Abstract
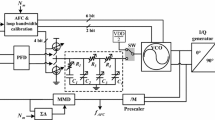
To appropriately configure the low pass filter (LPF) coefficients plays an important role in determining phase locked loop circuit performance. Most phase locked loop (PLL) design methods calculate LPF coefficients based on preselected loop bandwidth, phase margin, and then adjust LPF parameters to meet other specification requirements, i.e. locking time and phase noise. Such design approaches typically involve a number of iterative simulations, which are time consuming and are not very efficient. In this paper, we develop an analytical method to determine the allowable range of LPF coefficient values by considering unified PLL specification constraints. With the range identified, a clear guidance is obtained to facilitate LPF tuning and adaptive PLL design. For model validation, a charge pump PLL is designed and simulated using a 3rd party PLL simulation program—Cppsim.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hein, J., & Scott, J. W. (1988). z-domain model for discrete-time PLL’s. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, 35(11), 1393–1400.
Gardner, F. (1980). Charge-Pump Phase-Lock Loops. IEEE Transactions on Communications, COM-28(11), 1849–1858.
Novof, I. I., Austin, J., Kelkar, R., Strayer, D., & Wyatt, S. (1995). Fully integrated CMOS phase-locked loop with 15 to 240 MHz locking range and 50 ps jitter. IEEE Jounal Solid-State Circuits, 30(11), 1259–1266.
Hanumolu, P. K., Brownlee, M., Mayaram, K., & Moon, U. (2004). Analysis of charge-pump phase-locked loops. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systerms. I, Reg Papers, 51(9), 1665–1674.
Kratyuk, V., Hanumolu, P. K., Moon, Un.-Ku., & Mayaram, K. (2007). A design procedure for all-digital phase-locked loops based on a charge-pump phase-locked-loop analogy. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 54, 247–251.
Mansuri, Mozhgan., & Ken Yang, Chih.-Kong. (2002). Jitter optimization based on phase-locked loop design parameters. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 37(11), 1375–1382.
Erturk, M., Xia, T., & Clark, W. F. (2007). Gate voltage dependence of MOSFET 1/f noise statistics. IEEE Electron Device Letters, 28(9), 812–814.
Xia, T., Lo, J.C. (2003). On-chip short-time interval measurement for high-speed signal timing characterization. IEEE Asian Test Symposium, 326-331.
Antao, B. A. A., El-turky, F. M., & Leonowich, R. H. (1996). Behavioral modeling phase locked loop for mixed mode simulation. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 10, 45–65.
Limkumnerd, Sethapong, Eungdamrong, Duangrat (2005) Mathematical phase noise model for a phase-locked loop. ISCAS2005.
Egan, William. (2000). Frequency synthesis by phase lock (2nd ed., pp. 277–279). New York: Wiley.
Erturk, M., Xia, T., Anna, R., Newton, K. M., & Adler, E. (2005). Statistical BSIM Model of MOSFET 1/f Noise. IET Electronics Letters, 41(22), 1208–1209.
Erturk, M., Xia, T., Wolf, R. L., Scagnelli, D. P., Clark, W. F. (2008) “Statistical variations in VCO phase noise due to upconverted MOSFET 1/f noise,” IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (RFIC), 255-258.
Herzel, F., Osmany, S. A., & Scheytt, J. C. (2010). Analytical phase-noise modeling and charge pump optimization for fractional-N PLLs. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-I, 57(8), 1914–1924.
De Muer, Dram., & Steyaert, Michiel. S. J. (2003). The analysis of fractional-N frequency synthesizers for high-spectral purity. IEEE Transactions on Cricuits and Systems-II: Analog and Digital Signal Processing, 50, 784–793.
Li, Wen, Meiners, Jason (2000) Introduction to phase-locked loop system modeling.Texas Instruments Incorporated Analog Applications Journal, 5–11.
Michael H. Perrott: PLL simulation program-Cppsim. www.cppsim.com.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, B., Xia, T. & Wang, G. PLL low pass filter design considering unified specification constraints. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 80, 113–120 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-014-0312-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-014-0312-2