Abstract
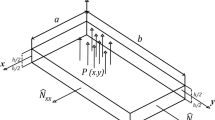
In this paper, wave and vibratory power transmission in a finite L-shaped Mindlin plate with two simply supported opposite edges are investigated using the wave approach. The dynamic responses, active and reactive power flow in the finite plate are calculated by the Mindlin plate theory (MPT) and classic plate theory (CPT). To satisfy the boundary conditions and continuous conditions at the coupled junction of the finite L-shaped plate, the near-field and far-field waves are entirely contained in the wave approach. The in-plane longitudinal and shear waves are also considered. The results indicate that the vibratory power flow based on the MPT is different from that based on the CPT not only at high frequencies but also at low and medium frequencies. The influence of the plate thickness on the vibrational power flow is investigated. From the results it is seen that the shear and rotary inertia correction of the MPT can influence the active and reactive power at the junction of the L-shaped plate not only at high frequencies but also at low and medium frequencies. Furthermore, the effects of structural damping on the active and reactive power flow at the junction are also analyzed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kessissoglou, N.J.: Active attenuation of the wave transmission through an L-plate junction. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 110(1), 267–277 (2001)
Kessissoglou, N.J.: An analytical and experimental investigation on active control of the flexural wave transmission in a simply supported bibbed plate. J. Sound Vib. 240(1), 73–85 (2001)
Keir, J., Kessissoglou, N.J., Norwood, C.: An analytical investigation of single actuator and error sensor control in connected plates. J. Sound Vib. 271(2), 635–649 (2004)
Kessissoglou, N.J.: Power transmission in L-shaped plates including flexural and in-plane vibration. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 115(3), 1157–1169 (2004)
Keir, J., Kessissoglou, N.J., Norwood, C.J.: Active control of connected plates using single and multiple actuators and error sensors. J. Sound Vib. 281(1), 73–97 (2005)
Mindlin, R.D.: Influence of rotary inertia and shear on flexural motions of isotropic, elastic plates. J. Appl. Mech. 18(1), 31–38 (1951)
Mindlin, R.D., Schachow, A., Deresiewicz, H.: Flexural vibrations of rectangular plate. J. Appl. Mech. 23(3), 430–436 (1956)
Dawe, D.J., Roufaeil, O.L.: Rayleigh-Ritz vibration analysis of Mindlin plates. J. Sound Vib. 69(3), 345–359 (1980)
Liew, K.M., Hung, K.C., Lim, M.K.: Vibration of Mindlin plates using boundary characteristic orthogonal polynomials. J. Sound Vib. 182(1), 77–90 (1995)
Lee, J.M., Kim, K.C.: Vibration analysis of rectangular isotropic thick plate using Mindlin plate characteristic functions. J. Sound Vib. 187(5), 865–877 (1995)
Liu, F.L., Liew, K.M.: Free vibration analysis of Mindlin sector plates: numerical solutions by differential quadrature method. Comput. Method Appl. M. 177(1–2), 77–92 (1999)
Xiang, Y., Liew, K.M., Kitipornchai, S.: Vibration analysis of rectangular Mindlin plates resting on elastic edge supports. J. Sound Vib. 204(1), 1–16 (1997)
Xiang, Y., Zhang, L.: Free vibration analysis of stepped circular Mindlin plates. J. Sound Vib. 280(3–5), 633–655 (2005)
Zhou, D.: Vibrations of Mindlin rectangular plates with elastically restrained edges using static Timoshenko beam functions with the Rayleigh-Ritz method. Int. J. Solids Struct. 38(32–33): 5565–5580 (2001)
Zhou, D., Lo, S.H., Au, F.T.K., et al.: Vibration analysis of rectangular Mindlin plates with internal line supports using static Timoshenko beam functions. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 44(12), 2503–2522 (2002)
Labuschagne, A., Rensburg, N.F.J., Merwe, A.J.: Vibration of a Reissner-Mindlin-Timoshenko plate-beam system. Math. Comput. Model 50(7–8), 1033–1044 (2009)
Hashemi, S.H., Omidi, M., Taher, H.R.D.: The validity range of CPT and Mindlin plate theory in comparison with 3-D vibrational analysis of circular plates on the elastic foundation. Eur. J. Mech. A-Solid 28(2), 289–304 (2009)
Akhavan, H., Hashemi, S.H., Taher, H.R.D., et al.: Exact solutions for rectangular Mindlin plates under in-plane loads resting on Pasternak elastic foundation. Part II: Frequency analysis. Comp. Mater. Sci. 44(3), 951–961 (2009)
Hashemi, S.H., Khorshidi, K., Taher, H.R.D.: Exact acoustical analysis of vibrating rectangular plates with two opposite edges simply supported via Mindlin plate theory. J. Sound Vib. 322(4–5), 883–900 (2009)
Xiang, Y., Lai, S.K., Zhou, L.: DSC-element method for free vibration analysis of rectangular Mindlin plates. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 52(4), 548–560 (2010)
Shen, H.S., Yang, J., Zhang, L.: Dynamic response of Reissner-Mindlin plates under thermomechanical loading and resting on elastic foundations. J. Sound Vib. 232(2), 309–329 (2000)
Yu, L., Shen, H.S., Hu, X.P.: Dynamic responses of Reissner-Mindlin plates with free edges resting on tensionless elastic foundations. J. Sound Vib. 299(1-2), 212–228 (2007)
Pan, X., Hansen, C.H.: The effect of error sensor location and type on the active control of beam vibration. J. Sound Vib. 165(3), 497–510 (1993)
Pan, X., Hansen, C.H.: Active control of vibratory power transmission along a semi-infinite plate. J. Sound Vib. 184(4), 585–610 (1995)
Mace, B.R.: Power flow between two continuous one-dimension subsystems: A wave solution. J. Sound Vib. 154(2), 289–319 (1992)
Mace, B.R.: The statistics of power flow between two continuous one dimension subsystems. J. Sound Vib. 154(2), 321–341 (1992)
McCollum, M.D., Cuschieri, J.M.: Bending and in-plane wave transmission in thick connected plates using statistical energy analysis. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 88(3), 1480–1485 (1990)
Cuschieri, J.M.: Structural power-flow analysis using a mobility approach of an L-shaped plate. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 87(3),1159–1165 (1990)
Cuschieri, J.M.: Parametric analysis of the power flow on an Lshaped plate using a mobility power flow approach. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 91(5), 2686–2695 (1992)
McCollum, M.D.: Vibrational power flow in thick connected plates. [Ph.D. Thesis], Florida Atlantic University Boca Raton (1988)
Cuschieri, J.M., McCollum, M.D.: Thick plate bending wave transmission using a mobility power flow approach. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 88(3), 1472–1479 (1990)
Cuschieri, J.M., McCollum, M.D.: In-plane and out-of-plane waves’ power transmission through a L-plate junction using the mobility power flow approach. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 100(2), 857–870 (1996)
Park, Y.H., Hong, S.Y.: Vibrational power flow models for transversely vibrating finite Mindlin plate. J. Sound Vib. 317(3–5), 800–840 (2008)
Liu, C.C., Li, F.M., Fang, B., et al.: Active control of power flow transmission in finite connected plate. J. Sound Vib. 329(20), 4124–4135 (2010)
Hu, C., Han, G., Li, F.M., et al.: Scattering of flexural waves and boundary-value problem in Mindlin’s plates of soft ferromagnetic material with a cutout. J. Sound Vib. 312(1–2), 151–165 (2008)
Bercin, A.N., Langley, R.S.: Application of the dynamic stiffness technique to the in-plane vibrations of plate structures. Comput. Struct. 59(5), 869–875 (1996)
Pao, Y.H., Mow, C.C.: Diffraction of elastic waves and dynamic stress concentrations. Crane, Russak & Company Inc US (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The project was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (2011CB711102) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (10672017, 11002045).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, CC., Li, FM., Liang, TW. et al. The wave and vibratory power transmission in a finite L-shaped Mindlin plate with two simply supported opposite edges. Acta Mech Sin 27, 785–795 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-011-0477-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-011-0477-1