Abstract
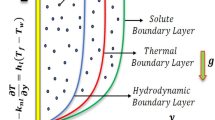
The heat transfer rate of the thermal Marangoni convective flow of a hybrid nanomaterial is optimized by using the response surface methodology (RSM). The thermal phenomenon is modeled in the presence of a variable inclined magnetic field, thermal radiation, and an exponential heat source. Experimentally estimated values of the thermal conductivity and viscosity of the hybrid nanomaterial are utilized in the calculation. The governing intricate nonlinear problem is treated numerically, and a parametric analysis is carried out by using graphical visualizations. A finite difference-based numerical scheme is utilized in conjunction with the 4-stage Lobatto IIIa formula to solve the nonlinear governing problem. The interactive effects of the pertinent parameters on the heat transfer rate are presented by plotting the response surfaces and the contours obtained from the RSM. The mono and hybrid nanomaterial flow fields are compared. The hybrid nanomaterial possesses enhanced thermal fields for nanoparticle volume fractions less than 2%. The irregular heat source and the thermal radiation enhance the temperature profiles. The high level of the thermal radiation and the low levels of the exponential heat source and the angle of inclination (of the magnetic field) lead to the optimized heat transfer rate (Nux = 7.462 75).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CHOI, S. U. S. and EASTMAN, J. A. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. Proceedings of the 1995 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, ASME, San Francisco, 66, 99–105 (1995)
HAYAT, T., KHAN, M. I., FAROOQ, M., ALSAEDI, A., and YASMEEN, T. Impact of Marangoni convection in the flow of carbon-water nanofluid with thermal radiation. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 106, 810–815 (2017)
KUZNETSOV, A. V. and NIELD, D. A. Natural convective boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a vertical plate. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 49, 243–247 (2010)
MEBAREK-OUDINA, F. Convective heat transfer of titania nanofluids of different base fluids in cylindrical annulus with discrete heat source. Heat Transfer-Asian Research, 48, 135–147 (2019)
BERREHAL, H., MABOOD, F., and MAKINDE, O. D. Entropy-optimized radiating water/FCNTs nanofluid boundary-layer flow with convective condition. The European Physical Journal Plus, 135, 1–21 (2020)
AHMED, A., KHAN, M., and AHMED, J. Thermal analysis in swirl motion of Maxwell nanofluid over a rotating circular cylinder. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 41(9), 1417–1430 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-020-2643-7
RANA, P., SHEHZAD, S. A., AMBREEN, T., and SELIM, M. M. Numerical study based on CVFEM for nanofluid radiation and magnetized natural convected heat transportation. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 334, 116102 (2021)
CHU, Y., KHAN, M. I., REHMAN, M. I. U., KADRY, S., QAYYUM, S., and WAQAS, M. Stability analysis and modeling for the three-dimensional Darcy-Forchheimer stagnation point nanofluid flow towards a moving surface. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 42(3), 357–370 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-021-2700-7
MAHANTHESH, B., SHASHIKUMAR, N. S., and LORENZINI, G. Heat transfer enhancement due to nanoparticles, magnetic field, thermal and exponential space-dependent heat source aspects in nanoliquid flow past a stretchable spinning disk. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 145, 3339–3347 (2021)
SURESH, S., VENKITARAJ, K. P., SELVAKUMAR, P., and CHANDRASEKAR, M. Synthesis of Al2O3-Cu/water hybrid nanofluids using two step method and its thermo physical properties. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 388, 41–48 (2011)
WAINI, I., ISHAK, A., and POP, I. Unsteady flow and heat transfer past a stretching/shrinking sheet in a hybrid nanofluid. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 136, 288–297 (2019)
MASKEEN, M. M., ZEESHAN, A., MEHMOOD, O. U., and HASSAN, M. Heat transfer enhancement in hydromagnetic alumina-copper/water hybrid nanofluid flow over a stretching cylinder. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 138, 1127–1136 (2019)
ALADDIN, N. A. L., BACHOK, N., and POP, I. Cu-Al2O3/water hybrid nanofluid flow over a permeable moving surface in presence of hydromagnetic and suction effects. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 59, 657–666 (2020)
MEHRYAN, S. A., KASHKOOLI, F. M., GHALAMBAZ, M., and CHAMKHA, A. J. Free convection of hybrid Al2O3-Cu water nanofluid in a differentially heated porous cavity. Advanced Powder Technology, 28, 2295–2305 (2017)
SHAH, N. A., ANIMASAUN, I. L., WAKIF, A., KORIKO, O. K., SIVARAJ, R., ADEGBIE, K. S., and PRASAD, K. V. Significance of suction and dual stretching on the dynamics of various hybrid nanofluids: comparative analysis between type I and type II models. Physica Scripta, 95, 095205 (2020)
WAQAS, H., FAROOQ, U., ALGHAMDI, M., MUHAMMAD, T., and ALSHOMRANI, A. S. On the magnetized 3D flow of hybrid nanofluids utilizing nonlinear radiative heat transfer. Physica Scripta, 96, 095202 (2021)
BHATTI, M. M., ABBAS, T., RASHIDI, M. M., and ALI, M. E. S. Numerical simulation of entropy generation with thermal radiation on MHD Carreau nanofluid towards a shrinking sheet. Entropy, 18, 200 (2016)
SHAH, Z., DAWAR, A., KUMAM, P., KHAN, W., and ISLAM, S. Impact of nonlinear thermal radiation on MHD nanofluid thin film flow over a horizontally rotating disk. Applied Sciences, 9, 1533 (2019)
QURESHI, M. A. Numerical simulation of heat transfer flow subject to MHD of Williamson nanofluid with thermal radiation. Symmetry, 13, 10 (2021)
MAMOURIAN, M., SHIRVAN, K. M., and MIRZAKHANLARI, S. Two phase simulation and sensitivity analysis of effective parameters on turbulent combined heat transfer and pressure drop in a solar heat exchanger filled with nanofluid by response surface methodology. Energy, 109, 49–61 (2016)
BIJAN, D. SAMAN, R., and JAVAD, A. E. Sensitivity analysis of entropy generation in nanofluid flow inside a channel by response surface methodology. Entropy, 18, 52 (2016)
MACKOLIL, J. and MAHANTHESH, B. Inclined magnetic field and nanoparticle aggregation effects on thermal Marangoni convection in nanoliquid: a sensitivity analysis. Chinese Journal of Physics, 69, 24–37 (2021)
MACKOLIL, J. and MAHANTHESH, B. Heat transfer enhancement using temperature-dependent effective properties of alumina-water nanoliquid with thermo-solutal Marangoni convection: a sensitivity analysis. Applied Nanoscience (2021) https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01631-4
SHAMPINE, L. F. and KIERZENKA, J. A BVP solver that controls residual and error. Journal of Numerical Analysis, Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 3, 27–41 (2008)
ARIFIN, N. M., NAZAR, R., and POP, I. Non-isobaric Marangoni boundary layer flow for Cu, Al2O3 and TiO2 nanoparticles in a water-based fluid. Meccanica, 46, 833–843 (2011)
Acknowledgement
The authors thank the management of CHRIST (Deemed to be University), Bangalore, India for encouragement and support. The authors are also grateful to the editors and anonymous reviewers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Citation: MACKOLIL, J. and MAHANTHESH, B. Optimization of heat transfer in the thermal Marangoni convective flow of a hybrid nanomaterial with sensitivity analysis. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 42(11), 1663–1674 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-021-2784-6
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mackolil, J., Mahanthesh, B. Optimization of heat transfer in the thermal Marangoni convective flow of a hybrid nanomaterial with sensitivity analysis. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 42, 1663–1674 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-021-2784-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-021-2784-6
Key words
- inclined magnetic field
- Marangoni boundary layer flow
- sensitivity analysis
- hybrid nanofluid
- exponential heat source
- response surface methodology (RSM)