Abstract
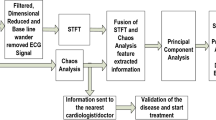
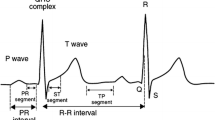
Electrocardiography (ECG) is a non-invasive test that is used for recording contraction and relaxation activities of the heart by using an electrocardiogram. Early detection of abnormalities of the heart through ECG is essential for reducing the prevalence of casualties due to cardiac arrests worldwide. In this study, physioNet ECG records have been considered for analysis. During recording, ECG signal is also affected by various noises, where analog filters fail due to the effect of temperature and drift, and digital filters fail due to inappropriate selection of passband and gain parameters. For adequate and frequent usage in the medical field, it demands correct and precise R-peak (QRS-complex) detection; which requires an appropriate combination of pre-processing, feature extraction and detection techniques. Therefore, independent component analysis (ICA) is used in the pre-processing stage due to nonlinear nature of the ECG signals and chaos analysis is applied for feature extraction for different ECG databases. The ICA method separates an individual signal from mixed signals by assuming that the original underlying source signals are mutually independently distributed. Chaos analysis examines the irregular attitude of the system and fits it into deterministic equations of motion. Chaos analysis is implemented by plotting different attractors against various time delay dimensions. R-peak detection is well known to be useful in diagnosing cardiac diseases. The R-peaks are detected using principal component analysis (PCA) which outperforms the existing state-of-the-art techniques.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luz, E. J. S., Schwartz, W. R., Chávez, G. C., & Menotti, D. (2016). ECG-based heartbeat classification for arrhythmia detection: A survey. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine,127, 144–164.
Vandeput, S.(2010). Heart rate variability: Linear and nonlinear analysis with applications in human physiology. Doctor in Engineering Sciences, Katholieke Universiteit, Leuven, Belgium.
Rajankar, S. O., & Talbar, S. N. (2017). Adaptive vector K-tree partitioning an entropy coder: Application to ECG compression. International Journal of Telemedicine and Clinical Practices Inderscience,2(3), 215–224.
Gupta, V., & Mittal, M. (2018). KNN and PCA classifier with autoregressive modelling during different ECG signal interpretation. Procedia Computer Science,125, 18–24.
Rajankar, S. O., & Talbar, S. N. (2019). An electrocardiogram signal compression techniques: a comprehensive review. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing,98(1), 59–74.
Gupta, V., & Mittal, M. (2018). Electrocardiogram signals interpretation using Chaos Theory. Journal of Advanced Research in Dynamical and Control Systems,9, 2392–2397.
Gorgels, A. P. M., Willerson, J. T., Wellens, H. J. J., Cohn, J. N., & Holmes, D. R. (2007). Cardiovascular medicine. London: Springer.
Kaya, Y., & Pehlivan, H. (2015). Comparison of classification algorithms in classification of ECG beats by time series. In 2015 IEEE conference on signal processing and communications applications (SIU) (pp. 407–410).
Perlman, O., Katz, A., Weissman, N., Amit, G., & Zigel, Y. (2014). Atrial electrical activity detection using linear combination of 12-lead ECG signals. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering,61, 1034–1043.
Javadi, M., Arani, S. A. A. A. A., Sajedin, A., & Ebrahimpour, R. (2013). Classification of ECG arrhythmia by a modular neural network based on mixture of experts and negatively correlated learning. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control,8, 289–296.
Liu, X., Yang, J., Zhu, X., Zhou, S., Wang, H., & Zhang, H. (2014). A novel R-peak detection method combining energy and wavelet transform in electrocardiogram signal. Biomedical Engineering: Applications, Basis and Communications,26, 1–9.
Kaya, Y., Pehlivan, H., & Tenekeci, M. E. (2017). Effective ECG beat classification using higher order statistic features and genetic feature selection. The Journal of Biological Research,28, 7594–7603.
Klingspor, M. (2015). Hilbert transform: Mathematical theory and applications to signal processing. Linkoping: Linkopings University.
Yeh, Y. C., Wang, W. J., & Chiou, C. W. (2009). Cardiac arrhythmia diagnosis method using LDA on ECG signals. Measurement,42, 778–789.
Andreao, R. V., Dorizzi, B., & Boudy, J. (2006). ECG signal analysis through hidden Markov models. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering,53, 1541–1549.
Malek, A., Katariya, S., Chow, Y., & Ghavamzadeh, M. (2017). Sequential multiple hypothesis testing with type i error control. In Proceedings of the 20th international conference on artificial intelligence and statistics, USA (pp. 1468–1476).
Li, Y., Yan, H., Hong, F., & Song, J. (2012). A new approach of QRS complex detection based on matched filtering and triangle character analysis. Australasian Physical & Engineering Sciences in Medicine,35, 341–356.
Zidelmal, Z., Amirou, A., Adnane, M., & Belouchrani, A. (2012). QRS detection based on wavelet coefficients. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine,107, 490–496.
He, R., Wang, K., Li, Q., Yuan, Y., Zhao, N., Liu, Y., et al. (2017). A novel method for the detection of R-peaks in ECG based on K-Nearest Neighbors and Particle Swarm Optimization. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing,82, 1–14.
Acharya, U. R., Fujita, H., Lih, O. S., Hagiwara, Y., Tan, J. H., & Adam, M. (2017). Automated detection of arrhythmias using different intervals of tachycardia ECG segments with convolutional neural network. Information Sciences,405, 81–90.
Rahhal, M. M. A., Bazi, Y., AlHichri, H., Alajlan, N., Melgani, F., & Yager, R. R. (2016). Deep learning approach for active classification of electrocardiogram signals. Information Sciences,345, 340–354.
Ahmadian, A., Karimifard, S., Sadoughi, H., & Abdoli, M. (2007). An efficient piecewise modeling of ECG signals based on hermitian basis functions. In IEEE 2007 engineering in medicine and biology society, Lyon, France (pp. 3180–3183).
Kaya, Y., & Pehlivan, H. (2015). Classification of premature ventricular contraction in ECG. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications,6, 34–40.
Rao, K. D. (1997). DWT Based Detection of R-peaks and Data Compression of ECG Signals. IETE Journal of Research,43, 345–349.
Kaur, H., & Rajni, R. (2017). Electrocardiogram signal analysis for R-peak detection and denoising with hybrid linearization and principal component analysis. Turkish Journal of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences,25, 2163–2175.
Sahambi, J., Tandon, S., & Bhatt, R. (1997). Using wavelet transforms for ECG characterization. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Magazine,16, 77–83.
Hongyan, X., & Minsong, H. (2008). A new qrs detection algorithm based on empirical mode decomposition. In IEEE 2008 2nd international conference ICBBE, Shanghai, China (pp. 693–696).
Aurobinda, A., Mohanty, B.P., & Mohanty, M.N. (2016). R-peak Detection of ECG using Adaptive Thresholding. In IEEE 2016 international conference on communication and signal processing, Madras, India (pp. 0284–0287).
Jaafar, H., Ramli, N.H., & Nasir, A.S.A. (2018). An improvement to The k-nearest neighbor classifier for ECG database. In IOP conference on series: materials science and engineering, Penang, Malaysia (pp. 1–10).
Pahim, O., & Sornmo, L. (1984). Software QRS detection in ambulatory monitoring-a review. Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing,22, 289–297.
Saini, I., Singh, D., & Khosla, A. (2013). QRS detection using K-Nearest Neighbor algorithm (KNN) and evaluation on standard ECG databases. Journal of Advanced Research,4, 331–344.
Petricek, M. (2010). Components in data analysis. In WDS’10 proceedings of contributed papers, 01–04 June 2010; Prague, Bohemia: Matfyzpress (pp. 82–87).
Kuzilek, J., Kremen, V., & SoucekF, Lhotska L. (2014). Independent component analysis and decision trees for ECG holter recording de-noising. Plos One,9, 1–9.
Sayadi, O., & Shamsollahi, M. B. (2007). Multiadaptive bionic wavelet transform: application to ECG denoising and baseline wandering reduction. Journal on Advances in Signal Processing,14, 1–11.
Rekik, S., & Ellouze, N. (2017). Enhanced and optimal algorithm for QRS detection. IRBM,38(1), 56–61.
Gupta, V., & Mittal, M. (2019). QRS complex detection Using STFT, chaos analysis, and PCA in standard and real-time ECG databases. Inst: Journal of The Institution of Engineers (India): Series B. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40031-019-00398-9.
Casdagli, M. (1992). Chaos and deterministic versus stochastic nonlinear modeling. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological),54, 303–328.
Nguomkam Negou, A., & Kengne, J. (2019). A minimal three-term chaotic flow with coexisting routes to chaos, multiple solutions, and its analog circuit realization. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-019-01436-8.
Nguomkam Negou, A., & Kengne, J. (2018). Dynamic analysis of a unique jerk system with a smoothly adjustable symmetry and nonlinearity: Reversals of period doubling, offset boosting and coexisting bifurcations. International Journal of Electronics and Communications,90, 1–19.
Xingyuan, W., & Juan, M. (2009). Wavelet-based hybrid ECG compression technique. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing,59(3), 301–308.
Mehta, S. S., Shete, D. A., Lingayat, N. S., & Chouhan, V. S. (2010). K-means algorithm for the detection and delineation of QRS-complexes in electrocardiogram. IRBM,31(1), 48–54.
Kutlu, Y., & Kuntalp, D. (2012). Feature extraction for ECG heartbeats using higher order statistics of WPD coefficients. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine,105, 257–267.
Dokur, Z., & Ölmez, T. (2001). ECG beat classification by a novel hybrid neural network. Computer methods and programs in Biomedicine,66, 167–181.
Stone, J. V. (2004). Independent component analysis: A tutorial introduction. Cambridge: Bradford Books, The MIT Press.
Naik, G. R., & Kumar, D. K. (2011). An overview of independent component analysis and its applications. Informatica,35, 63–81.
Lai, Q., Tsafack, N., Kengne, J., & Zhao, X. W. (2018). Coexisting attractors and circuit implementation of a new 4D chaotic system with two equilibria. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals,107, 92–102.
Lai, Q., & Chen, S. (2016). Coexisting attractors generated from a new 4D smooth chaotic system. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems,14(4), 1124–1131.
Akgul, A., Calgan, H., Koyuncu, I., Pehlivan, I., & Istanbullu, A. (2015). Chaos-based engineering applications with a 3D chaotic system without equilibrium points. Nonlinear Dynamics,1, 1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-015-2501-7.
Acharya, R., Kumar, A., Bhat, P. S., Lim, C. M., Lyengar, S. S., Kannathal, N., et al. (2004). Classification of cardiac abnormalities using heart rate signals. Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing,42, 288–293.
Eckman, J. P., Kamphorst, S. O., & Ruelle, D. (1987). Recurrence plots of dynamical systems. Europhsics Letters,4, 973–977.
Skiadas, C. H., & Skiadas, C. (2016). Handbook of applications of chaos theory (1st ed.). New York: Taylor & Francis, CRC Press.
Abarbanel, H. D. I. (1996). Analysis of Observed Chaotic Data (2nd ed.). New York: Springer.
Bradley, E., & Kantz, H. (2015). Nonlinear time-series analysis revisited. Journal of Chaos,25, 09761001–09761010.
Kaplan, D. T., & Glass, L. (1992). Direct test for determinism in a time series. Physical Review Letters,68, 427–430.
Briggs, K. (1987). Simple experiments in chaotic dynamics. American Journal of Physics,55, 1083–1089.
Alickovic, E., & Subasi, A. (2015). Effect of Multiscale PCA de-noising in ECG beat classification for diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing,34, 513–533.
Sheetal, A., Singh, H., & Kaur, A. (2019). QRS detection of ECG signal using hybrid derivative and MaMeMi filter by effectively eliminating the baseline wander. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing,98(1), 1–9.
Ren, S., Panahi, S., Rajagopal, K., Akgul, A., Pham, V.-T., & Jafari, S. (2018). A new chaotic flow with hidden attractor: The first hyperjerk system with no equilibrium. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung. https://doi.org/10.1515/zna-2017-0409.
Nguomkam Negou, A., Kengne, J., & Tchiotsop, D. (2018). Periodicity, chaos and multiple coexisting attractors in a generalized Moore-Spiegel system. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals,107, 275–289.
Luo, X., & Small, M. (2007). On a dynamical system with multiple chaotic attractors. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos,17(9), 3235–3251.
Gupta, V., & Mittal, M. (2018). Dimension reduction and classification in ECG signal interpretation using FA and PCA: A comparison. Jangjeon Mathematical Society,21(4), 765–777.
Sahoo, S., Biswal, P., Das, T., & Sabut, S. (2016). De-noising of ECG signal and QRS detection using hilbert transform and adaptive thresholding. Procedia Technology,25, 68–75.
Ghaffari, A., Golbayani, H., & Ghasemi, M. (2008). A new mathematical based QRS detector using continuous wavelet transform. Computers & Electrical Engineering,34, 81–91.
Yazdani, S., & Vesin, J. M. (2016). Extraction of QRS fiducial points from the ECG using adaptive mathematical morphology. Digital Signal Processing,56, 100–109.
Manikandan, M. S., & Soman, K. P. (2012). A novel method for detecting R-peaks in electrocardiogram signal. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control,7, 118–128.
Li, C., Zheng, C., & Tai, C. (1995). Detection of ECG characteristic points using wavelet transforms. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering,1, 21–28.
Lee, J., Jeong, K., Yoon, J., Lee, M. (1996). A simple real-time QRS detection algorithm, In Proceedings of the 18th IEEE annual international conference engineering in medicine and biology society, Netherlands (pp. 1396–1398).
Poli, R., Cagnoni, S., & Valli, G. (1995). Genetic design of optimum linear and nonlinear QRS detectors. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering,42(11), 1137–1141.
Afonso, V., Tompkins, W. J., Nguyen, T., & Luo, S. (1999). ECG beat detection using filter banks. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering,46(2), 192–202.
Pan, J., & Tompkins, W. J. (1985). A real-time QRS detection algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering,3, 230–236.
Martis, R. J., Acharya, U. R., Lim, C. M., & Suri, J. S. (2013). Characterization of ECG beats from cardiac arrhythmia using discrete cosine transform in PCA framework. Knowledge-Based Systems,45, 76–82.
Martis, R. J., Acharya, U. R., Mandana, K. M., Ray, A. K., & Chakraborty, C. (2012). Application of principal component analysis to ECG signals for automated diagnosis of cardiac health. Expert Systems with Applications,39, 11792–11800.
Chiu, C. C., Lin, T. H., & Liau, B. Y. (2005). Using correlation coefficient in ECG waveform for arrhythmia detection. Biomedical Engineering: Applications, Basis and Communications,17, 37–42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, V., Mittal, M. & Mittal, V. R-peak detection based chaos analysis of ECG signal. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 102, 479–490 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-019-01556-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-019-01556-1