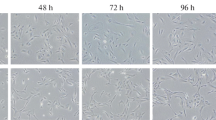
We studied the effect of bFGF on human retinal pigment epithelial cells in vitro In ARPE-19 cells, enhanced expression of KLF4 mRNA and reduced expression of PAX6, MITF, and OTX2 mRNA specific for retinal pigment epithelium were observed after bFGF application. The expression of KLF4 mRNA peaked in 72 h after bFGF application and then sharply decreased, which was accompanied by a 3-fold increase in TUBB3 mRNA expression (neuronal marker). Immunocytochemical analysis showed that in the presence of bFGF, some cells retained epithelial properties and showed positive staining for connexin-43, while others had long axon-like processes and demonstrated positive staining for βIII-tubulin, which attests to their neuronal transdifferentiation. Despite the prevalence of the epithelial properties, ARPE-19 cells under the influence of bFGF can show proneuronal properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kuznetsova AV, Milyushina LA, Mikaelian AS, Zinovieva RD, Grigoryan EN, Aleksandrova MA. Dedifferentiation of adult human retinal pigment epithelial cells in vitro. Mol. Med. 2010;(6):23-29. Russian.
Akrami H, Soheili Z.S, Khalooghi K, Ahmadieh H, Rezaie-Kanavi M, Samiei S, Davari M, Ghaderi S, Sanie-Jahromi F. Retinal pigment epithelium culture;a potential source of retinal stem cells. J. Ophthalmic Vis. Res. 2009;4(3):134-141.
Azuma N, Tadokoro K, Asaka A, Yamada M, Yamaguchi Y, Handa H, Matsushima S, Watanabe T, Kohsaka S, Kida Y, Shiraishi T, Ogura T, Shimamura K, Nakafuku M. The Pax6 isoform bearing an alternative spliced exon promotes the development of the neural retinal structure. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005;14(6):735-745.
Bharti K, Nguyen MT, Skuntz S, Bertuzzi S, Arnheiter H. The other pigment cell: specification and development of the pigmented epithelium of the vertebrate eye. Pigment Cell Res. 2006;19(5):380-394.
Carr AJ, Vugler AA, Yu L, Semo M, Coffey P, Moss SE, Greenwood J. The expression of retinal cell markers in human retinal pigment epithelial cells and their augmentation by the synthetic retinoid fenretinide. Mol. Vis. 2011;17:1701-1715.
Chen S, Fariss RN, Kutty RK, Nelson R, Wiggert B. Fenretinide-induced neuronal differentiation of ARPE-19 human retinal pigment epithelial cells is associated with the differential expression of Hsp70, 14-3-3, pax-6, tubulin beta-III, NSE, and bag-1 proteins. Mol. Vis. 2006;12:1355-1363.
Dunn KC, Aotaki-Keen AE, Putkey FR, Hjelmeland LM. ARPE-19, a human retinal pigment epithelial cell line with differentiated properties. Exp. Eye Res. 1996;62(2):155-169.
Eguizabal C, Montserrat N, Veiga A, Izpisua Belmonte JC. Dedifferentiation, transdifferentiation, and reprogramming: future directions in regenerative medicine. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2013;31(1):82-94.
Fang J, Shaw PX, Wang Y, Goldberg JL. Krüppel-Like Factor 4 (KLF4) is not required for retinal cell differentiation. eNeuro. 2016;3(1):pii: ENEURO.0117-15.2016. doi: https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0117-15.2016.
Grigorian EN. Competence factors of retinal pigment epithelium cells for reprogramming in the neuronal direction during retinal regeneration in newts. Izv. Akad. Nauk. Ser. Biol. 2015;(1):5-16.
Grigoryan EN, Markitantova YV, Avdonin PP, Radugina EA. Study of regeneration in amphibians in age of molecular-genetic approaches and methods. Genetika. 2013;49(1):55-72.
Kojima A, Nakahama K, Ohno-Matsui K, Shimada N, Mori K, Iseki S, Sato T, Mochizuki M, Morita I. Connexin 43 contributes to differentiation of retinal pigment epithelial cells via cyclic AMP signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008;366(2):532-538.
Kuznetsova AV, Aleksandrova MA, Kurinov AM, Chentsova EV, Makarov P.V. Plasticity of adult human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. 2016;9(11):20 892-20 906.
Kuznetsova AV, Aleksandrova MA. Heterogeneity of retinal pigment epithelial cells from adult human eye in different culturing systems. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017;162(4):569-577.
Kuznetsova AV, Kurinov AM, Aleksandrova MA. Cell models to study regulation of cell transformation in pathologies of retinal pigment epithelium. J. Ophthalmol. 2014;2014. ID 801787. doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/801787.
Lotz S, Goderie S, Tokas N, Hirsch SE, Ahmad F, Corneo B, Le S, Banerjee A, Kane RS, Stern JH, Temple S, Fasano CA. Sustained levels of FGF2 maintain undifferentiated stem cell cultures with biweekly feeding. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56289. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0056289.
Luz-Madrigal A, Grajales-Esquivel E, McCorkle A, DiLorenzo AM, Barbosa-Sabanero K, Tsonis PA, Del Rio-Tsonis K. Reprogramming of the chick retinal pigmented epithelium after retinal injury. BMC Biol. 2014;12:28. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7007-12-28.
Martinez-Morales JR, Del Bene F, Nica G, Hammerschmidt M, Bovolenta P, Wittbrodt J. Differentiation of the vertebrate retina is coordinated by an FGF signaling center. Dev. Cell. 2005;8(4):565-574.
Milyushina LA, Kuznetsova AV, Grigoryan EN, Aleksandrova MA. Phenotypic plasticity of retinal pigment epithelial E. V. Shafei, A. M. Kurinov, et al. cells from adult human eye in vitro. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2011;151(4):506-511.
Milyushina LA, Poltavtseva RA, Marei MV, Podgornyi OV, Sukhikh GT, Aleksandrova MA. In vitro phenotypic modification of pigmented epithelium cells from human eye at early stages of development. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2009;148(1):113-119.
Milyushina LA, Verdiev BI, Kuznetsova AV, Aleksandrova MA. Expression of multipotent and retinal markers in pigment epithelium of adult human in vitro. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2012;153(1):157-162.
Mochii M, Mazaki Y, Mizuno N, Hayashi H, Eguchi G. Role of Mitf in differentiation and transdifferentiation of chicken pigmented epithelial cell. Dev. Biol. 1998;193(1):47-62.
Pittack C, Grunwald GB, Reh TA. Fibroblast growth factors are necessary for neural retina but not pigmented epithelium differentiation in chick embryos. Development. 1997;124(4):805-816.
Sakaguchi DS, Janick LM, Reh TA. Basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2) induced transdifferentiation of retinal pigment epithelium: generation of retinal neurons and glia. Dev. Dyn. 1997;209(4):387-398.
Salero E, Blenkinsop TA, Corneo B, Harris A, Rabin D, Stern JH, Temple S. Adult human RPE can be activated into a multipotent stem cell that produces mesenchymal derivatives. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;10(1):88-95.
Schwegler JS, Knorz MC, Akkoyun I, Liesenhoff H. Basic, not acidic fibroblast growth factor stimulates proliferation of cultured human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Mol. Vis. 1997;3:10.
Sparrow JR, Hicks D, Hamel CP. The retinal pigment epithelium in health and disease. Curr. Mol. Med. 2010;10(9):802-823.
Taranova OV, Magness ST, Fagan BM, Wu Y, Surzenko N, Hutton SR, Pevny LH. SOX2 is a dose-dependent regulator of retinal neural progenitor competence. Genes Dev. 2006;20(9):1187-1202.
Yan RT, He L, Zhan W, Wang SZ. Induction of ectopic retinalike tissue by transgenic expression of neurogenin. PLoS One. 2015;10(1):e0116171. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0116171.
Zhao S, Thornquist SC, Barnstable CJ. In vitro transdifferentiation of embryonic rat retinal pigment epithelium to neural retina. Brain Res. 1995;677(2):300-310.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Kletochnye Tekhnologii v Biologii i Meditsine, No. 2, pp. 128-136, June, 2017
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shafei, E.V., Kurinov, A.M., Kuznetsova, A.V. et al. Reprogramming of Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells under the Effect of bFGF In Vitro . Bull Exp Biol Med 163, 574–582 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-017-3852-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-017-3852-5