Abstract
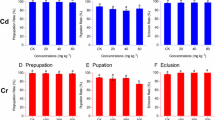
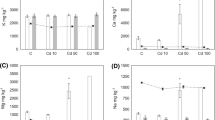
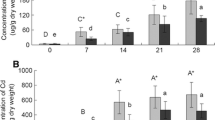
We tested the effect of cadmium (25, 130 μg Cd g−1), administered via Chinese cabbage (Brassica chinensis L.) as food on life-history parameters and gut microflora of tritonymphs and adults of the oribatid mite, Archegozetes longisetosus Aoki. Both concentrations of Cd had an adverse effect on offspring mortality, and the higher concentration also reduced female fecundity, as well as the number of bacteria, fungi and actinomycetes, and it changed the community structure of bacteria; the proportion of gram-negative bacteria increased while that of gram-positive bacteria declined. Interestingly, at the lower Cd concentration microflora was more abundant and diverse than in the control group, especially in the tritonymphs, although the mean activity of gut microflora was reduced. The higher Cd concentration reduced microflora activity both in the tritonymphs and adults.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babich H, Stotzky G (1977) Sensitivity of various bacteria, including actinomycetes, and fungi to cadmium and the influence of pH on sensitivity. Appl Environ Microbiol 33:681–695
Barkay T, Tripp SC, Olson BH (1985) Effect of metal-rich sewage sludge application on the bacterial communities of grasslands. Appl Environ Microbiol 49:333–337
Behan-Pelletier VM (1999) Oribatid mite biodiversity in agroecosystems: role for bioindication. Agr Ecosyst Environ 74:411–423
Berthet P (1963) Mesure de la consummation d’oxygene des Oribates (Acariens) de la litiere des forêts. In: Doeksen J, van der Drift J (eds) Soil organisms. North-Holland, Amsterdam, pp 18–31
Boguszewska J (1980) Isolation and some properties of extracellular amylases of Fusarium martii. Acta Mycol 16:237–245 in polish
Cavalli V (1946) Sull’attivita antibatterica del cloruro di cadmio. Atti Accad Fisiocrit Siena Sez Med Fis 14:578–588
Denneman CAJ, Van Straalen NM (1991) The toxicity of lead and copper in reproduction tests using the oribatid mite Platynothrus peltifer. Pedobiologia 35:305–311
Djukic D, Mandic L (2006) Microorganisms as indicators of soil pollution with heavy metals. Acta Agriculturae Serbica 11:45–55
Drobne D, Rupnik M, Lapanje A, Strus J, Janc M (2002) Isopod gut microflora parameters as endpoints in toxicity studies. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:604–609
Filzek PDB, Spurgeon DJ, Broll G, Svendsen C, Hankard PK, Kammenga JE, Donker MH, Weeks JM (2004a) Pedological characterisation of sites along a transect from a primary Cadmium/Lead/Zinc Smelting Works. Ecotoxicology 13:725–737
Filzek PDB, Spurgeon DJ, Broll G, Svendsen C, Hankard PK, Parekh N, Stubberud HE, Weeks JM (2004b) Metal effects on soil invertebrate feeding: measurements using the Bait Lamina method. Ecotoxicology 13:807–816
Frostegard A, Tunlid A, Baath E (1993) Phospholipid fatty acid composition, biomass, and activity of microbial communities from two soil types experimentally exposed to different heavy metals. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:3605–3617
Giller KE, Witter E, McGrath SP (1998) Toxicity of heavy metals to microorganisms and microbial processes in agricultural soils: a review. Soil Biol Biochem 30:1389–1414
Hankin L, Zucker M, Sands DC (1971) Improved solid medium for the detection and enumeration of pectolytic bacteria. Appl Microbiol 22:205–209
Haq MA (1982) Feeding habits of ten species of oribatid mites (Acari: Oribatei) from Malbar, South India. Indian J Acarol 6:39–50
Haq MA (1996) Nutritional diversity of oribatid mites in relation to soil fertility. J Karnatak Univ Sci 40 (Special Issue):76–96
Haq MA, Prabhoo NR (1977) Observations on the feeding habits of oribatid mites from the soils of Kerala (Acarina: Cryptostigmata)—pahphytophages. Entomon 1:133–137
Heethoff M, Laumann M, Bergmann P (2007) Adding to the reproductive biology of the parthenogenetic oribatid mite Archegozetes longisetosus (Acari, Oribatida, Trhypochthoniidae). Turk J Zool 31:151–159
Hutton M (1984) Impact of airborne metal contamination on a deciduous woodland system. In: Sheehan PJ, Miller DR, Butler GC (eds) Effects of pollutants at the ecosystem level. Wiley, New York
Kado CI, Hesket MG (1970) Selective media for isolation of Agrobacterium, Corynebacterium, Erwinia, Pseudomonas and Xanthomonas. Phytopathology 60:969–976
Kobierski M (2004) Copper, zinc, manganese and iron concentrations in soils of 27 and 30-year-old apple tree orchards. Acta Sci Pol Hortorum Cultus 3:161–170
Lapanje A, Rupnik M, Drobne D (2007) Gut bacterial community structure (Porcellio scaber, Isopoda, Crustacea) as a measure of community level response to long-term and short-term metal pollution. Environ Toxicol Chem 26:755–763
Lavelle P (1997) Faunal activities and soil processes: adaptive strategies that determine ecosystem function. Adv Ecol Res 27:93–132
Ludwig M, Kratzmann M, Alberti G (1991) Accumulation of heavy metals in two oribatid mites. In: Dusbábek F, Bukva V (eds) Modern Acarology, vol 1. Academia, Prague and SPB Academic Publishing bv, The Hague, pp 431–437
Ludwig M, Kratzmann M, Alberti G (1993) The influence of some heavy metals on Steganacarus magnus (Acari, Oribatida). Z Angew Zool 4:455–467
Norton RA, Palmer SC (1991) The distribution, mechanisms and evolutionary significance of parthenogenesis in oribatid mites. In: Schuster R, Murphy PW (eds) The Acari—Reproduction, development and life-history strategies. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 107–136
Palmer SC, Norton RA (1990) Further experimental proof of thelytokous parthenogenesis in oribatid mites (Acari: Oribatida: Desmonomata). Exp Appl Acarol 8:149–159
Palmer SC, Norton RA (1992) Genetic diversity in thelytokous oribatid mites (Acari: Acariformes: Desmonomata). Biochem Ecol Syst 20:219–231
Rajapaksha RMCP, Tobor-Kapłon MA, Baath E (2004) Metal toxicity affects fungal and bacterial activities in soil differently. Appl Environ Microb 70:2966–2973
Romandini P, Tallandini L, Beltramini M, Salvato B, Manzano M (1992) Effects of copper and cadmium on growth, superoxide dismutase and catalase activities in different yeast strains. Comp Biochem Physiol 103C:255–262
Schatz H, Behan-Pelletier VM (2008) Global diversity of oribatids (Oribatida: Acari: Arachnida). Hydrobiologia 595:323–328
Seniczak A (2006) The influence of heavy metals on the soil mites. In: Gabryś G, Ignatowicz S (eds) Postępy Polskiej Akarologii. Wydawnictwo SGGW, Warszawa, pp 293–303
Seniczak A (2007) Preliminary studies on the toxicity of copper and lead in Pergalumna nervosa (Berlese, 1914) (Acari, Oribatida) in laboratory tests. In: Tajovský K, Schlaghamerský J, Pižl V (eds) Contributions to soil zoology in Central Europe. II. České Budějovice, Czech Republic, pp 131–134
Seniczak A, Seniczak S (2002) The effect of cadmium on Archegozetes longisetosus (Acari, Oribatida) in laboratory conditions. Eur J Soil Biol 38:315–317
Seniczak S, Seniczak A (2008) Oribatid mites (Acari, Oribatida) as bioindicators of forest habitats. In: Gwiazdowicz D (ed) Selected problems of acarological research in forests. Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Przyrodniczego w Poznaniu, Poznań, pp 41–58
Seniczak S, Stefaniak O (1978) The microflora of the effect of the alimentary canal of Oppia nitens (Acarina, Oribatei). Pedobiologia 18:110–119
Seniczak S, Klimek A, Gackowski G, Kaczmarek S, Zalewski G (1997) Effect of copper smelting air pollution on the mites (Acari) associated with young Scots Pine forests polluted by a copper smelting works at Głogów, Poland. II. Soil mites. Water Air Soil Poll 97:287–302
Seniczak A, Ignatowicz S, Seniczak S (2000) Effect of some heavy metals on the bionomy of mite Archegozetes longisetosus (Acari, Oribatida) in the laboratory conditions. Ecol Chem Eng 10:1085–1091
Siepel H (1994) Structure and function of soil microarthropod communities. Dissertation, Wageningen, 136 pp
Simkiss K, Watkins B (1991) Differences in zinc uptake between snails (Helix aspersa (Muller)) from metal and bacteria-polluted sites. Funct Ecol 5:787–794
Smrž J (2000) A modified test for chitinase and cellulase activity in soil mites. Pedobiologia 44:186–189
Smrž J, Norton RA (2004) Food selection and internal processing in Archegozetes longisetosus (Acari, Oribatida). Pedobiologia 48:111–120
Sobczak E, Duszkiewicz W, Grzybowski R (1978) Theory and laboratory on general and technical microbiology (In Polish). Skrypt SGGW-AR w Warszawie
Stebbing ARD (1982) Hormesis—the stimulation of growth by low levels of inhibitors. Sci Total Environ 22:213–234
Stefaniak O, Seniczak S (1976) The microflora of the alimentary canal of Achipteria coleoptrata (Acarina, Oribatei). Pedobiologia 16:185–194
Stefaniak O, Seniczak S (1981) The effect of fungal diet on the development of Oppia nitens (Acari, Oribatei) and on the microflora of its alimentary tract. Pedobiologia 21:202–210
Stefaniak O, Seniczak S (1983) Intestinal microflora in representatives of different feeding groups of soil moss mites (Acarida, Oribatida). In: Lebrun Ph, André HM, De Medts A, Gregoire-Wibo C, Wauthy G (eds) New trends in soil biology. Dieu-Brichart, Ottignies, Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, pp 622–624
Strojan CL (1978) The impact of zinc smelter emission on forest litter arthropods. Oikos 31:41–46
Strzelczyk E, Szpotański T (1989) Cellulolytic and pectinolytic activity of streptomyces isolated from root-free soil, rhizosphere and mycorrhizosphere of pine (Pinus sylvestris L.). Biol Fertil Soils 9:269–272
Tyler G, Balsberg-Påhlsson AM, Bengtsson G, Bååth E, Tranvik L (1989) Heavy-metal ecology of terrestrial plants, microorganisms and invertebrates. A review. Water Air Soil Poll 47:189–215
Van Straalen NM, Schobben JH, De Goede RM (1989) Population consequences of cadmium toxicity in soil microarthropods. Ecotox Environ Safe 17:190–204
Walter DE, Proctor HC (1999) Mites. Ecology, evolution and behaviour. University of New South Wales Press, Sydney
Wolf MM, Rockett CL (1984) Habitat changes affecting bacterial composition in the alimentary canal of oribatid mites (Acari: Oribatida). Int J Acarol 10:209–215
Woodring JP, Cook EF (1962) The biology of Ceratozetes cisalpinus Berlese, Scheloribates laevigatus Koch and Oppia neerlandica Oudemans (Oribatei) with a description of all stages. Acarologia 4:101–137
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to Prof. R. A. Norton (SUNY College of Environmental Science and Forestry in Syracuse, NY, USA) for his thorough revision of this manuscript and many valuable suggestions and comments that highly improved this manuscript, and for the language corrections. We thank Dr. M. Kobierski (Department of Soil Science, University of Technology and Life Sciences in Bydgoszcz) for preparing contaminated food and determination of its Cd content. We express our sincere gratitude to both anonymous reviewers and the editor for their helpful suggestions and improvements of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seniczak, A., Ligocka, A., Seniczak, S. et al. The influence of cadmium on life-history parameters and gut microflora of Archegozetes longisetosus (Acari: Oribatida) under laboratory conditions. Exp Appl Acarol 47, 191–200 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-008-9210-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-008-9210-6