Abstract
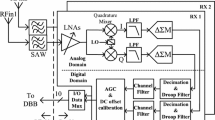
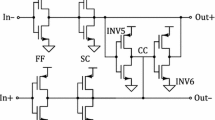
This paper introduces a 2 GHz continuous-time (CT) fourth order current-mode (CM) band-pass 0.18 μm CMOS delta sigma modulator (DSM) utilizing a fully balanced active inductor. The proposed active inductor takes advantage of positive feedback topology and features accurate loss compensation as well as independent tunability of quality factor and resonant frequency. Based on this active inductor, a CM Ultra High Frequency (UHF) resonator is also proposed, exhibiting a very small on-chip area. Moreover, a high speed CM quantizer working with one single clock is brought into eliminate the error introduced by clock generators. The post layout simulation of the DSM exhibits a peak SNDR of 43.6 dB at 500 MHz with a 40 MHz signal bandwidth while the center frequency can be tuned between 450 and 500 MHz. The measured results give an averaged SNDR of 33 dB with 40 MHz signal bandwidth, where the center frequency is tunable from 300 MHz to 350 MHz. This design consumes only 45 mW under 1.8 V power supply and occupies an area of 0.133 mm2.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vassilious, I., et al. (2006). CMOS tuner for mobile TV. In IEEE Communications Magazine (Vol. 44, Issue 12), December 2006.
Cherry, J., & Snelgrove, W. (2000). Continuous-time delta–sigma modulators for high-speed A/D conversion: Theory, practice and fundamental performance limits. Dordrecht: Kluwer.
Baker, R. J., Li, H. W., & Boyce, D. E. (1997). CMOS circuit design, layout and simulation. In IEEE Press series on microelectronic systems.
Gao, W., Cherry, J. A., & Snelgrove, W. M. (1998). A 4 GHz fourth-order SiGe HBT bandpass ΔΣ modulator. In Proc. of Symp. on VLSI circuits (pp. 174–175).
Raghavan, G., Jensen, J. F., Laskowski, J., Kardos, M., Case, M. G., Sokolich, M., et al. (2001). Architecture, design and test of continuous-time tunable intermidiate-frequency bandpass delta–sigma modulators. IEEE Solid-State Circuits, 36, 5–13.
Stubberud, P., & Dagher, E. H. (2005). Metastability requirements for a 2 GHz CMOS ΔΣ modulator. In IEEE ICSEng 2005 (pp. 263–268).
Tang, A., Yuan, F., & Law, E. (2008). A new WiMAX sigma–delta modulator with constant-Q active inductors. In IEEE ISCAS 2008, May 2008.
Thomas, K. P. J., Rana, R. S., & Lian, Y. (2005).A 1 GHz CMOS fourth-order continuous-time bandpass sigma delta modulator for RF receiver front end A/D conversion. In Proc. of conference on Asia South Pacific Design Automation 2005 (pp. 665–670).
Naderi, A., Sawan, M., & Savaria, Y. (2008). On the design of under-sampling continuous-time bandpass delta–sigma modulator for gigahertz frequency conversion. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I, 55(11), 3488–3499.
Chen, Q., El-Sankary, K., &, El-Masry, E. (2008). A UHF continuous-time current-mode band-pass delta–sigma modulator based on active inductor. In IEEE MWSCAS 2008, Aug 2008.
Wu, Y., Ding, X., Ismail, M., & Olsson, H. (2003). RF bandpass filter design based on CMOS active inductors. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Analog and Digital Signal Processing, 50(12), 942–949.
Wu, M., Yang, J., & Lee, C.-Y. (2004). A constant power consumption CMOS LC oscillator using improved high-Q active inductor with wide tuning-range. In IEEE MWSCAS (Vol. 3, pp. 347–350), July 2004.
DiClemente, D., & Yuan, F. (2006). An area-efficient CMOS current-mode phase-locked loop. In IEEE MWSCAS (Vol. 2, pp. 574–578), Aug 2006.
Zhuo, W., de Gyvez, J. P., & Sanchez-Sinencio, E. (1998). Programmable low noise amplifier with active-inductor load. In Proc. IEEE ISCAS ‘98 (Vol. 4, pp. 365–368), June 1998.
Hsieh, H.-H., Liao, Y.-T., & Lu, L. H. (2007). A compact quadrature hybrid MMIC using CMOS active inductors. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 55, 1098–1104.
Ismail, M., Wassenaar, R., & Morrison, W. (1991). A high-speed continuous-time bandpass VHF filter in MOS technology. In Proc. IEEE ISCAS ‘91 (Vol. 3, pp. 1761–1764), June 1991.
Yodprasit, U., & Ngarmnil, J. (2000). Q-enhancing technique for rf CMOS active inductor. In IEEE ISCAS (Vol. 5, pp. 589–592), May 2000.
Thanachayanont, A. &, Sae Ngow, S. (2002). Low voltage high-Q VHF CMOS transistor-only active inductor. In IEEE MWSCAS 2002 (pp. 552–555), Aug 2002.
Razavi, B. (2001). Design of analog CMOS integrated circuits, Chap. 7. McGraw Hill Companies, Inc.
Shoaei, O., & Snelgrove, M. (1995). A multi-feedback design for LC bandpass delta–sigma modulators. In Proc. IEEE ISCAS ‘95 (Vol. 5, pp. 171–174), May 1995.
Gao, W., Shoaei, O., & Snelgrove, W. M. (1997). Excess loop delay effects in continuous-time delta–sigma modulators and the compensation solution. IEEE ISCAS ‘97 (Vol. 1, pp. 65–68), June 1997.
Koli, K., & Halonen, K. A. I. (2002). CMOS current amplifiers: Speed versus nonideality. Dordrecht: Kluwer.
Freitas, D. A., & Current, K. W. (1983). CMOS current comparator circuit. Electronics Letters, 19, 695–697.
Traff, H. (1992). Novel approach to high speed CMOS current comparators. Electronics Letters, 8, 310–312.
Tang, A. T. K., & Toumazou, C. (1994). High performance CMOS current comparator. Electronics Letters, 30, 5–6.
Giannini, V., Craninckx, J., Come, B., Malcovati, P., & Baschirotto, A. (2006). 1.5 GHz fully differential latched current comparator with 20nA of sensitivity. Ph.D. Research in Microelectronics and Electronics.
Yin, G. M., Eynde, F. O., & Sansen, W. (1992). A high-speed CMOS comparator with 8-b resolution. Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 27(2), 208–211.
Choi, M., & Abidi, A. A. (2001). A 6-b 1.3-Gsample/s A/D converter in 0.35-μm CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid State Circuit, 36(12), 1847–1858.
Chang, B., Park, J., & Kim, W. (1996). A 1.2 GHz CMOS dual-modulus prescaler using new dynamic D-Type Flip-Flops. IEEE Journal of Solid State Circuits, 31, 749–752.
Goll, B., & Zimmermann, H. (2005). A low-power 2-GSample/s comparator in 120 nm CMOS technology. In Proc. of ESSCIRC 2005, Sept 2005.
Luh, L., Choma, J., Jr., & Draper, J. (2000). A high-speed fully differential current switch. IEEE Transactions on Circuit and System: Analog and Digital Signal Processing, 47(4), 358–363.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge CMC (Canada Microsystem Corporation) for their support in fabrication and equipment loan services. Also the authors would like to thank Ian McKenzie, Mark LeBlanc and Chris Hill for their support in testing fixture setup and Munir Tarar and Amro Elshurafa for their advice during the chip measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Q., El-Sankary, K. & El-Masry, E. A UHF current-mode continuous-time band-pass delta sigma modulator using fully balanced active inductor. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 67, 261–272 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-010-9534-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-010-9534-0