Abstract
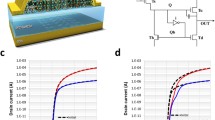
A reliable driving scheme that can compensate for the inherent instability of hydrogenated amorphous silicon (a-Si:H) thin film transistors (TFTs) is essential for implementation of large-area devices including displays and sensor arrays for bio-imaging applications. In particular, for high precision and high-resolution devices, the technique should be accurate and fast. A new driving scheme is presented that enables control of the DC and transient shift in the threshold voltage (V T ) and gate voltage of drive/amplifier TFT, while fulfilling the timing requirements for the different applications. The transient shift in the gate voltage has been known to contribute as much as 10% error in controlling the DC shift in the V T whereas it is less than 0.5% for the driving scheme presented here.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nathan, A., Kumar, A., Sakariya, K., Servati, P., Sambandan, S., Karim, K. S., & Striakhilev, D. (2004). Amorphous silicon thin film transistor circuit integration for organic LED displays on glass and plastic. IEEE Journal of Solid State Circuits, 39, 1477–1486.
Nathan, A., Chaji, G. R., & Ashtiani, S. J. (2005). Driving schemes for a-Si and LTPS AMOLED displays. IEEE Journal of Display Technology, 1, 267–277, Dec.
Karim, K. S., Nathan, A., & Rowlands, J. A. (2003). Amorphous silicon active pixel sensor readout circuit for digital imaging. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 50(1) 200–208.
Powell, M. J., Berkel, C., & Hughes, J. R. (1989). Time and temperature dependence of instability mechanisms in amorphous silicon thin-film transistors. Journal of Applied Physics Letters, 54, 1323–1325.
Aziz, H., Popovic, Z. D., Hu, N., Hor, A., & Xu, G. (1999). Degradation mechanism of small molecule-based organic light-emitting devices. Science, 283, 1900–1902.
Sheu, B. J., & Hu, C. (1984). Switch-induced error voltage on a switched capacitor. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, Sc-19, 519–525.
Wegmann, G., Vitoz, E. A., & Rahali, F. (1987). Charge injection in analog MOS switches. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, Sc-22, 1091–1097.
Chaji, G. R., Safavian, N., & Nathan, A. (2005). Dynamic-effect compensating technique for stable a-Si:H AMOLED displays. Proceedings of IEEE MIDWEST, Cincinnati, USA, Aug. 2005, pp. 786–789.
Safavian, N., Chaji, G. R., Nathan, A., & Rowlands, J. A. (2006). Three-TFT image sensor for real-time digital X-ray imaging. IEE Electronics Letters, 42(3) 31–32.
Sanford, J. L. & Libsch, F. R. (2003). TFT AMOLED Pixel Circuits and Driving Methods. In SID Int. Symposium, Baltimore, May 2003, pp. 10–13.
He, Y., Hattori, R., & Kanicki, J. (2001). Improved a-Si:H TFT circuits for active-matrix organic light emitting displays. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 48(7) 1322–1325.
Ashtiani, S. J., Servati, P., Striakhilev, D., & Nathan, A. (2005). A 3-TFT current-programmed pixel circuit for active-matrix organic light-emitting diode displays. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 52(7), 1514–1518.
Servati, P., & Nathan, A. (2002). Modeling of the reverse characteristics of a-Si:H TFTs. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 49(5) 812–819.
Kabir, M. Z., Kasap, S. O., Zhao, W., & Rowlands, J. A. (2003). Direct conversion X-ray sensors: sensitivity, DQE and MTF. IEE Proceedings Circuits Devices and Systems, 150(4), 258–266.
Razavi, B. (2001) Design of analog CMOS integrated circuits (1st ed.). McGraw-Hill.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaji, G.R., Safavian, N. & Nathan, A. Compensation technique for DC and transient instability of thin film transistor circuits for large-area devices. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 56, 143–151 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-007-9082-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-007-9082-4