Abstract
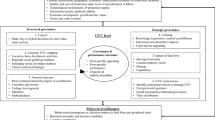
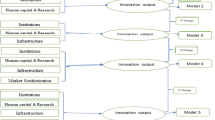
This study constructs the research and development (R&D) and operation processes as a value-chain framework, in which R&D results in the successful applications of patents. These patents are then used to generate final outputs in the operation. We introduce an empirical model extended from the value-chain model to compute the R&D and the operation efficiencies for 21 of China’s high-tech businesses in a single implementation. The findings are presented as follows. First, R&D efficiency is not related to operation efficiency. Second, communication businesses have relatively higher performance in R&D and operation efficiencies, whereas electronics and computer businesses have high operation efficiency, but low R&D efficiency. Finally, for improving the efficiencies, the patents that do not effectively create value should be reduced.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asakawa, K., & Som, A. 2008. Internationalization of R&D in China and India: Conventional wisdom versus reality. Asia Pacific Journal of Management, 25(3): 375–394.
Banker, R. D., Charnes, A. C., & Cooper, W. W. 1984. Some models for estimating technical and scale inefficiencies in data envelopment analysis. Management Science, 30: 1078–1092.
Charnes, A. C., Cooper, W. W., & Rhodes, E. L. 1978. Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. European Journal of Operational Research, 2: 429–444.
Chen, Y., & Zhu, J. 2004. Measuring information technology’s indirect impact on firm performance. Information Technology and Management, 5(1–2): 9–22.
China National Bureau of Statistics. 2008. China high-tech industry statistics yearbook. Beijing: China National Bureau of Statistics.
Cook, W. D., Liang, L., Zha, Y., & Zhu, J. 2009. A modified super-efficiency DEA model for infeasibility. Journal of Operational Research Society, 60: 276–281.
Cooper, W. W., Sinha, K. K., & Sullivan, R. S. 1996. Evaluating the information content of a measure of plant output: An application to high-technology manufacturing. Annals of Operations Research, 68: 329–360.
Daniel, W. W. 1990. Applied nonparametric statistics. Boston: PWS-Kent.
Dutta, S., Narasimhan, O., & Rajiv, S. 1999. Success in high-technology markets: Is marketing capability critical?. Marketing Science, 18(4): 547–568.
Färe, R., & Grosskopf, S. 1996. Productivity and intermediate products: A frontier approach. Economics Letters, 50: 65–70.
Färe, R., & Grosskopf, S. 2000. Network DEA. Socio-Economic Planning Sciences, 34: 35–49.
Farrell, M. J. 1957. The measurement of productive efficiency. Journal of Royal Statistical Society, 120(3): 253–290.
Griliches, Z. 1979. Issue in assessing the contribution of R&D to productivity growth. Bell Journal of Economics, 10: 92–116.
Griliches, Z., & Mairesse, J. 1984. Productivity and R&D at the firm level. In Z. Griliches (Ed.). R&D, patents, and productivity: 339–374. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Hagedoorn, J., & Cloodt, M. 2003. Measuring innovative performance: Is there an advantage in using multiple indicators?. Research Policy, 32: 1365–1379.
Hu, A. 2001. Ownership, government R&D, private R&D, and productivity in Chinese industry. Journal of Comparative Economics, 29: 136–157.
Huang, H., & Xu, C. 1998. Soft budget constraint and the optimal choices of research and development projects financing. Journal of Comparative Economics, 26: 62–79.
Hwang, S. N., & Kao, T. L. 2006. Measuring managerial efficiency in non-life insurance companies: An application of two-stage data envelopment analysis. International Journal of Management, 23(3): 699–720.
Isobe, T., & Makino, S. 2008. Technological capabilities and firm performance: The case of small manufacturing firms in Japan. Asia Pacific Journal of Management, 25(3): 413–428.
Kao, C., & Hwang, S. N. 2008. Efficiency decomposition in two-stage data envelopment analysis: An application to non-life insurance companies in Taiwan. European Journal of Operational Research, 185: 418–429.
Lin, D., Liang, Q., Xu, Z., Li, R., & Xie, W. 2008. Does knowledge management matter for information technology applications in China?. Asia Pacific Journal of Management, 25(3): 489–507.
Lin, W. T., & Shao, B. B. M. 2006. Assessing the input effect on productive in production systems: The value of information technology capital. International Journal of Production Research, 44(9): 1799–1819.
Ma, Y. F., & Goo, Y. J. 2005. Technical efficiency and productivity change in China’s high- and new-technology industry development zones. Asian Business & Management, 4: 331–355.
Mansfield, E. 1980. Basic research and productivity increase in manufacturing. American Economic Review, 70(5): 863–873.
Psillaki, M., Tsolas, I. E., & Margaritis, D. 2010. Evaluation of credit risk based on firm performance. European Journal of Operational Research, 201(3): 873–881.
Seiford, L. M., & Zhu, J. 1999. Profitability and marketability of the top 55 US commercial banks. Management Science, 45(9): 1270–1288.
Sexton, T. R., & Lewis, H. F. 2003. Two-stage DEA: An application to major league baseball. Journal of Productivity Analysis, 19: 227–249.
Sheu, H. J., & Yang, C. Y. 2005. Insider ownership and firm performance on Taiwan’s electronics industry: A technical efficiency perspective. Managerial and Decision Economics, 26: 307–318.
Shiha, K. K. 1996. Moving frontier analysis: An application of data envelopment analysis for competitive analysis of a high-technology manufacturing plant. Annals of Operations Research, 66: 197–218.
Thore, S., Phillips, F., Ruefli, T. W., & Yue, P. 1996. DEA and the management of the product cycle: The US computer industry. Computer Operations Research, 23(4): 341–356.
Verma, D., & Sinha, K. K. 2002. Toward a theory of project interdependencies in high-tech R&D environments. Journal of Operations Management, 20: 451–468.
Xu, E., & Zhang, H. 2008. The impact of state shares on corporate innovation strategy and performance in China. Asia Pacific Journal of Management, 25(3): 473–487.
Yang, J., & Liu, C. Y. 2006. New product development: An innovation diffusion perspective. The Journal of High Technology Management Research, 17: 17–26.
Yang, Q., & Jiang, X. J. 2007. Location advantages and subsidiaries’ R&D activities in emerging economics: Exploring the effect of employee mobility. Asia Pacific Journal of Management, 24(3): 341–358.
Zabala-Iturriagagoitia, J. M., Voigt, P., Gutierrez-Gracia, A., & Jimenes-Saez, F. 2007. Regional innovation systems: How to assess performance. Regional Studies, 41(5): 661–672.
Zhang, A., Zhang, Y., & Zhao, R. 2003. A study of the R&D efficiency and productivity of Chinese firms. Journal of Comparative Economics, 31: 444–464.
Zhu, J. 2003. Quantitative models for performance evaluation and benchmarking: Data envelopment analysis with spreadsheets and DEA Excel solver. Worcester, MA: Worcester Polytechnic Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiu, Yh., Huang, Cw. & Chen, YC. The R&D value-chain efficiency measurement for high-tech industries in China. Asia Pac J Manag 29, 989–1006 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10490-010-9219-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10490-010-9219-3