Abstract
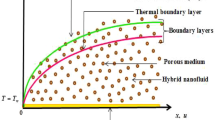
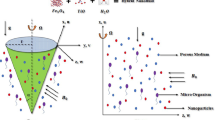
Bioconvection research is primarily focused on the augmentation of energy and mass species, which has implications in the processes intensification, mechanical, civil, electronics, and chemical engineering branches. Advanced bioconvection technology sectors include cooling systems for electronic devices, building insulation, and geothermal nuclear waste disposal. Hence, the present investigation is mainly discoursing the impact of Marangoni convention Casson nanoliquid flow under gyrotactic microorganisms over the porous sheet. The partial differential equations (PDEs) are re-structured into ordinary differential equations (ODEs) via suitable similar variables. These ODEs are numerically solved with the help of the spectral relaxation method (SRM). The numerical outcomes are illustrated graphically for various parameters over velocity, temperature, concentration, and bioconvection profiles. Three-dimensional (3D) views of important engineering parameters are illustrated for various parameters. The velocity of the Casson nanoliquid increases with increasing the Marangoni parameter but decreases against higher porosity parameter. The surface drag force enhances for enhancement in the Marangoni number. The rate of mass transmission is higher for reaction rate constraint but diminishes for activation energy parameter. The higher radiative values augment the rate of heat transmission.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ψ (x, y):
-
stream function
- \(\overline u ,\overline v \) :
-
velocity components
- x, y :
-
coordinate axes
- β :
-
casson parameter
- ν :
-
kinematic viscosity
- μ :
-
dynamic viscosity
- ρ :
-
density
- k :
-
thermal conductivity
- c p :
-
specific heat
- K* :
-
permeability of porous medium
- \(\overline T \) :
-
temperature inside boundary layer
- \({\overline T _{\rm{w}}}\) :
-
uniform constant temperature
- \({\overline T _\infty }\) :
-
ambient temperature
- \({\overline T _0}\) :
-
characteristic temperature
- q r :
-
radiative heat flux
- D B :
-
Brownian diffusion coefficient
- l :
-
characteristic length
- a :
-
stretching constant
- \(K_{\rm{r}}^2\) :
-
reaction rate
- E a :
-
activation energy
- K :
-
Boltzmann’s constant
- \(\overline C \) :
-
concentration
- \({\overline C _{\rm{w}}}\) :
-
uniform constant concentration
- \({\overline C _\infty }\) :
-
free stream concentration
- \(\overline N \) :
-
concentration motile of microorganisms
- σ :
-
surface tension
- σ* :
-
Stephan-Boltzmann constant
- k* :
-
mean absorption coefficient
- D m :
-
microorganism diffusion coefficient
- ρ c p :
-
heat capacitance
- γT:
-
coefficient of temperature surface tension
- C f :
-
skin friction coefficient
- Nu :
-
Nusselt number
- Sh :
-
Sherwood number
- j w :
-
wall mass flux
- τ w :
-
shear stress.
- f:
-
base fluid
- nf:
-
nanofluid
References
CHOI, S. U. S. and EASTMAN, J. A. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. Conference: International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exhibition, San Francisco, CA (1995)
BUONGIORNO, J. Convective transport in nanofluids. Journal of Heat Transfer, 128, 240–250 (2006)
TURKYILMAZOGLU, M. Fully developed slip flow in a concentric annuli via single and dual phase nanofluids models. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 179, 104997 (2019)
KHAN, M., Ahmed, J., Sultana, F., and SARFRAZ, M. Non-axisymmetric Homann MHD stagnation point flow of Al2O3-Cu/water hybrid nanofluid with shape factor impact. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 41(5), 1125–1138 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-020-2611-5
JAFARIMOGHADDAM, A., TURKYILMAZOGLU, M., ROSCA, A. V., and POP, I. Complete theory of the elastic wall jet: a new flow geometry with revisited two-phase nanofluids. European Journal of Mechanics-B / Fluids, 86, 25–36 (2021)
TURKYILMAZOGLU, M. Nanoliquid film flow due to a moving substrate and heat transfer. The European Physical Journal Plus, 135, 781 (2020)
RAMESH, G. K., PRASANNAKUMARA, B. C., GIREESHA, B. J., and RASHIDI, M. M. Casson fluid flow near the stagnation point over a stretching sheet with variable thickness and radiation. Journal of Applied Fluid Mechanics, 9, 1115–1022 (2016)
ALI, L., LIU, X., ALI, B., MUJEED, S., and ABDAL, S. Finite element analysis of thermo-diffusion and multi-slip effects on MHD unsteady flow of Casson nano-fluid over a shrinking/stretching sheet with radiation and heat source. Applied Sciences, 9, 5217 (2019)
IBRAHIM, W. and ANBESSA, T. Three-dimensional MHD mixed convection flow of Casson nanofluid with hall and ion slip effects. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2020, 8656147 (2020)
KUMAR, R. N., GOWDA, R. J. P., MADHUKESH, J. K., PRASANNAKUMARA, B. C., and RAMESH, G. K. Impact of thermophoretic particle deposition on heat and mass transfer across the dynamics of Casson fluid flow over a moving thin needle. Physica Scripta, 96, 075210 (2021)
KOTRESH, M. J., RAMESH, G. K., SHASHIKALA, V. K. R., and PRASANNAKUMARA, B. C. Assessment of Arrhenius activation energy in stretched flow of nanofluid over a rotating disc. Heat Transfer (2020) https://doi.org/10.1002/htj.22006
KHAN, M. I., ALZAHRANI, F., HOBINY, A., and ALI, Z. Estimation of entropy generation in Carreau-Yasuda fluid flow using chemical reaction with activation energy. Journal of Materials and Research Technology, 9, 9951–9964 (2020)
WAQAS, M., JABEEN, S., HAYAT, T., SHEHZAD, S. A., and ALSAEDI, A. Numerical simulation for nonlinear radiated Eyring-Powell nanofluid considering magnetic dipole and activation energy. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 112, 104401 (2020)
KHAN, M. I. and ALZAHRANI, F. Activation energy and binary chemical reaction effect in nonlinear thermal radiative stagnation point flow of Walter-B nanofluid: numerical computations. International Journal of Modern Physics B, 34, 2050132 (2020)
RAMESH, G. K. Analysis of active and passive control of nanoparticles in viscoelastic nanomaterial inspired by activation energy and chemical reaction. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 550, 123964 (2020)
AYUB, M., MALIK, M. Y., IJAZ, M., ALQARNI, M. S., and ALQAHTANI, A. S. Cattaneo-Christov double-diffusion model for viscoelastic nanofluid with activation energy and nonlinear thermal radiation. Multidiscipline Modeling in Materials and Structures, 16, 93–120 (2019)
TURKYILMAZOGLU, M. Thermal radiation effects on the time-dependent MHD permeable flow having variable viscosity. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 50, 88–96 (2011)
AHMED, A., KHAN, M., IRFAN, M., and AHMED, J. Transient MHD flow of Maxwell nanofluid subject to non-linear thermal radiation and convective heat transport. Applied Nanoscience, 10, 5361–5373 (2020)
MAKINDE, O. D. and ANIMASAUN, I. L. Bioconvection in MHD nanofluid flow with nonlinear thermal radiation and quartic autocatalysis chemical reaction past an upper surface of a paraboloid of revolution. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 109, 159–171 (2016)
IJAZ, M., NADEEM, S., AYUB, M., and MANSOOR, S. Simulation of magnetic dipole on gyrotactic ferromagnetic fluid flow with nonlinear thermal radiation. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetery, 143, 2053–2067 (2021)
SHEHZAD, S. A., REDDY, M. G., RAUF, A., and ABBAS, Z. Bioconvection of Maxwell nanofluid under the influence of double diffusive Cattaneo-Christov theories over isolated rotating disk. Physica Scripta, 95, 045207 (2020)
ABBASI, A., MABOOD, F., FAROOQ, W., and BATOOL, M. Bioconvective flow of viscoelastic nanofluid over a convective rotating stretching disk. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 119, 104921 (2020)
MAKINDE, O. D. and ANIMASAUN, I. L. Thermophoresis and Brownian motion effects on MHD bioconvection of nanofluid with nonlinear thermal radiation and quartic chemical reaction past an upper horizontal surface of a paraboloid of revolution. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 221, 733–743 (2016)
SHEHZAD, S. A., MUSHTAQ, T., ABBAS, Z., RAUF, A., KHAN, S. U., and TLILI, I. Dynamics of bioconvection flow of micropolar nanoparticles with Cattaneo-Christov expressions. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 41(9), 1333–1344 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-020-2645-9
RASOOL, G., SHAFIQ, A., and TLILI, I. Marangoni convective nanofluid flow over an electromagnetic actuator in the presence of first-order chemical reaction. Heat Transfer—Asian Research, 49, 274–288 (2020)
REHMAN, A., GUL, T., SALLEH, Z., MUKHTAR, S., HUSSAIN, F., NISAR, K. S., and KUMAM, P. Effect of the Marangoni convection in the unsteady thin film spray of CNT nanofluids. Processes, 7, 7060392 (2019)
KHAN, M. I., QAYYUM, S., CHU, Y. M., KHAN, N. B., and KADRY, S. Transportation of Marangoni convection and irregular heat source in entropy optimized dissipative flow. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 120, 105031 (2021)
SADIQ, M. A. and HAYAT, T. Characterization of Marangoni forced convection in Casson nanoliquid flow with Joule heating and irreversibility. Entropy, 22, 22040433 (2020)
RASHID, U., BALEANU, D., LIANG, H., ABBAS, M., IQBAL, A., and RAHMAN, J. Marangoni boundary layer flow and heat transfer of graphene-water nanofluid with particle shape effects. Processes, 8, 8091120 (2020)
QAYYUM, S. Dynamics of Marangoni convection in hybrid nanofluid flow submerged in ethylene glycol and water base fluids. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 119, 104962 (2020)
KHASHI’IE, N. S., ARIFIN, N. M., POP, I., NAZAR, R., HAFIDZUDDIN, E. H., and WAHI, N. Thermal Marangoni flow past a permeable stretching/shrinking sheet in a hybrid Cu-Al2O3/water nanofluid. Sains Malaysiana, 49, 211–222 (2020)
SANKAD, G. C., MAHARUDRAPPPA, I., and DHANGE, M. Y. Bioconvection in Casson fluid flow with gyrotactic microorganisms and heat transfer over a linear stretching sheet in presence of magnetic field. Advances in Mathematics Scientific Journal, 10, 155–169 (2021)
COLIN, S. International journal of heat and technology: foreword. International Journal of Heat and Technology, 26, 107 (2008)
ALWAWI, F. A., ALKASASBEH, H. T., RASHAD, A. M., and IDRIS, R. Natural convection flow of sodium alginate based Casson nanofluid about a solid sphere in the presence of a magnetic field with constant surface heat flux. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1366, 012005 (2019)
MOTSA, S. S. A new spectral relaxation method for similarity variable nonlinear boundary layer flow systems. Chemical Engineering Communications, 201, 241–256 (2014)
ETWIRE, C. J., SEINI, I. Y., RABIU, M., and MAKINDE, O. D. Impact of thermophoretic transport of Al2O3 nanoparticles on viscoelastic flow of oil-based nanofluid over a porous exponentially stretching surface with activation energy. Engineering Transactions, 67, 387–410 (2019)
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the editors and referees for the positive feedback and helpful suggestions, which improve the manuscript’s presentation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Citation: MADHUKESH, J. K., RAMESH, G. K., PRASANNAKUMARA, B. C., SHEHZAD, S. A., and ABBASI, F. M. Bio-Marangoni convection flow of Casson nanoliquid through a porous medium in the presence of chemically reactive activation energy. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 42(8), 1191–1204 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-021-2753-7
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madhukesh, J.K., Ramesh, G.K., Prasannakumara, B.C. et al. Bio-Marangoni convection flow of Casson nanoliquid through a porous medium in the presence of chemically reactive activation energy. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 42, 1191–1204 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-021-2753-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-021-2753-7