Abstract
Over the past few decades, topological segmentation has been much studied, especially for structured environments. In this work, we first propose a set of criteria to assess the quality of topological segmentation, especially for semi-structured environments in 2D. These criteria provide a general benchmark for different segmentation algorithms. Then we introduce an incremental approach to create topological segmentation for semi-structured environments. Our novel approach is based on spectral clustering of an incremental generalized Voronoi decomposition of discretized metric maps. It extracts sparse spatial information from the maps, and builds an environment model which aims at simplifying the navigation task for mobile robots. Experimental results in real environments show the robustness and the quality of the topological map created by the proposed method. Extended experiments for urban search and rescue missions are performed to show the global consistency of the proposed incremental segmentation method using six different trails, during which the test robot traveled 1.8 km in total.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Please notice that the metric is to assess the quality of a segmentation result, rather than a parameter to be optimized.
\(r_g\) is chosen to be 3 empirically.
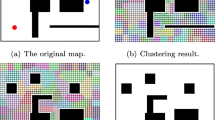
Considering the limited space, we only show the final result of the segmentation here.
References
Ahn, S., Doh, N. L., Lee, K., & Chung, W. K. (2003). Incremental and robust construction of generalized Voronoi graph (GVG) for mobile guide robot. In: Proceedings. 2003 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent robots and systems (IROS 2003) (Vols. 3, 4, pp. 3757–3762), doi:10.1109/IROS.2003.1249739.
Aurenhammer, F. (1991). Voronoi diagrams: A survey of a fundamental geometric data structure. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 23(3), 345–05.
Baber, C., Houghton, R., McMaster, R., Salmon, P., Stanton, N., Stewart, R., et al. (2004). Field studies in the emergency services. HFI-DTC Technical Report/WP, I1.1/1, 1.
Balaguer, B., Balakirsky, S., Carpin, S., & Visser, A. (2009). Evaluating maps produced by urban search and rescue robots: Lessons learned from robocup. Autonomous Robots, 27(4), 449–64.
Barraquand, J., & Latombe, J. (1991). Robot motion planning: A distributed representation approach. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 10(6), 628.
Beeson, P. (2008). Creating and utilizing symbolic representations of spatial knowledge using mobile robots. PhD thesis, The University of Texas at Austin.
Beeson, P., Modayil, J., & Kuipers, B. (2010). Factoring the mapping problem: Mobile robot map-building in the hybrid spatial semantic hierarchy. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 29(4), 428–59.
Blanco, D., Boada, B., Moreno, L., & Salichs, M. (2000). Local mapping from online laser voronoi extraction. In: Proceedings. 2003 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2000) (Vol. 1, pp 103–108).
Blanco, J., Fernández-Madrigal, J., & Gonzalez, J. (2008). Toward a unified bayesian approach to hybrid metric-topological slam. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 24(2), 259–70.
Brunskill, E., Kollar, T., & Roy, N. (2007). Topological mapping using spectral clustering and classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2007) (pp. 3491–3496).
Burke, J., Murphy, R., Rogers, E., Lumelsky, V., & Scholtz, J. (2004). Final report for the DARPA/NSF interdisciplinary study on human-robot interaction. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C: Applications and Reviews, 34(2), 103–12.
Choi, J., Choi, M., Chung, W. K. (2009a). Incremental topological modeling using sonar gridmap in home environment. In: IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, IEEE (pp. 3582–3587). doi:10.1109/IROS.2009.5354247, http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/lpdocs/epic03/wrapper.htm?arnumber=5354247
Choi, J., Choi, M., Lee, K., & Chung, W. K. (2009b). Topological modeling and classification in home environment using sonar gridmap. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (pp. 3892–3898).
Choi, J., Choi, M., Nam, S., & Chung, W. (2011). Autonomous topological modeling of a home environment and topological localization using a sonar grid map. Autonomous Robots, 30(4), 351–68.
Choi, J., Choi, M., Suh, I. H., & Chung W. K. (2010). Topological localization using sonar gridmap matching in home environment. In: IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, IEEE (pp. 4910–4915).
Choset, H. (1997). Incremental construction of the generalized Voronoi diagram, the generalized Voronoi graph, and the hierarchical generalized Voronoi graph. In: 1st CGC Workshop on Computation Geometry (Vol. 2, Issue 3).
Choset, H., & Nagatani, K. (2001). Topological simultaneous localization and mapping (slam): Toward exact localization without explicit localization. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 17(2), 125–37.
Civera, J., Davison, A. J., & Montiel, J. (2008). Inverse depth parametrization for monocular slam. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 24(5), 932–45.
Dolgov, D., & Thrun, S. (2009). Autonomous driving in semi-structured environments: Mapping and planning. In: : Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA’09), IEEE (pp. 3407–3414).
Drysdale, R, III. (1979). Generalized voronoi diagrams and geometric searching. Stanford: Stanford University.
Elfes, A. (1989). Using occupancy grids for mobile robot perception and navigation. Computer, 22(6), 46–57.
Fabri, A., & Pion, S. (2009). CGAL: The computational geometry algorithms library. In: Proceedings of the 17th ACM SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, ACM (pp. 538–539).
Friedman, S., Pasula, H., & Fox, D. (2007). Voronoi random fields: Extracting the topological structure of indoor environments via place labeling. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI) (Vol. 35)..
Galindo, C., Saffiotti, A., Coradeschi, S., Buschka, P., Fernandez-Madrigal, J., & González, J. (2005). Multi-hierarchical semantic maps for mobile robotics. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2005 (IROS 2005) (pp. 2278–2283).
Gianni, M., Papadakis, P., Pirri, F., Liu, M., Pomerleau, F., Colas, F., Zimmermann, K., Svoboda, T., Petricek, T., & Kruijff, G., et al. (2011). A unified framework for planning and execution-monitoring of mobile robots. In: Workshops at the Twenty-Fifth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence.
Hagen, L., & Kahng, A. (1992). New spectral methods for ratio cut partitioning and clustering. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 11(9), 1074–85.
Kalra, N., Ferguson, D., & Stentz, A. (2009). Incremental reconstruction of generalized Voronoi diagrams on grids. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 57(2), 123–8.
Karavelas, M. (2004). A robust and efficient implementation for the segment voronoi diagram. In: International Symposium on Voronoi Diagrams in Science and Engineering, Citeseer (pp. 51–62).
Kruijff, G. J., Colas, F., Svoboda, T., van Diggelen, J., Balmer, P., Pirri, F., & Worst, R. (2012a). Designing intelligent robots for human-robot teaming in Urban Search & Rescue. In: AAAI 2012 Spring Symposium on Designing Intelligent Robots, AAAI.
Kruijff, G. J., Janicek, M., Keshavdas, S., Larochelle, B., Zender, H., Smets, N., Mioch, T., Neerincx, M., van Diggelen, J., Colas, F., Liu, M., Pomerleau, F., Siegwart, R., Hlavac, V., Svoboda, T., Petricke, T., Reinstein, M., Zimmerman, K., Pirri, F., & Gianni, M. (2012b). Experience in system design for human–robot teaming in Urban Search & Rescue. In: Field and Service Robotics. London: Springer.
Latecki, L., & Lakämper, R. (1999). Convexity rule for shape decomposition based on discrete contour evolution. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 73(3), 441–54.
Lau, B., Sprunk, C., & Burgard, W. (2010). Improved updating of euclidean distance maps and Voronoi diagrams. In: IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Taipei, Taiwan.
Lee, Y., Kwon, T., & Song, J. (2007). Slam of a mobile robot using thinning-based topological information. International Journal of Control Automation and Systems, 5(5), 577.
Liu, M., & Siegwart, R. (2012). DP-FACT: Towards topological mapping and scene recognition with color for omnidirectional camera. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA).
Liu, M., & Siegwart, R. (2013). Topological mapping and scene recognition with lightweight color descriptors for an omnidirectional camera. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 29, 1353–1365.
Liu, M., Davide Scaramuzza, R. S., Cédric P., & Chen, Q. (2009). Scene recognition with omnidirectional vision for topological map using lightweight adaptive descriptors. In: IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, IROS 2009.
Liu, M., Colas, F., & Siegwart, R. (2011). Regional topological segmentation based on mutual information graphs. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA 2011), Shanghai.
Liu, M., Colas, F., Pomerleau, F., & Siegwart, R. (2012a). A Markov semi-supervised clustering approach and its application in topological map extraction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS).
Liu, M., Wang, L., & Siegwart, R. (2012b). DP-fusion: A generic framework for online multi sensor recognition. In: IEEE Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems (MFI), IEEE.
Luxburg, U. V. (2006). A tutorial on spectral clustering. Statistics and Computing, (pp. 395–416). doi:10.1007/s11222-007-9033-z.
McNamara, T. (1986). Mental representations of spatial relations 1. Cognitive Psychology, 18(1), 87–121.
Nadler, B., & Galun, M. (2007). Fundamental limitations of spectral clustering. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 19, 1017.
Ranganathan, P., Hayet, J., Devy, M., Hutchinson, S., & Lerasle, F. (2002). Topological navigation and qualitative localization for indoor environment using multi-sensory perception. Robotics and Autonomous systems, 41(2), 137–144.
Rosenberg, A., & Hirschberg, J. (2007). V-measure: A conditional entropy-based external cluster evaluation measure. In: Proceedings of the 2007 Joint Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and Computational Natural Language Learning (pp. 410–420).
Rosin, P. (2000). Shape partitioning by convexity. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Part A: Systems and Humans, 30(2), 202–210.
Ryu, B., & Yang, H. (1999). Integration of reactive behaviors and enhanced topological map for robust mobile robot navigation. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Part A: Systems and Humans, 29(5), 474–485.
Shi, J., & Malik, J. (2000). Normalized cuts and image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 22(8), 888–905.
Shi, L., Kodagoda, S., & Dissanayake, G. (2012). Application of semi-supervised learning with Voronoi graph for place classification. In: 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, (IROS 2012).
Song, J., & Liu, M. (2013). A Hidden Markov model approach for Voronoi localization. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO).
Strasdat, H., Montiel, J., & Davison, A. J. (2010). Real-time monocular slam: Why filter? In: The 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) (pp. 2657–2664).
Tapus, A., & Siegwart, R. (2005). Incremental robot mapping with fingerprints of places. In: 2005 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2005) (pp. 2429–2434).
Thrun, S. (1998). Learning metric-topological maps for indoor mobile robot navigation. Artificial Intelligence, 99(1), 21–71.
Tomatis, N., Nourbakhsh, I., & Siegwart, R. (2003). Hybrid simultaneous localization and map building: A natural integration of topological and metric. Robotics and Autonomous systems, 44(1), 3–14.
Zelnik-Manor, L., & Perona, P. (2004). Self-tuning spectral clustering. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 17(1601–1608), 16.
Zender, H., Martínez Mozos, O., Jensfelt, P., Kruijff, G., & Burgard, W. (2008). Conceptual spatial representations for indoor mobile robots. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 56(6), 493–502.
Zivkovic, Z., Bakker, B., & Krose, B. (2006). Hierarchical map building and planning based on graph partitioning. In: Proceedings 2006 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, ICRA 2006, IEEE (pp. 803–809).
Zwynsvoorde, D. V., Simeon, T., & Alami, R. (2000). Incremental topological modeling using local Voronoi-like graphs. In: Proceedings 2000 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligence Robots and Systems (IROS 2000).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by HKUST project IGN13EG03; General Research Fund by Research Grants Council Hong Kong, “Heterogeneous multi-robot systems for hospital services (HeMRS)”, 16206014; partially supported by the EU FP7 project NIFTi (contract # 247870) and EU FP7 TRADR project (contract 609763).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Colas, F., Oth, L. et al. Incremental topological segmentation for semi-structured environments using discretized GVG. Auton Robot 38, 143–160 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10514-014-9398-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10514-014-9398-8