduction using the short mixing, heating and quenching times achievable in a microfluidic device. Nanoscale 4:4450–4454. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2nr11666a
Fu L-M, Ju W-J, Tsai C-H, Hou H-H, Yang R-J, Wang Y-N (2013) Chaotic vortex micromixer utilizing gas pressure driving force. Chem Eng J 214:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.10.032
Harnett CK, Templeton J, Dunphy-Guzman KA, Senousy YM, Kanouff MP (2008) Model based design of a microfluidic mixer driven by induced charge electroosmosis. Lab Chip 8:565–572. https://doi.org/10.1039/b717416k
Huang L, Peng F, Yu H, Wang H (2009) Preparation of cuprous oxides with different sizes and their behaviors of adsorption, visible-light driven photocatalysis and photocorrosion. Solid State Sci 11:129–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2008.04.013
Jain M, Yeung A, Nandakumar K (2009) Induced charge electro osmotic mixer: Obstacle shape optimization. Biomicrofluidics 3:22413. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3167279
Kang HW, Leem J, Yoon SY, Sung HJ (2014) Continuous synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles in a microfluidic system for photovoltaic application. Nanoscale 6:2840–2846. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3nr06141h
Kang Z, Chen J, Wu SY, Chen K, Kong SK, Yong KT, Ho HP (2015) Trapping and assembling of particles and live cells on large-scale random gold nano-island substrates. Sci Rep 5:9978. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep09978
Kim SJ, Wang F, Burns MA, Kurabayashi K (2009) Temperature-programmed natural convection for micromixing and biochemical reaction in a single microfluidic chamber. Anal Chem 81:4510–4516. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac900512x
Kim J, Kwon Y, Lee H (2013) Metal ion-assisted reshaping of Cu2O nanocrystals for catalytic applications. J Mater Chem A 1:14183. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ta13182c
Kulkarni JA, Tam YYC, Chen S, Tam YK, Zaifman J, Cullis PR, Biswas S (2017) Rapid synthesis of lipid nanoparticles containing hydrophobic inorganic nanoparticles. Nanoscale 9:13600–13609. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nr03272b
Kwon Y, Soon A, Han H, Lee H (2015) Shape effects of cuprous oxide particles on stability in water and photocatalytic water splitting. J Mater Chem A 3:156–162. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ta04863f
Lam YC, Chen X, Yang C (2005) Depthwise averaging approach to cross-stream mixing in a pressure-driven microchannel flow. Microfluid Nanofluid 1:218–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-004-0013-8
Lee S, Liang CW, Martin LW (2011) Synthesis, control, and characterization of surface properties of Cu(2)O nanostructures. ACS Nano 5:3736–3743. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn2001933
Lim CY, Lam YC, Yang C (2010) Mixing enhancement in microfluidic channel with a constriction under periodic electro-osmotic flow. Biomicrofluidics 4:14101. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3279790
Liu Z, Lu Y, Yang B, Luo G (2011) Controllable Preparation of Poly(butyl acrylate) by Suspension Polymerization in a Coaxial Capillary Microreactor. Ind Eng Chem Res 50:11853–11862. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie201497b
Liu Y, Deng Y, Zhang P, Liu Z, Wu Y (2013) Experimental investigation of passive micromixers conceptual design using the layout optimization method. J Micromech Microeng 23:075002. https://doi.org/10.1088/0960-1317/23/7/075002
Loucaides N, Ramos A, Georghiou GE (2012) Configurable AC electroosmotic pumping and mixing. Microelectron Eng 90:47–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2011.04.007
Lu Y et al (2018) On-chip acoustic mixer integration of electro-microfluidics towards in situ and efficient mixing in droplets. Microfluidics Nanofluidics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-018-2169-7
Mallea RT, Bolopion A, Beugnot J-C, Lambert P, Gauthier M (2017) Laser-Induced Thermocapillary Convective Flows: a New Approach for Noncontact Actuation at Microscale at the Fluid/Gas Interface. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 22:693–704. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmech.2016.2639821
Miyakawa M, Hiyoshi N, Nishioka M, Koda H, Sato K, Miyazawa A, Suzuki TM (2014) Continuous syntheses of Pd@Pt and Cu@Ag core-shell nanoparticles using microwave-assisted core particle formation coupled with galvanic metal displacement. Nanoscale 6:8720–8725. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4nr00118d
Ng WY, Goh S, Lam YC, Yang C, Rodriguez I (2009) DC-biased AC-electroosmotic and AC-electrothermal flow mixing in microchannels. Lab Chip 9:802–809. https://doi.org/10.1039/b813639d
Nian J-N, Hu C-C, Teng H (2008) Electrodeposited p-type Cu2O for H2 evolution from photoelectrolysis of water under visible light illumination. International J Hydrog Energy 33:2897–2903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.03.052
Pan Y-J, Ren C-M, Yang R-J (2007) Electrokinetic flow focusing and valveless switching integrated with electrokinetic instability for mixing enhancement. J Micromech Microeng 17:820–827. https://doi.org/10.1088/0960-1317/17/4/020
Pradhan TK, Panigrahi PK (2015) Thermocapillary convection inside a stationary sessile water droplet on a horizontal surface with an imposed temperature gradient. Exp Fluids. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-015-2051-2
Qu H et al (2017) On-chip integrated multiple microelectromechanical resonators to enable the local heating, mixing and viscosity sensing for chemical reactions in a droplet. Sens Actuators B: Chem 248:280–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.03.173
Roy T, Sinha A, Chakraborty S, Ganguly R, Puri IK (2009) Magnetic microsphere-based mixers for microdroplets. Phys Fluids 21:027101. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3072602
Santana HS, Silva JL, Taranto OP (2019) Optimization of micromixer with triangular baffles for chemical process in millidevices. Sens Actuators B: Chem 281:191–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.10.089
Sugioka H (2010) Chaotic mixer using electro-osmosis at finite Peclet number. Phys Rev E 81:036306. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.81.036306
Vela E, Hafez M, Régnier S (2009) Laser-induced thermocapillary convection for mesoscale manipulation. Int J Optomechatronics 3:289–302. https://doi.org/10.1080/15599610903389477
Velez-Cordero JR, Velazquez-Benitez AM, Hernandez-Cordero J (2014) Thermocapillary flow in glass tubes coated with photoresponsive layers. Langmuirs 30:5326–5336. https://doi.org/10.1021/la404221p
Wang S, Huang X, Yang C (2011) Mixing enhancement for high viscous fluids in a microfluidic chamber. Lab Chip 11:2081–2087. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0lc00695e
Wang S, Huang X, Yang C (2012) Microfluidic bubble generation by acoustic field for mixing enhancement. J Heat Transfer 134:051014. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4005705
Wang Z, Zhang H, Yang Y, Qu H, Han Z, Pang W, Duan X (2017) Wireless Controlled Local Heating and Mixing Multiple Droplets Using Micro-Fabricated Resonator Array for Micro-Reactor Applications. IEEE Access 5:25987–25992. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2017.2766270
Wang H, Shi L, Zhou T, Xu C, Deng Y (2018) A novel passive micromixer with modified asymmetric lateral wall structures. Asia-Pac J Chem Eng 13:e2202. https://doi.org/10.1002/apj.2202
Winterer F, Maier CM, Pernpeintner C, Lohmuller T (2018) Optofluidic transport and manipulation of plasmonic nanoparticles by thermocapillary convection. Soft Matter 14:628–634. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7sm01863k
Wu Z, Li D (2007) Mixing and flow regulating by induced-charge electrokinetic flow in a microchannel with a pair of conducting triangle hurdles. Microfluid Nanofluid 5:65–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-007-0227-7
Yang J et al (2018) Size-tunable capture of mesoscopic matters using thermocapillary vortex. Appl Phys Lett 113:131602. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5037862
Yesiloz G, Boybay MS, Ren CL (2017) Effective thermo-capillary mixing in droplet microfluidics integrated with a microwave heater. Anal Chem 89:1978–1984. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b04520
Yu N et al (2018) Integrated obstacle microstructures for gas-liquid separation and flow switching in microfluidic networks. Sens Actuators B: Chem 256:735–743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.09.207
Zhang F, Chen H, Chen B, Wu J (2016) Alternating current electrothermal micromixer with thin film resistive heaters. Adv Mech Eng 8:168781401664626. https://doi.org/10.1177/1687814016646264
Zhang K, Ren Y, Hou L, Feng X, Chen X, Jiang H (2018) An efficient micromixer actuated by induced-charge electroosmosis using asymmetrical floating electrodes. Microfluidics Nanofluidics 22:10–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-018-2153-2
Zhang K, Ren Y, Tao Y, Liu W, Jiang T, Jiang H (2019) Efficient micro/nanoparticle concentration using direct current-induced thermal buoyancy convection for multiple liquid media. Anal Chem 91:4457–4465. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b05105
Zhao Y, Zhao C, He J, Zhou Y, Yang C (2013) Collective effects on thermophoresis of colloids: a microfluidic study within the framework of DLVO theory. Soft Matter 9:7726. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3sm27720h
Zheng J, Xing X, Yang J, Shi K, He S (2018) Hybrid optofluidics and three-dimensional manipulation based on hybrid photothermal waveguides. NPG Asia Mater 10:340–351. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41427-018-0026-5
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.11672095, No.11872165, No. 11702075, No. 11702035). Self-Planned Task (SKLRS201803B) of State Key Laboratory of Robotics and System (HIT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, K., Ren, Y., Hou, L. et al. Continuous microfluidic mixing and the highly controlled nanoparticle synthesis using direct current-induced thermal buoyancy convection. Microfluid Nanofluid 24, 1 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-019-2306-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-019-2306-y