Abstract
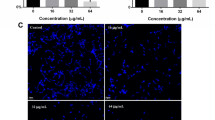
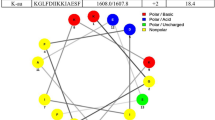
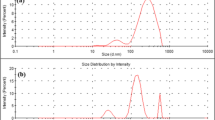
The ability of the human fungal pathogen Candida albicans to reversibly switch between different morphological forms and establish biofilms is crucial for establishing infection. Targeting phenotypic plasticity and biofilm formation in C. albicans represents a new concept for antifungal drug discovery. The present study evaluated the influence of cyclic lipopeptide biosurfactant produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain AR2 on C. albicans biofilms. The biosurfactant was characterized as a mixture of iturin and fengycin by MALDI-TOF and amino acid analysis. The biosurfactant exhibited concentration dependent growth inhibition and fungicidal activity. The biosurfactant at sub-minimum growth inhibition concentration decreased cell surface hydrophobicity, hindered germ tube formation and reduced the mRNA expression of hyphae-specific gene HWP1 and ALS3 without exhibiting significant growth inhibition. The biosurfactants inhibited biofilm formation in the range of 46–100 % depending upon the concentration and Candida strains. The biosurfactant treatment dislodged 25–100 % of preformed biofilm from polystyrene plates. The biosurfactant retained its antifungal and antibiofilm activity even after exposure to extreme temperature. By virtue of the ability to inhibit germ tube and biofilm formation, two important traits of C. albicans involved in establishing infection, lipopeptides from strain AR2 may represent a potential candidate for developing heat stable anti-Candida drugs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Argimon S, Wishart JA, Leng R, Macaskill S, Mavor A, Alexandris T, Nicholls S, Knight AW, Enjalbert B, Walmsley R, Odds FC, Gow NA, Brown AJ (2007) Developmental regulation of an adhesin gene during cellular morphogenesis in the fungal pathogen Candida albicans. Eukaryot Cell 6:682–692
Cannon RD, Lamping E, Holmes AR, Niimi K, Tanabe K, Niimi M, Monk BC (2007) Candida albicans drug resistance another way to cope with stress. Microbiology 153:3211–3217
Coleman JJ, Ghosh S, Okoli I, Mylonakis E (2011) Antifungal activity of microbial secondary metabolites. PLoS ONE 6:e25321
De Araujo LV, Abreu F, Lins U, Anna LMdMS, Nitschke Mr, Freire DMGe (2011) Rhamnolipid and surfactin inhibit Listeria monocytogenes adhesion. Food Res Int 44:481–488
Dhanjal S, Cameotra SS (2010) Aerobic biogenesis of selenium nanospheres by Bacillus cereus isolated from coalmine soil. Microb Cell Fact 9:52
Finkel JS, Mitchell AP (2011) Genetic control of Candida albicans biofilm development. Nat Rev Microbiol 9:109–118
Fracchia L, Cavallo M, Allegrone G, Martinotti MG (2010) A Lactobacillus-derived biosurfactant inhibits biofilm formation of human pathogenic Candida albicans biofilm producers. In: Méndez-Vilas A (ed) Current research, technology and education topics in applied microbiology and microbial biotechnology. Formatex Research Centre, Badajoz, pp 827–837
Gauwerky K, Borelli C, Korting HC (2009) Targeting virulence: a new paradigm for antifungals. Drug Discov Today 14:214–222
Hoyer LL, Green CB, Oh SH, Zhao X (2008) Discovering the secrets of the Candida albicans agglutinin-like sequence (ALS) gene family: a sticky pursuit. Med Mycol 46:1–15
Janek T, Lukaszewicz M, Krasowska A (2012) Antiadhesive activity of the biosurfactant pseudofactin II secreted by the Arctic bacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens BD5. BMC Microbiol 12:24
Jin Y, Yip HK, Samaranayake YH, Yau JY, Samaranayake LP (2003) Biofilm-forming ability of Candida albicans is unlikely to contribute to high levels of oral yeast carriage in cases of human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Clin Microbiol 41:2961–2967
Kim PI, Ryu J, Kim YH, Chi YT (2010) Production of biosurfactant lipopeptides Iturin A, fengycin and surfactin A from Bacillus subtilis CMB32 for control of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. J Microbiol Biotechnol 20:138–145
Kim KS, Kim YS, Han I, Kim MH, Jung MH et al (2011) Quantitative and qualitative analyses of the cell death process in Candida albicans treated by antifungal agents. PLoS ONE 6(12):e28176. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0028176
Li X, Yan Z, Xu J (2003) Quantitative variation of biofilms among strains in natural populations of Candida albicans. Microbiology 149:353–362
Lin SC, Jiang HJ (1997) Recovery and purification of the lipopeptide biosurfactant of Bacillus subtilis by ultrafiltration. Biotechnol Technol 11:413–416
Maget-Dana R, Thimon L, Peypoux F, Ptak M (1992) Surfactin/iturin A interactions may explain the synergistic effect of surfactin on the biological properties of iturin A. Biochimie 74:1047–1051
Mulligan CN (2005) Environmental applications for biosurfactants. Environ Pollut 133:183–198
Nett JE, Guite KM, Ringeisen A, Holoyda KA, Andes DR (2008) Reduced biocide susceptibility in Candida albicans biofilms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52:3411–3413
Ongena M, Jacques P (2008) Bacillus lipopeptides: versatile weapons for plant disease biocontrol. Trends Microbiol 16:115–125
Ongena M, Jourdan E, Adam A, Paquot M, Brans A, Joris B, Arpigny JL, Thonart P (2007) Surfactin and fengycin lipopeptides of Bacillus subtilis as elicitors of induced systemic resistance in plants. Environ Microbiol 9(4):1084–1090
Onishi J, Meinz M, Thompson J et al (2000) Discovery of novel antifungal (1,3)-beta-d-glucan synthase inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44:368–377
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45
Pons A, Roca P, Aguilo C, Garcia FJ, Alemany M, Palou A (1981) A method for the simultaneous determination of total carbohydrate and glycerol in biological samples with the anthrone reagent. J Biochem Biophys Methods 4:227–231
Raaijmakers JM, de Bruijn I, Nybroe O, Ongena M (2010) Natural functions of lipopeptides from Bacillus and Pseudomonas: more than surfactants and antibiotics. FEMS Microbiol Rev 34:1037–1062
Rivardo F, Turner R, Allegrone G, Ceri H, Martinotti M (2009) Anti-adhesion activity of two biosurfactants produced by Bacillus spp. prevents biofilm formation of human bacterial pathogens. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83:541–553
Rodrigues AG, Mardh PA, Pina-Vaz C, Martinez-de-Oliveira J, Fonseca AF (1999) Germ tube formation changes surface hydrophobicity of Candida cells. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol 7:222–226
Romano A, Vitullo D, Di Pietro A, Lima G, Lanzotti V (2011) Antifungal Lipopeptides from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain BO7. J Nat Products 74:145–151
Romero D, de Vicente A, Rakotoaly RH et al (2007) The iturin and fengycin families of lipopeptides are key factors in antagonism of Bacillus subtilis toward Podosphaera fusca. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 20:430–440
Roongsawang N, Washio K, Morikawa M (2011) Diversity of nonribosomal Peptide synthetases involved in the biosynthesis of lipopeptide biosurfactants. Int J Mol Sci 12:141–172
Rosseti IB, Wagner C, Fachinetto R, Taube Junior P, Costa MS (2011) Candida albicans growth and germ tube formation can be inhibited by simple diphenyl diselenides [(PhSe)2, (MeOPhSe)2, (p-Cl-PhSe)2, (F3CPhSe)2] and diphenyl ditelluride. Mycoses 54:506–513
Sardi JC, Scorzoni L, Bernardi T, Fusco-Almeida AM, Mendes-Giannini MJ (2013) Candida species: current epidemiology, pathogenicity, biofilm formation, natural antifungal products and new therapeutic options. J Med Microbiol 62:10–24
Singh AK, Cameotra SS (2013) Efficiency of lipopeptide biosurfactants in removal of petroleum hydrocarbons and heavy metals from contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 1–10
Song B, Rong YJ, Zhao MX, Chi ZM (2013) Antifungal activity of the lipopeptides produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens anti-CA against Candida albicans isolated from clinic. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:7141–7150
Tabbene O, Kalai L, Ben Slimene I, Karkouch I, Elkahoui S, Gharbi A, Cosette P, Mangoni ML, Jouenne T, Limam F (2011) Anti-Candida effect of bacillomycin d-like lipopeptides from Bacillus subtilis B38. FEMS Microbiol Lett 316:108–114
Thimon L, Peypoux F, Wallach J, Michel G (1995) Effect of the lipopeptide antibiotic, iturin A, on morphology and membrane ultrastructure of yeast cells. FEMS Microbiol Lett 128:101–106
Tsang PW, Bandara HM, Fong WP (2012) Purpurin suppresses Candida albicans biofilm formation and hyphal development. PLoS ONE 7:e50866
Tyagi AK, Malik A (2010) In situ SEM, TEM and AFM studies of the antimicrobial activity of lemon grass oil in liquid and vapour phase against Candida albicans. Micron 41:797–805
Walencka E, Rozalska S, Sadowska B, Rozalska B (2008) The influence of Lactobacillus acidophilus-derived surfactants on staphylococcal adhesion and biofilm formation. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 53:61–66
Zhang Y, Cai C, Yang Y, Weng L, Wang L (2011) Blocking of Candida albicans biofilm formation by cis-2-dodecenoic acid and trans-2-dodecenoic acid. J Med Microbiol 60:1643–1650
Zhang X, Jacob MR, Rao RR, Wang YH, Agarwal AK, Newman DJ, Khan IA, Clark AM, Li XC (2012) Antifungal cyclic peptides from the marine sponge. Res Rep Med Chem 2:7–14
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Director, IMTECH for providing the facilities for this work. AKS and RR are thankful to UGC and CSIR for fellowship, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. 1
Growth of C. albicans strains in the presence of biosurfactant produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain AR2. Growth was carried out at 30 °C with agitation rate of 200 rpm. Results are expressed as mean ± SD of values obtained from triplicate experiments. Supplementary material 1 (PPTX 109 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rautela, R., Singh, A.K., Shukla, A. et al. Lipopeptides from Bacillus strain AR2 inhibits biofilm formation by Candida albicans . Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 105, 809–821 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-014-0135-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-014-0135-2