Abstract
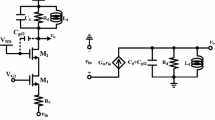
This paper presents a wideband low noise amplifier (LNA) which consist cascade of two stages. First stage, a complimentary common gate (CCG) stage is utilized to consume low power and low chip area while second stage is the mutually coupled common source (CS) stage used to generate high gain at high frequency. The concept of current reuse technique is used in CCG stage to save the dc power. While for the objective of low chip area, mutually coupled inductors are used, mathematically equivalent to a transformer. CCG stage provides high gain at low frequency. A frequency dependent load is generated by mutually coupled CS stage to transfer this gain at high frequency and then this load is transferred to the CCG stage using load transformation technique. This help a lot in achieving wide band input matching hence low noise figure (NF). Proposed LNA is verified mathematically and simulated in 90-nm CMOS process. The measured 3-dB bandwidth is 4.7–14.7 GHz with maximum voltage gain of 17.2 dB, minimum NF of 1.8 dB and S11 < − 10.3 dB. Maximum available power gain (GA) is 11.9 dB and maximum operating power gain is 11.4 dB at frequency of 13.2 GHz.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brandolini, M., Sosio, M., & Svelto, F. (2007). A 750 mV fully integrated direct conversion receiver front-end for GSM in 90-nm CMOS. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 42(6), 1310–1317.
Chen, H.-C., Wang, T., Chiu, H.-W., Kao, T.-H., & Lu, S.-S. (2009). 0.5-V 5.6-GHz CMOS receiver subsystem. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech., 57(2), 329–335.
Balankutty, A., Yu, S.-A., Feng, Y., & Kinget, P. (2010). A 0.6-V zero-IF/low-IF receiver with integrated fractional-N synthesizer for 2.4-GHz ISM-band applications. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits, 45(3), 538–553.
Balankutty, A., & Kinget, P. R. (2011). An ultra-low voltage, low-noise, high linearity 900-MHz receiver with digitally calibrated in-band feed-forward interferer cancellation in 65-nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits, 46(10), 2268–2283.
Heydari, P. (2007). Design and analysis of a performance-optimized CMOS UWB distributed LNA. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits, 42(9), 1892–1905.
Yu, Y. H., Chen, Y. J., & Heo, D. (2007). A 0.6-V low power UWB CMOS LNA. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett., 17(3), 229–231.
Chen, M., & Lin, J. (2009). A 0.1–20 GHz low-power self-biased resistive feedback LNA in 90 nm digital CMOS. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett., 19(5), 323–325.
Fu, C. T., Kuo, C. N., & Taylor, S. (2010). Low-noise amplifier design with dual reactive feedback for broadband simultaneous noise and impedance matching. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech., 58(4), 795–806.
Jussila, J., & Sivonen, P. (2008). A 1.2-V highly linear balanced noise-cancelling LNA in 0.13-µm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits, 43(3), 579–587.
Chen, K. H., & Liu, S. I. (2012). Inductorless wideband CMOS low-noise amplifiers using noise-canceling technique. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I, Reg. Pap., 59(2), 305–314.
W. Sanghyun, K. Woonyun, J. Laskar, A 3.6 mW differential common-gate CMOS LNA with positive-negative feedback, in IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference Digest of Technical Paper (ISSCC), pp. 218–219
Kim, J., Hoyos, S., & Martinez, J. S. (2010). Wideband common-gate CMOS LNA employing dual negative feedback with simultaneous noise, gain, and bandwidth optimization. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Techn., 58(9), 2340–2351.
Meaamar, A., Boon, C. C., Yeo, K. S., & Do, A. V. (2010). A wideband low power low-noise amplifier in CMOS technology. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I, Reg. Pap., 57(4), 773–782.
Kim, C. W., Kang, M. S., Anh, P. T., Kim, H. T., & Lee, S. G. (2005). An ultra-wideband CMOS low noise amplifier for 3–5-GHz UWB system. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits, 40(2), 544–547.
Chen, H.-K., Lin, Y.-S., & Lu, S.-S. (2010). Analysis and design of a 1.6–28-GHz compact wideband LNA in 90-nm CMOS using a π-match input network. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech., 58(8), 2092–2104.
J.H. Zhan, S. Taylor, A 5 GHz resistive-feedback CMOS LNA for low-cost multi-standard applications, in IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference Digest Technical Papers (ISSCC), pp. 721–730.
Perumana, B., Zhan, J. H., Taylor, S., Carlton, B., & Laskar, J. (2008). Resistive-feedback CMOS low-noise amplifiers for multiband applications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech., 56(5), 1218–1225.
Sapone, G., & Palmisano, G. (2011). A 3–10-GHz low-power CMOS low-noise amplifier for ultra-wideband communication. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech., 59(3), 678–686.
Liang, W., Leung, H. F., & Luong, H. C. (2017). Design and analysis of CMOS LNAs with transformer feedback for wideband input matching and noise cancellation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.-I, 64, 1626–1635.
Qin, P., & Xue, Q. (2017). Design of wideband LNA employing cascaded complimentary common gate and common source stages. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Lett., 27(6), 587–589.
Borremans, J., Wambacq, P., Soens, C., Rolain, Y., & Kuijk, M. (2008). Low-area active-feedback low-noise amplifier design in scaled digital CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits, 43(11), 2422–2433.
Saberkari, A., Kazemi, S., Shirmohammadli, V., & Yagoub, M. C. (2016). gm-boosted flat gain UWB low noise amplifier with active inductor-based input matching network. Integr. VLSI J., 52, 323–333.
Razavi, B. (2016). Design of Analog CMOS Integrated Circuits. New York: Tata McGraw Hill.
Parvizi, M., Allidana, K., & Parvizi, M. (2015). A sub-mW, ultra-low-voltage, wideband low-noise amplifier design technique. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst., 23(6), 1111–1121.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, M., Deolia, V.K. A wideband design analysis of LNA utilizing complimentary common gate stage with mutually coupled common source stage. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 98, 575–585 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-018-1355-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-018-1355-6